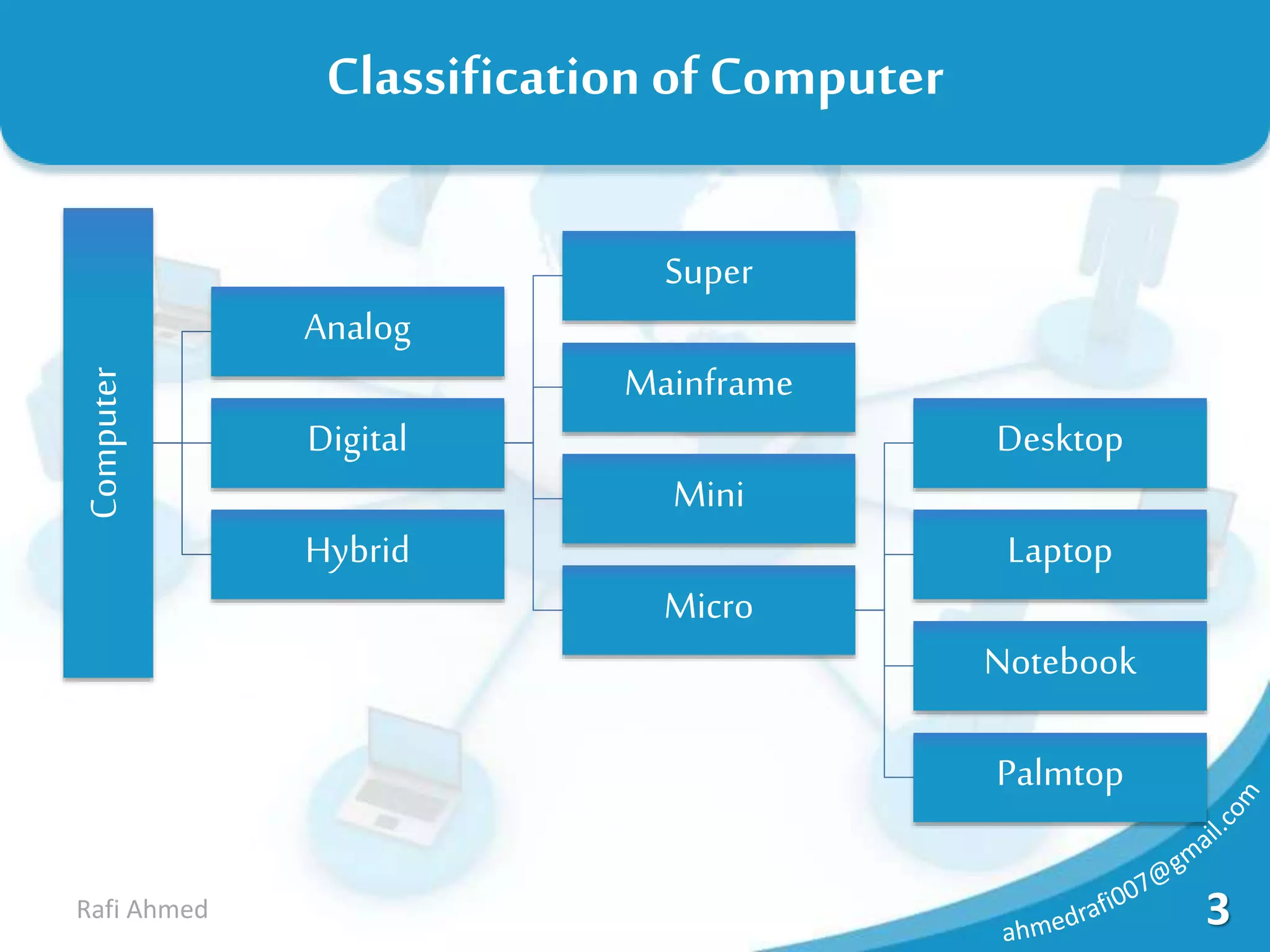
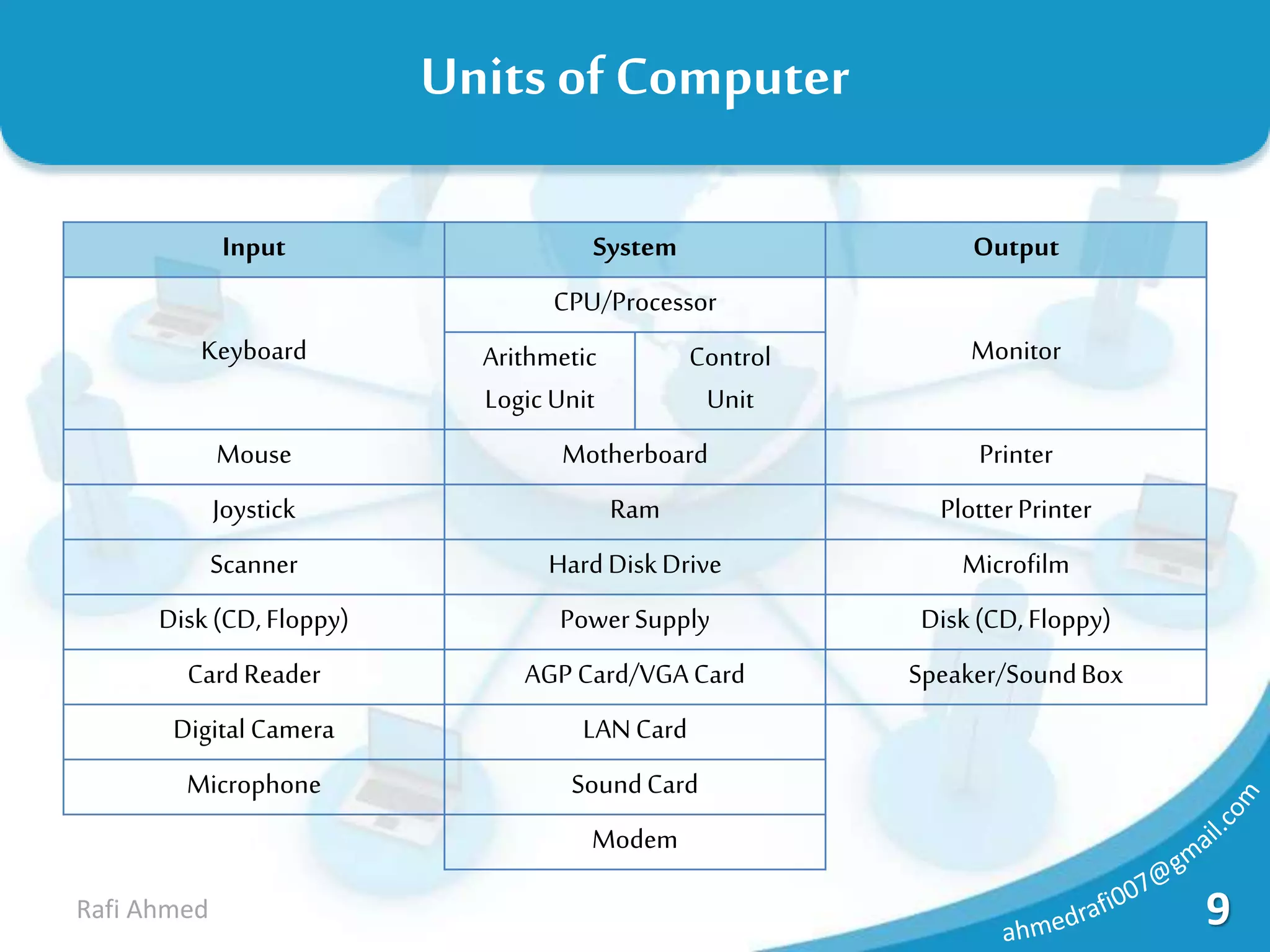
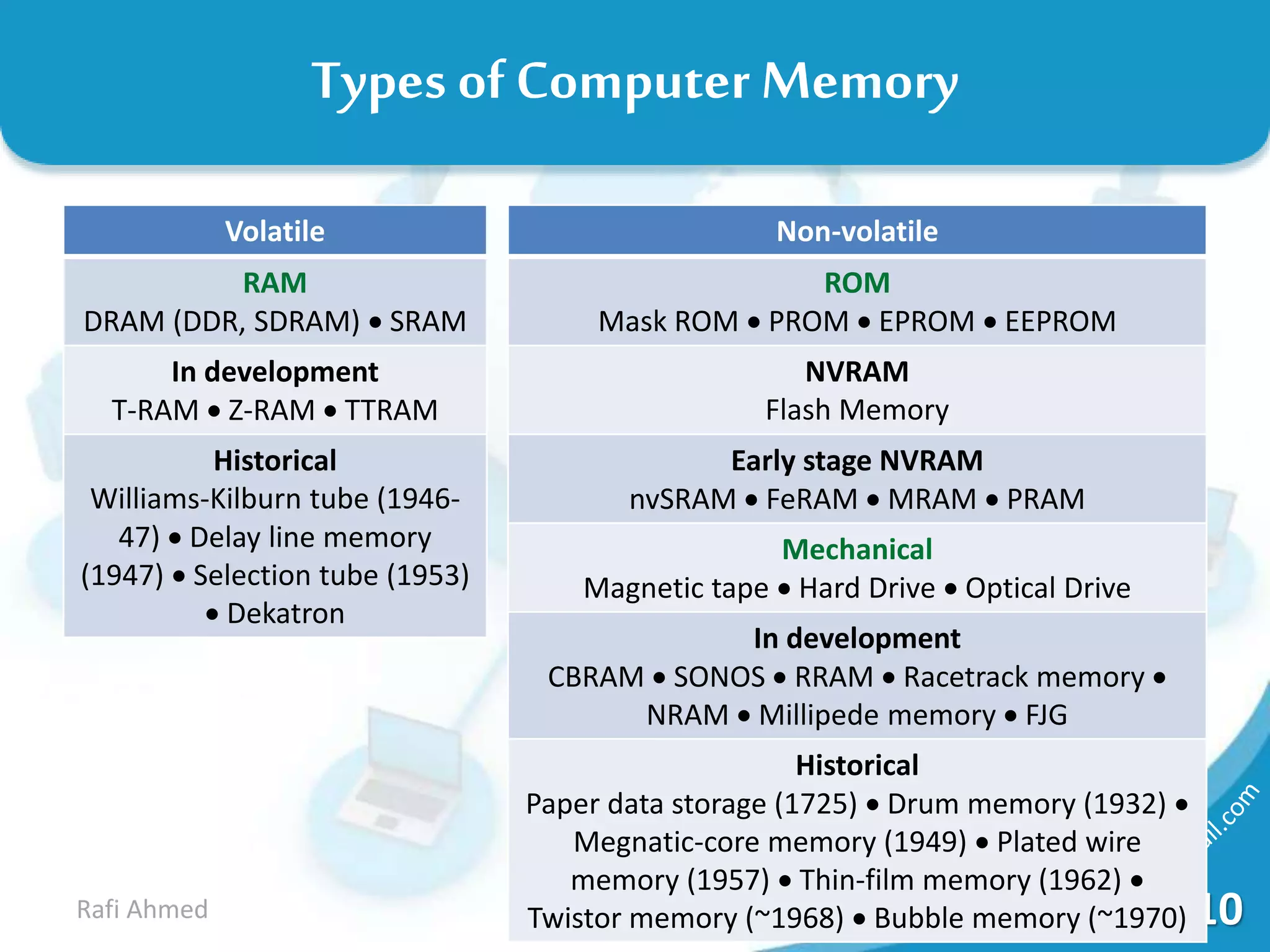
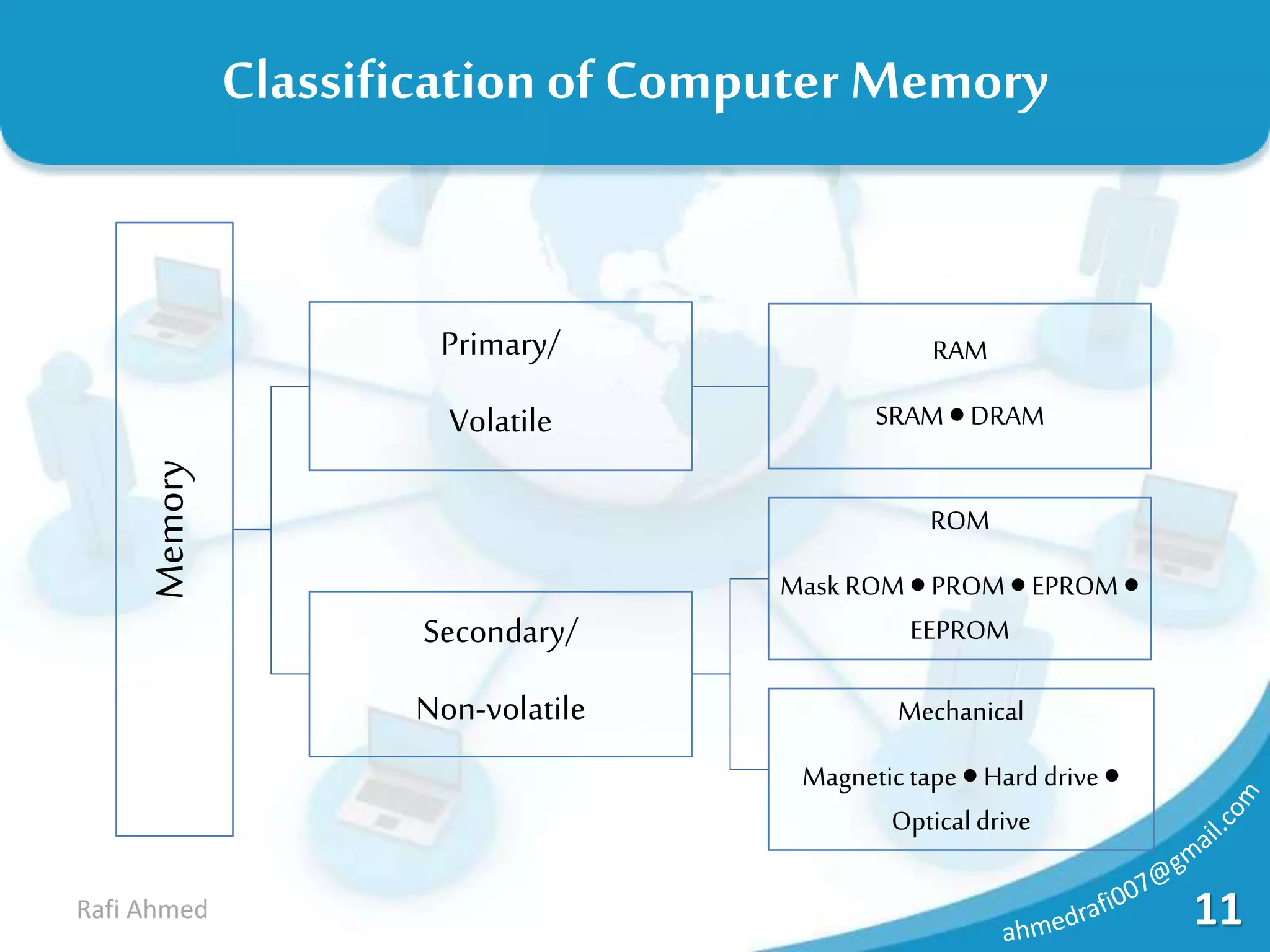
