Cereal and Legume Technology lecture slides3.pdf
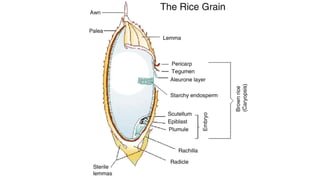
- 3. Rice • The rice grain (rough rice or paddy) consists of an outer protective covering, the hull, and the rice caryopsis or fruit (brown, cargo, dehulled or dehusked rice). • Brown rice consists of the outer layers of pericarp, seed-coat and nucellus; the germ or embryo; and the endosperm. • The endosperm consists of the aleurone layer and the endosperm proper, consisting of the subaleurone layer and the starchy or inner endosperm. • The aleurone layer encloses the embryo. Pigment is confined to the pericarp
- 4. • The hull (husk) constitutes about 20 percent of the rough rice weight, but values range from 16 to 28 percent. • The distribution of brown rice weight is Pericarp:1-2% Aleurone plus nucellus and seed-coat: 4-6% Germ: 1% Scutellum: 2% Endosperm: 90-91% Rice
- 5. • The endosperm cells are thin-walled and packed with amyloplasts containing compound starch granules. • The two outermost cell layers (the subaleurone layer) are rich in protein and lipid and have smaller amyloplasts and compound starch granules than the inner endosperm.
- 6. Rice classification • There is no international standard for brown rice grain size and shape. The following scale for size is generally used: • Extra long >7.5mm; • Long 6.61 - 7.5mm • Medium 5.51 - 6.6mm • Short <5.50 mm. • Length-to-width ratio is used to characterize grain shape as follows: • Slender >3.0 • Medium 2.1 - 3.0 • Bold 1.1 - 2.0 • Round < 1.0.
- 7. Cereal Storage • Cereal grains are extremely responsive to storage because their moisture content at harvest is relatively low and bio-deterioration is much slow. • Harvesting is seasonal but the need for fresh cereal products is continuous. The least requirement for storage, therefore, is for the period between harvests. • Under appropriate conditions, storage can be achieved for many years without serious loss of quality is possible.
- 8. Hazards besetting cereal grain storage • Excessive moisture content • Excessive temperature • Microbial infestation • Insect infestation • Rodent predation • Bird predation • Biochemical deterioration • Mechanical damage through handling The complexity of storage problems results from the matrix of interactions of the various hazards
- 9. Moisture content and storage temperature • The safe moisture contents for storage varies according to the type of cereal but it is widely assumed that they are equivalent to the equilibrium moisture content of the respective grains at 75% RH and 25°C Cereal types Moisture % Barley 14.3(25-28 0C) Maize 14.3 Oats 13.4 Rice 14.0 Ryes 14.9(25-28 0C) Sorghum 15.3 Durum Wheat 14.1 Red Wheat 14.7 White Wheat 15.0
- 10. Storage facilities In the commercial context storage facilities are needed for three purposes: 1. Holding stocks on the farm prior to sale. 2. Centralization before distribution or processing during the year following harvest. 3. Storage of annual surpluses over a longer period. • Long term safe storage targets protection against dampness caused by weather or other sources, micro-organisms, high temperature, insects, rodents and birds, objectionable odours and contaminants. • Clearly the simplest stores such as piles on the ground, unprotected, are suitable for short periods only. • Careful design is essential to address requirements of ventilation and exclusion of insects. • Other simple stores, system is suited to cob maize rather than threshed grains, as adequate space for air movement within the store is essential.
- 11. Milling of Grains • Milling is a process in which grains such as oats, wheat, rice, and corn are dehulled and ground into smaller pieces or flours to improve palatability, reduce cooking time, and create food products. • Each type of grain has a unique processing method that yields a wide range of products • Usually includes removal of the outer hull which contains tough fibrous material. • The grains may then be toasted, soaked, or cooked to soften and release the starch and other carbohydrates.
- 12. Difference Between Wet Milling and Dry Milling • Dry milling uses particle-on-particle contact to reduce material size • Wet milling involves dispersing the material in a liquid and using solid, grinding elements to reduce size. • Products can be broken down through either one of these processes, but wet milling tends to be a more intensive process than dry milling. • Wet milling, also known as wet grinding, is a process through which particles that are suspended in a liquid slurry are dispersed in that liquid by shearing or crushing. • Once the milling process is complete, these particles are ready for use or can be dried and separated for incorporation into additional products.
