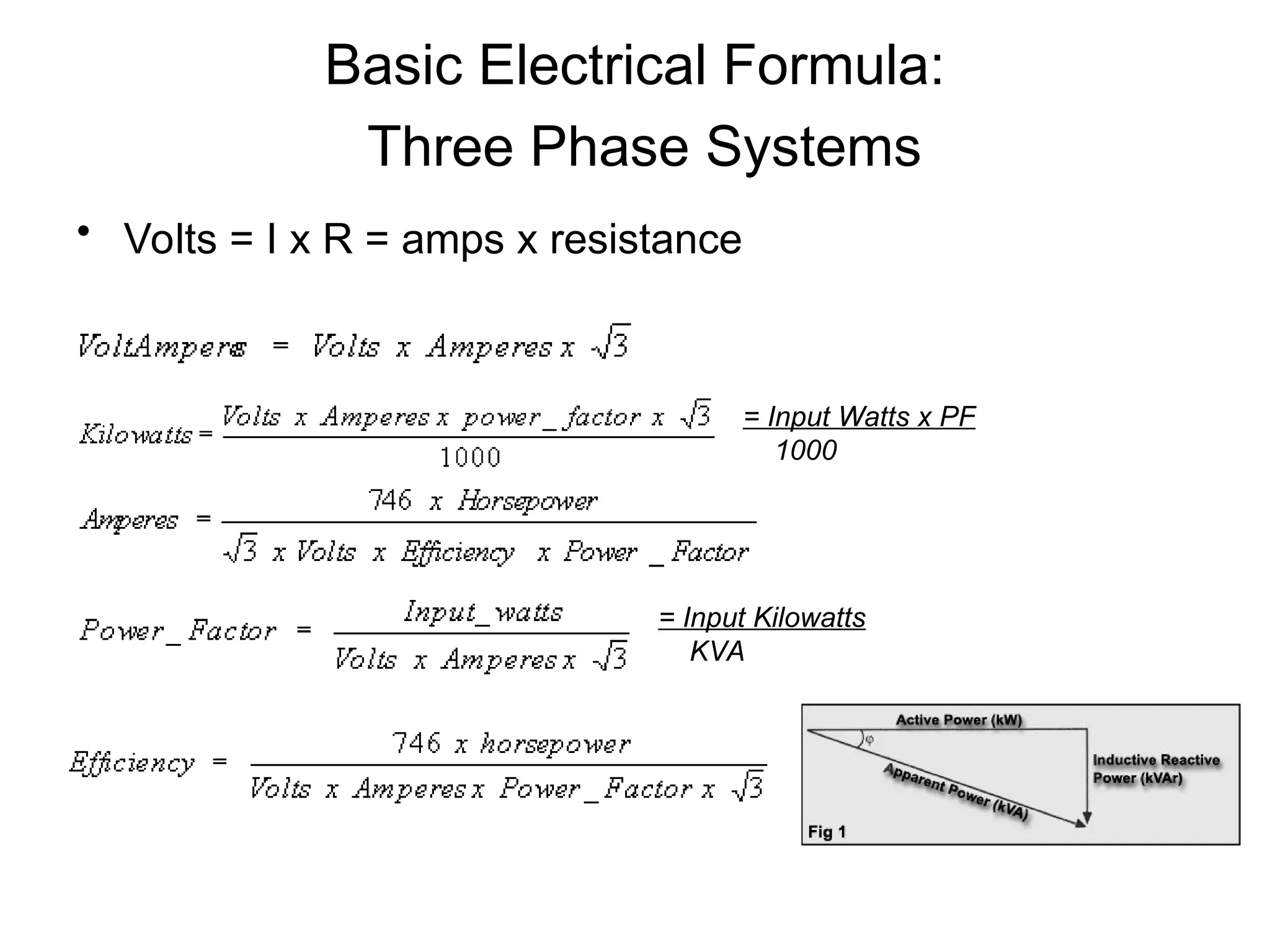
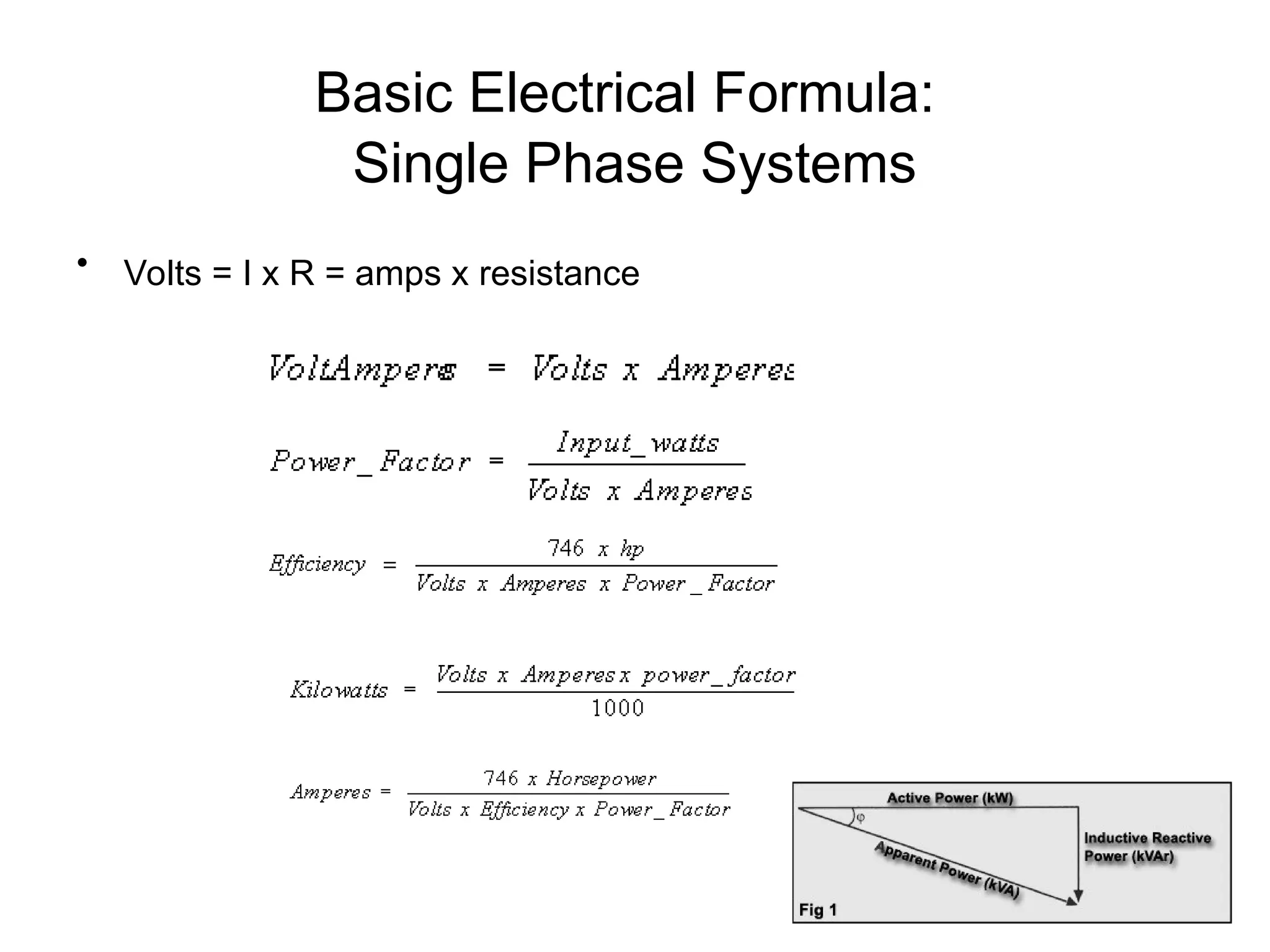