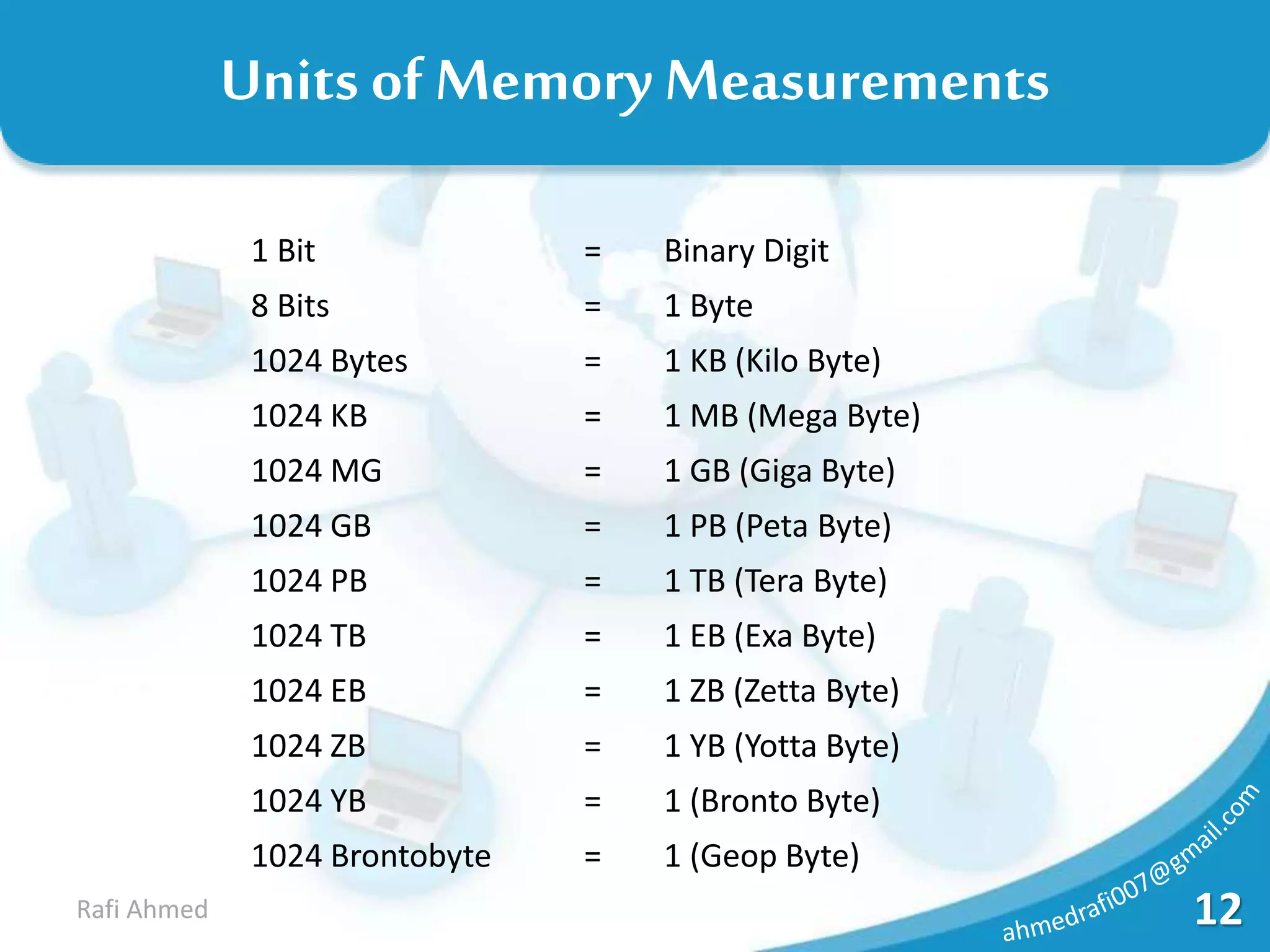
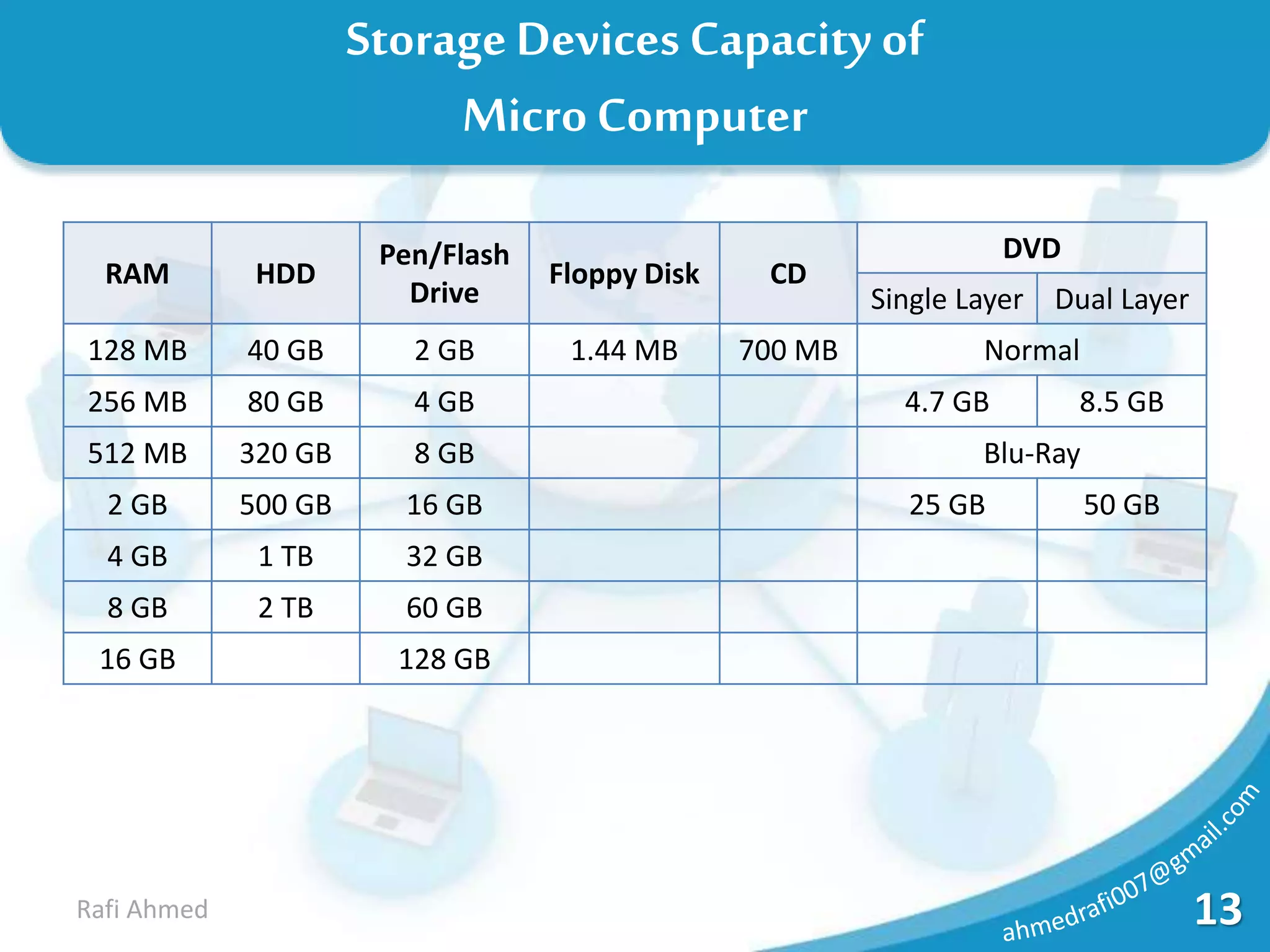
A computer is a device that processes data under the control of stored instructions to produce information. Computers can be analog or digital, and classified as supercomputers, mainframes, minis, micros, desktops, laptops, or palmtops. The two main types of supercomputers are the Tianhe-2 in China and Titan in the United States. Computers have various components like a CPU, memory, and input/output devices. Memory can be volatile RAM or non-volatile ROM, and is measured in bits, bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, and larger units. Storage devices have varying capacities depending on their type.