- 13. Difference Between Wet Milling and Dry Milling • Wet milling is more complex than dry milling due to the addition of a liquid, but this process also has the power to reduce a product into finer particles. • This allows for the production of a greater variety of by-products and also can result in improved physical properties in your final product. • By contrast, dry milling utilizes no liquid element, and is most frequently used for the particle size reduction of dry materials like powders and granules, or de-agglomerating and de-lumping bulk materials. • While dry milling is a less intensive process, which often makes it the first method considered, wet milling is the best and most efficient way to get to your preferred particle size if extremely small particles are the goal.
- 14. Maize Processing • Processed by either dry or wet milling • In dry milling, there are 2 methods: Traditional – Germ is not removed Modern- Germ is removed • Non-degerming dry milling is carried out on a local basis in small mills or modern roller mills using sifters • Maize is ground to make coarse whole mill of 85-95% extraction rates • Wet and dry milling processes involving degerming are carried out in large commercial mills. • Dry milling not involving degerming is susceptible to oxidation and rancidity (germ has high amount of oil : 32-35%)
- 15. Maize Processing • Tempering and degerming removes most of the germ and hull and leaves the endosperm as free of oil and fibre as possible to recover maximum yield of endosperm as possible • Maize is cleaned to remove dirt, stones, chaff, broken kernel and extraneous plant material. • It is then conditioned by adding water achieve 20-25% moisture – moistened kernels are allowed to equilibrate for 1-3hrs • Conditioning aims to loosen the germ, toughen the bran and mellow the endosperm
- 16. Maize Processing Cont….. • Degerming and dehulling are carried out in the following 3 ways: Beall degerminator Roller mills and sifters Impact machines(eg. Entoleters & gravity separators) • The germ and hull are removed, endosperm reduced in size to grits with roller mills • A complex array of roller mills and particle size separating equipment is used to purify and size endosperm products • All products are then dried prior to packaging and bulk storage
- 17. Entoleter
- 18. Roller Mill
- 19. Typical Process Grain Receipt Milling Grading Drying Degerming Storage Cooling Conditioning Cleaning Drying Packaging
- 20. Wet Milling • Maize is processed into starch, protein, fiber, and oil-rich germ in a process referred to as “wet milling.” • The actual wet milling is preceded by grain cleaning and steeping steps and then makes use of sieving and density-based separations in an aqueous environment to subsequently isolate germ, bran, protein, and starch.
- 21. Cleaners Steep tanks Centrifugal separators Starch washing Grind mills Germ separators Maize Washing screens Starch and nutritive sweeteners Steep water evaporators Steep water Germ Gluten Bran Condensed fermented maize extractives Germ extractors Oil Corn germ mill Gluten meal Gluten feed WET MILLING PROCESS
- 22. Cleaning • All impurities such as chaff, stones, dust, broken or insect infested grains and other foreign materials are removed byscreening and aspirating
- 23. Steeping • Water used for steeping and is usually carried out at about 50°C for 28 to 48 hrs to achieve a final moisture content of 45% • The steeping water contains 0.1–0.2% sulfur dioxide, for two reasons. • First, it aids in stopping the growth of putrefactive organisms. • Second, the bisulfite ion reacts with disulfide bonds in the matrix proteins of the maize and reduces the average molecular weight of the proteins, making them more soluble. • As a result, the release of starch from the protein matrix is much easier and more complete. • During steeping, the level of sulfur dioxide in the steep water decreases as more of the bisulfite ion reacts with the protein.
- 24. Germ Recovery • The wet and soft maize kernel is torn in a degerminating unit having a metallic stationary and a rotating plate, with projecting teeth • Frees the germ without any grinding • The germ, being lighter, is separated by centrifugal forces or floatation method
- 25. Milling • After germ separation and screening of the coarse particles, the mixture contains gluten, starch and hull • In this step, the endosperm and hull are ground by either stone mill or modern entoleters to release the rest of the starch • Here only the starch is released with little size reduction of the hulls
- 26. Hull Recovery • The milled slurry containing ground starch is passed through a series of hexagonal reels where the coarser hulls and fibres are removed
- 27. Separation • Slurry containing starch and gluten is concentrated and the lighter gluten particles are separated from the relatively heavier starch particles by centrifugal force
- 28. Wheat Milling • The milling of wheat consists of the separation of bran and germ from the endosperm and reduction of endosperm into fine flour • The traditional procedure for milling wheat has been stone grinding to obtain whole wheat flour. • This method results in 90-95% extraction rate and retains almost all the nutrients of the grain while simultaneously eliminating that part of the grain which is most indigestible like cellulose and phytic acid which binds and carries away minerals. • In modern milling, the wheat is subjected to cleaning to remove various types of impurities together with damaged kernels.