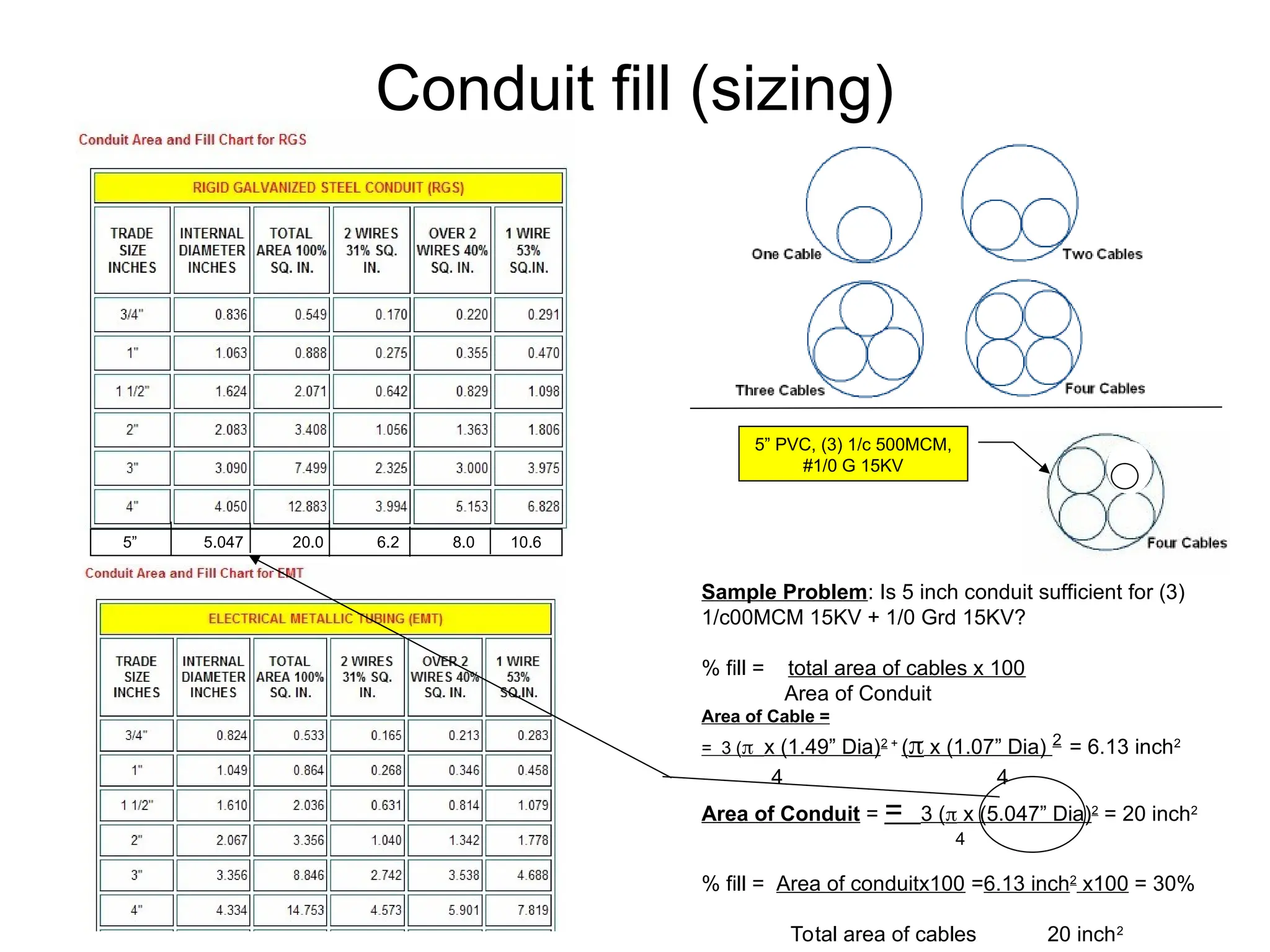
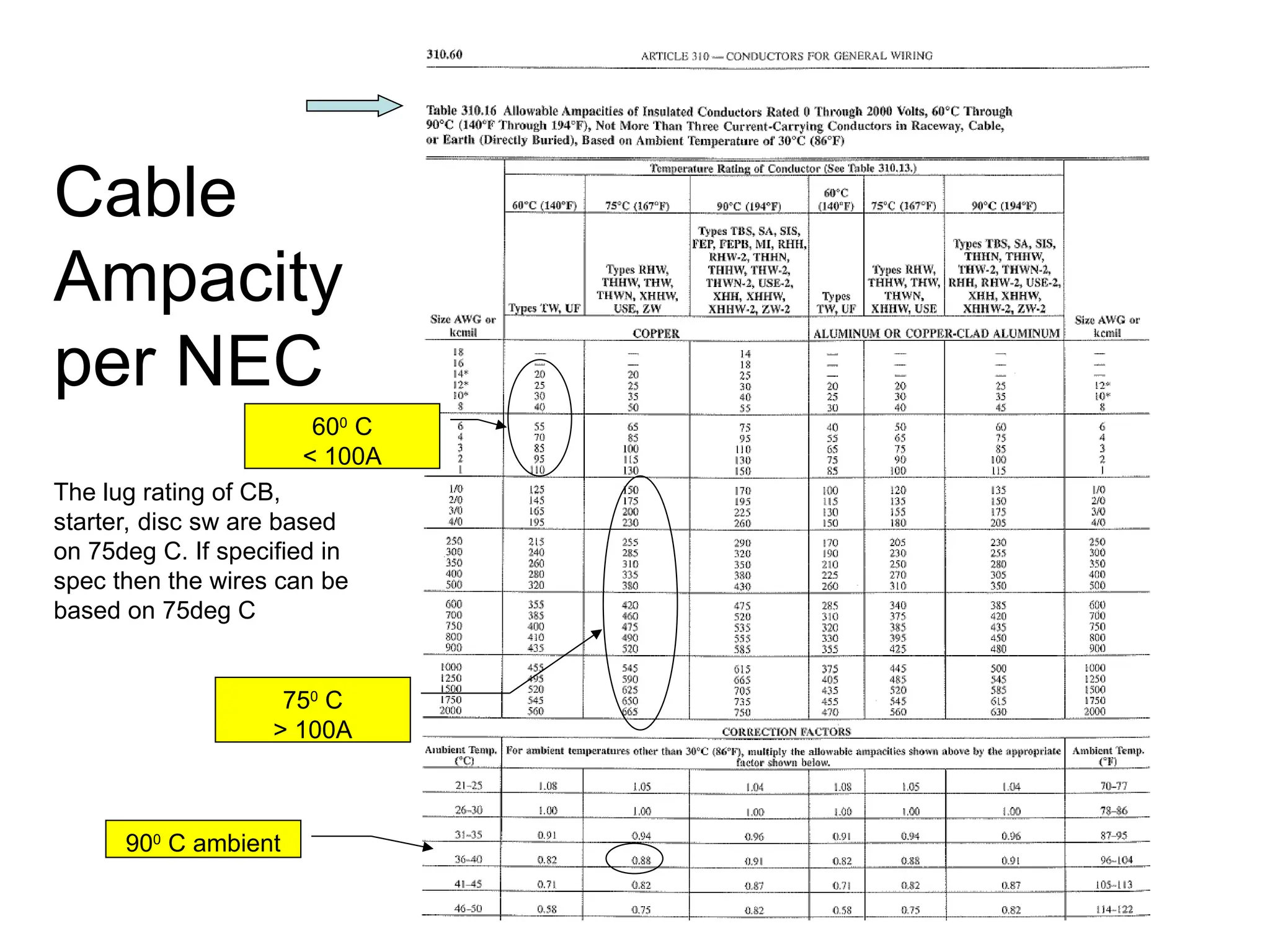
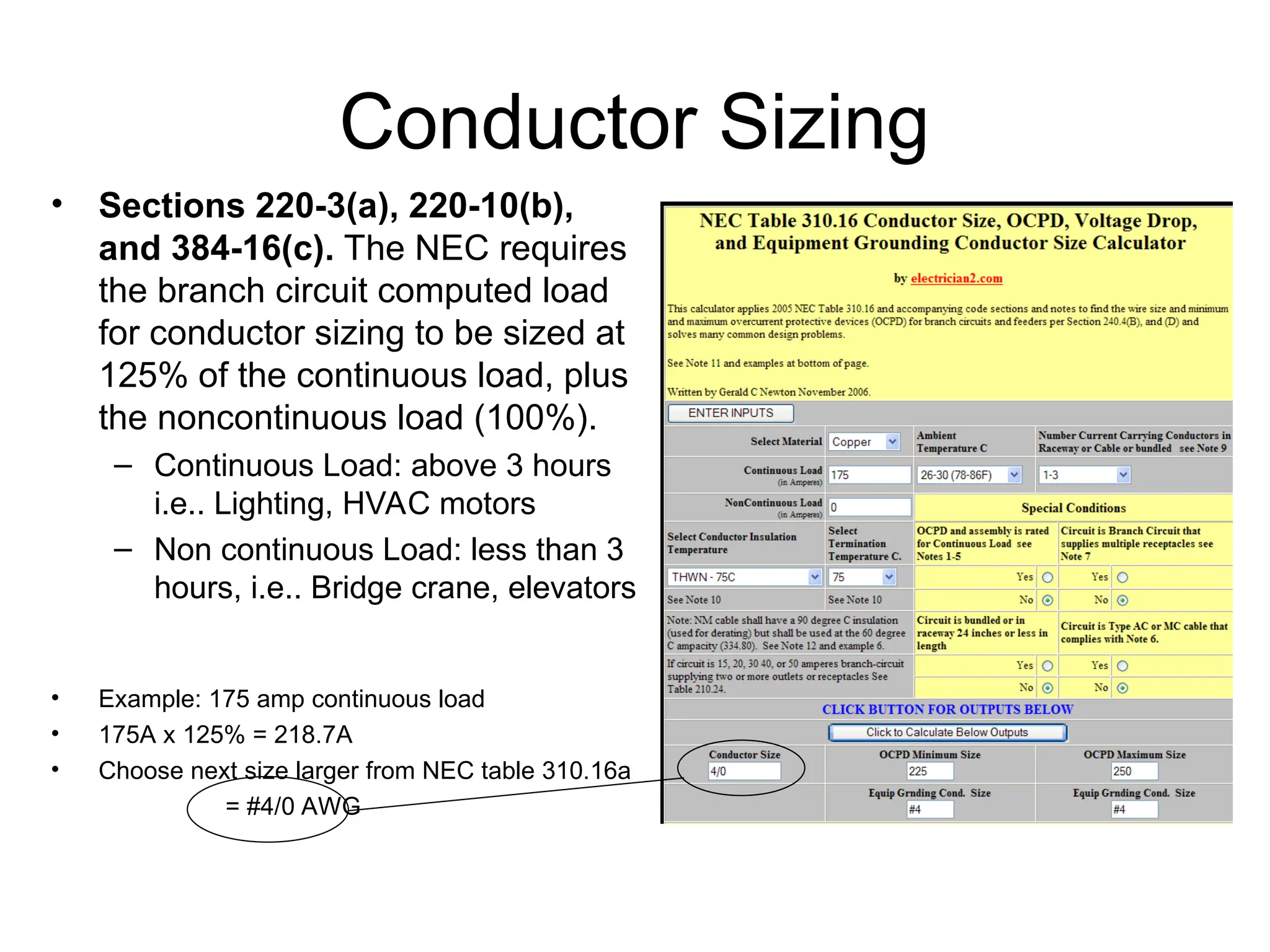
