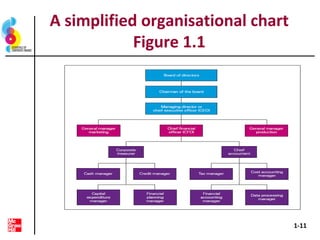
This document provides an introduction to the key concepts of financial management. It outlines that financial management involves understanding business finance decisions, the goals of financial management, different business organizations, and conflicts between managers and owners. The document then provides an overview of the four basic areas of finance - corporate finance, investments, financial institutions, and international finance. It describes some of the job opportunities within each area and concludes by defining business finance and the role of the financial manager.