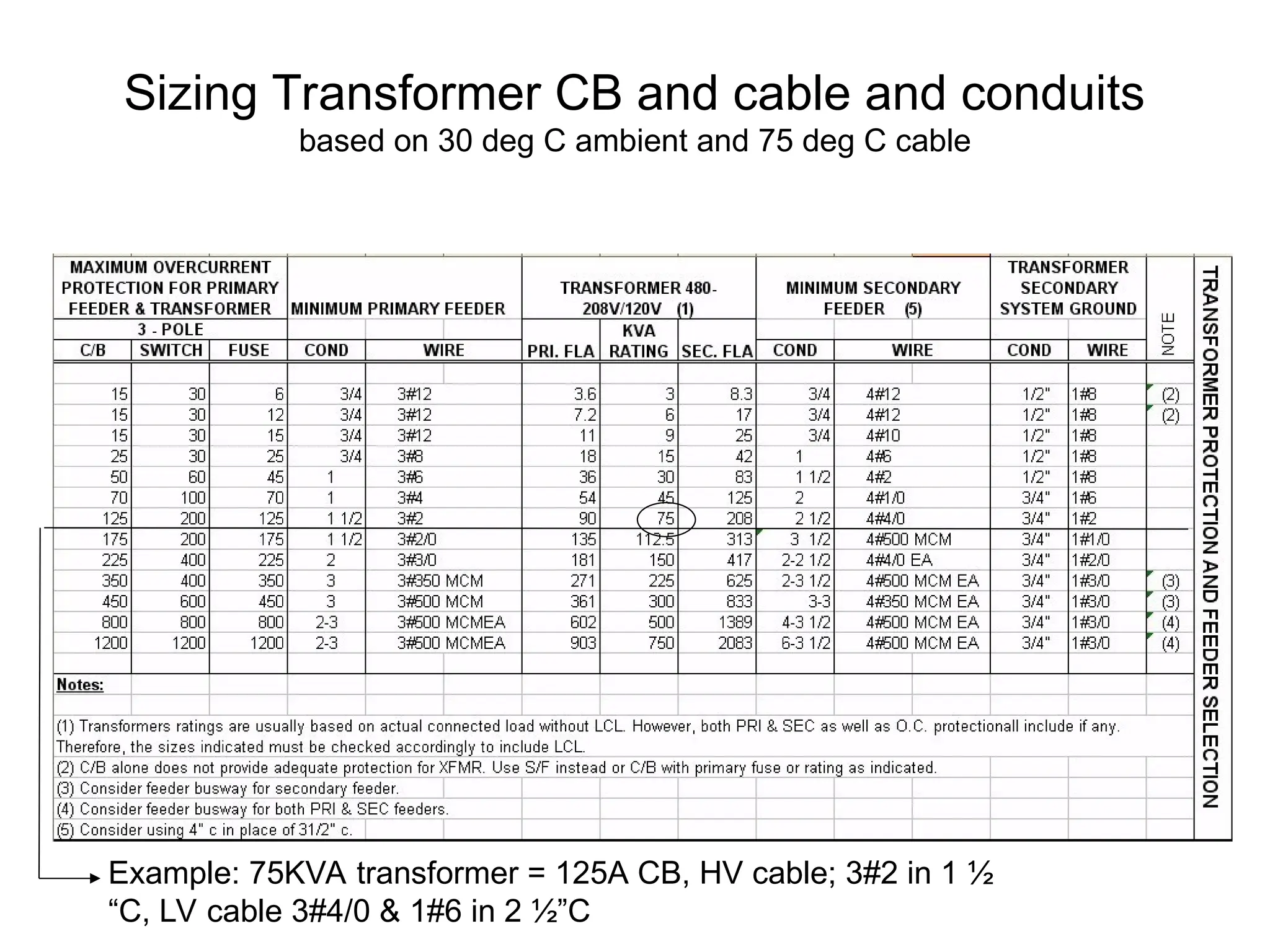
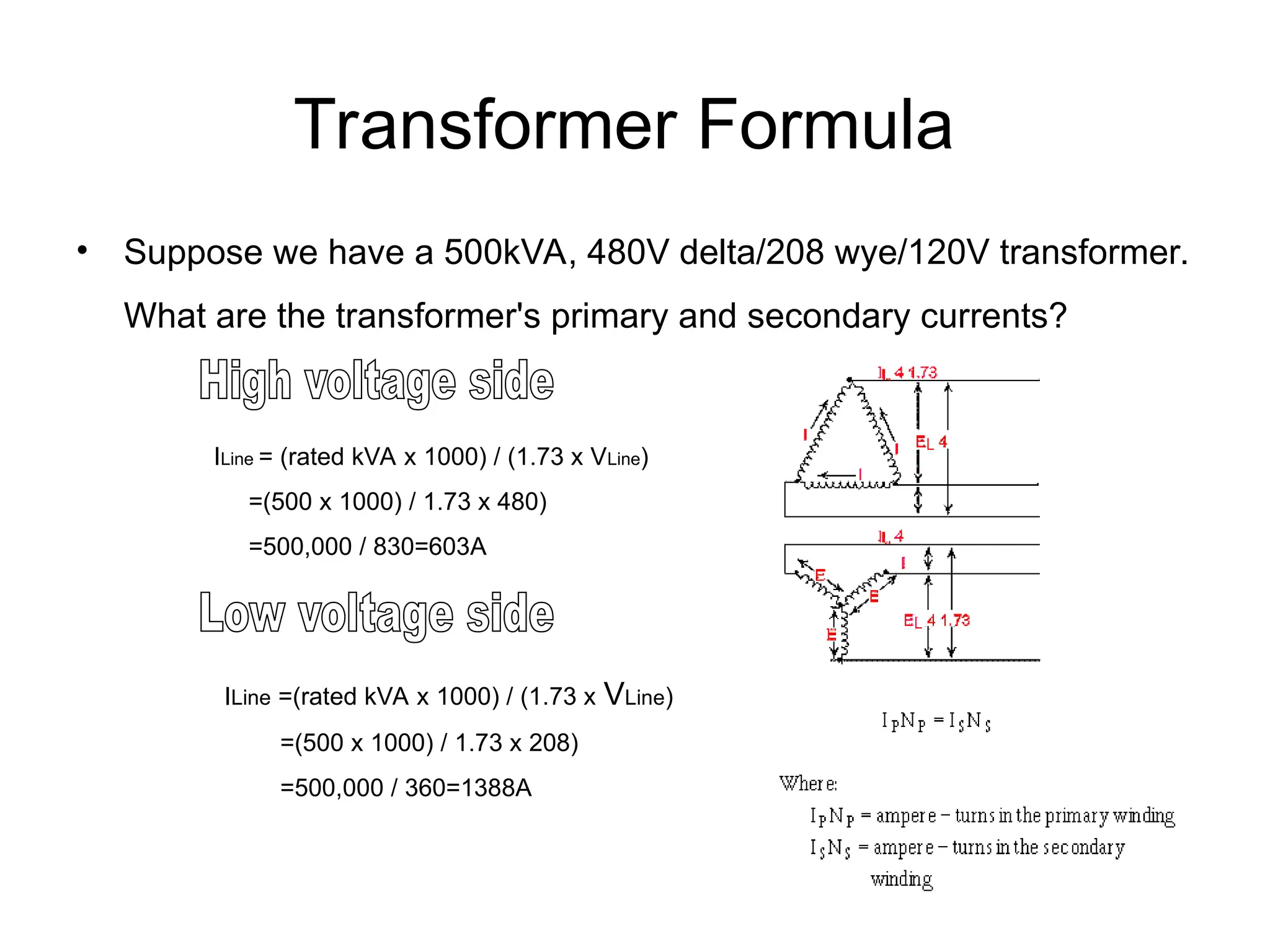
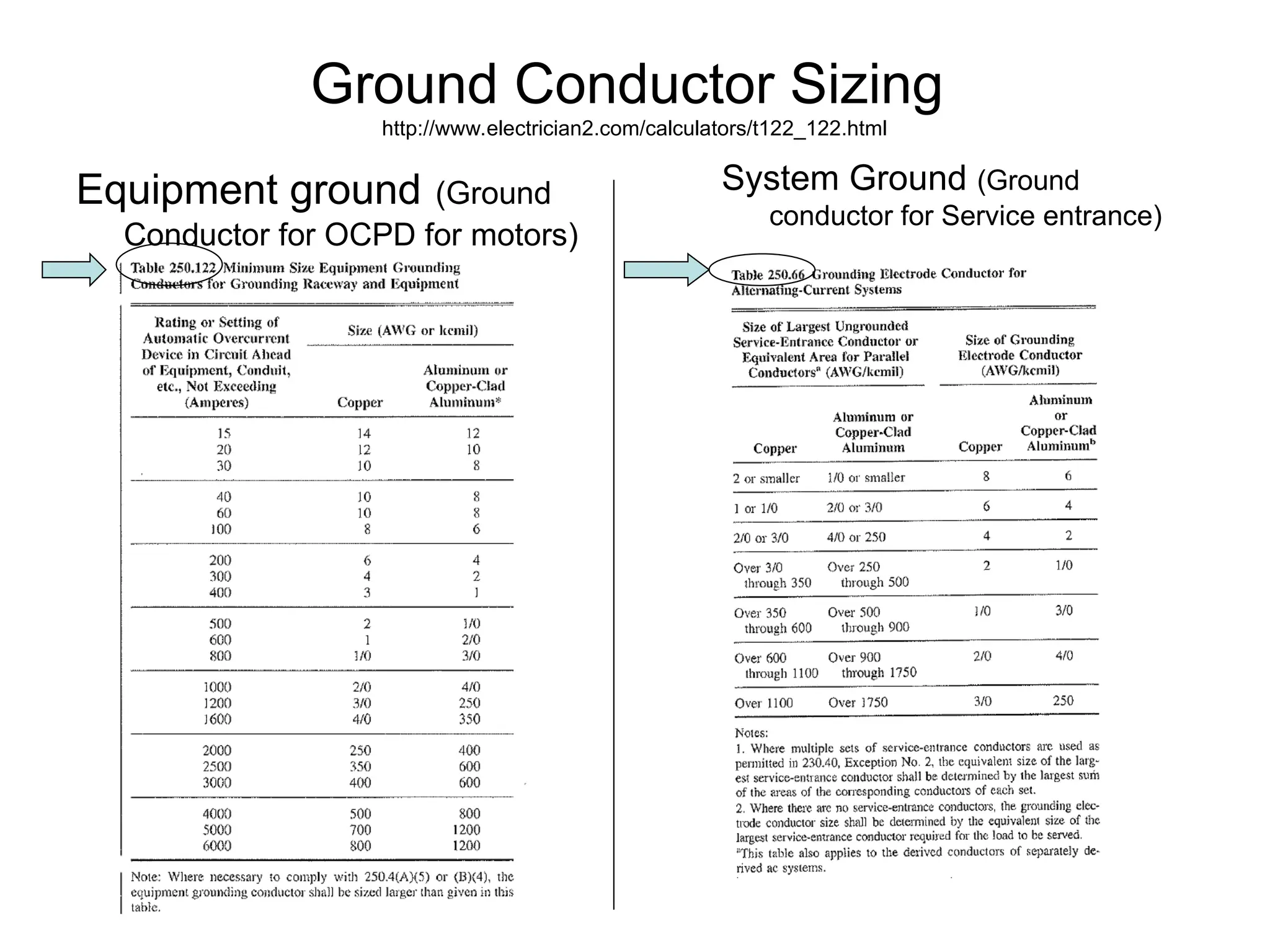
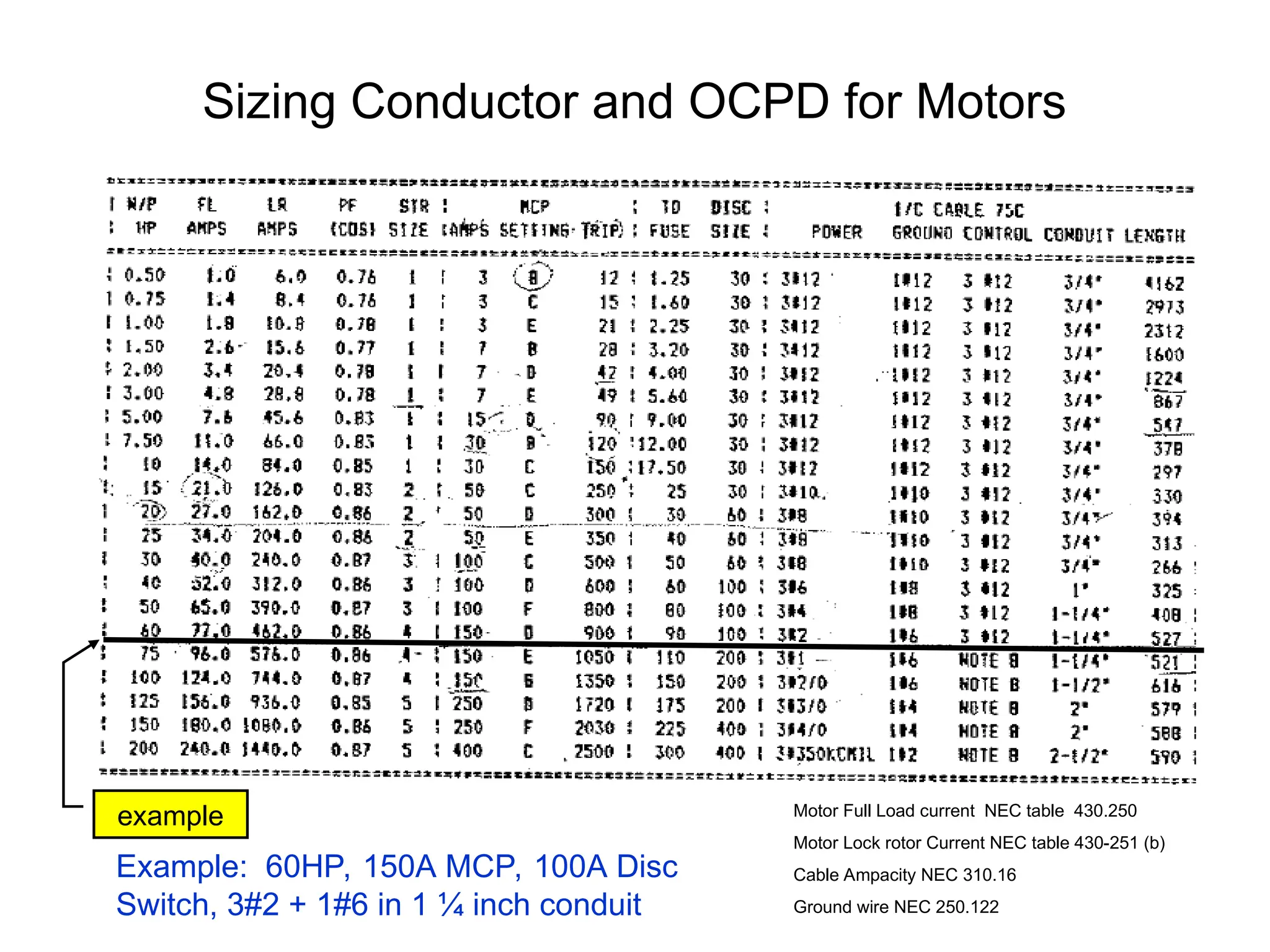
The document covers basic electrical design principles, emphasizing the importance of avoiding heat and conserving energy while adhering to electrical codes like the NEC. It provides detailed information on different types of enclosures, electrical formulas, conduit fill calculations, and sizing for transformers, cables, and conductors. Additionally, it highlights key principles and rules of thumb for effective electrical design.