- 29. Cleaning • Vibrating Screen: Grain is removed of various types of impurities together with damaged, shrunken and broken kernels which are collectively known as screenings. This removes bits of straw and other coarse materials and second screen removes foreign materials like seeds. • Aspirator: The stream of grain is directed across screens while air sucks off the dust and lighter impurities. • Disc separator: After the aspirator it moves into a disc separator consisting of discs revolving on a horizontal axis. The surface of the discs indented to catch individual grains of wheat but reject larger or smaller material. • Scourer: The wheat then moves into the scourer, a machine in which beaters attached to a central shaft throw the wheat violently against the surrounding drum, buffing each kernel and breaking off the kernel hairs. • Magnetic Separator: The stream of wheat next passes over a magnetic separator that pulls out iron and steel particles contaminated during harvesting.
- 31. Aspirator
- 32. Scourer
- 34. Conditioning / Tempering • Carried out primarily to improve the physical state of grain for milling. • In conditioning moisture content of wheat kernel is adjusted by heating and cooling of the grain for definite period of time, in order to obtain the desired moisture content and distribution • At this adjusted moisture wheat endosperm becomes mellow and bran becomes tough. • Bran that absorbs proper amount of moisture becomes elastic and will not splinter during grinding to contaminate the flour with fine particles, and thus flour becomes whiter in colour. • The endosperm becomes mellower and more friable, thereby reducing the amount of power required to grind it. • Several methods are employed to condition the wheat e.g heating the wheat, application of warm water, application of live steam, or just intensive mixing of wheat and water
- 35. Conditioning / Tempering cont.. • Three factors affect the rate and level of water penetration into the kernel: temperature, amount of water (% moisture content) and time. • The ideal water and wheat temperature for tempering condition is 25°C. • Higher temperature will increase the rate of penetration into the kernel. • Temperature above 50°C will change endosperm starch and protein characteristics.
- 36. Typical moisture contents of tempered wheat and tempering times Type of wheat Optimum moisture content of tempered wheat Tempering time (Hrs) Hard spring wheat 16 -17% 36 Hard red winter wheat 15.5 -16.5% 24 Soft wheat 14.5 - 15.5% 10 Durum wheat 16 - 17.5% 6
- 37. Milling • Wheat flour milling is a process that consists of controlled breaking, reduction and separation involving 3 basic processes: Grinding: Fragmenting the grain or its parts Sieving: Classifying mixtures of particles based on its particle size Purifying: Separating bran from endosperm particles based on their terminal velocity, by means of air currents. • Grinding of the wheat occurs between two cast rolls (break rolls) that rotate against each other. These rollers are fluted and they are not in contact with each other • The upper roller rotates 2.5 times for each rotation of the lower one. • Hence, the grain is engaged between fluted grooves of the rolls and broken or cut by the faster roll as it is held back by the slower roll. • There are usually 4 or 5 sets of rollers for this process
- 39. Wheat Milling Process • This initial stage in milling process is referred as breaks. The breaks are used in the grinding steps to crack and separate the bran, germ and endosperm from each other • The outer husk is collected separately as bran. • The middlings are separated into three grades: fine, medium, coarse in an operation called gradual reduction system ( up to 12 sets of rolls) • Here the rolls are smooth and one rotates only one and a quarter times for each rotation of the other. • These three streams are then put through purifiers consisting of a long, narrow, sieve set. • The sieves become coarser progressively in size of mesh from head to tail. • The sieve section is connected to a fan and the air is drawn up through each sieve section to draw off branny particles
- 40. Bleaching • The flour contains a slightly yellowish colour due to xanthophylls • Therefore the flour has to be bleached by oxidation. However, this process may be slow due to bulk storage • Flour bleaching is a chemical treatment that removes yellow xanthophyll and other pigments from milled grains to produce whiter, finer-grain flour • Commercially-used flour bleaching agents include: Chlorine gas Chlorine dioxide Nitrogen dioxide Calcium and benzoyl peroxides Azodicarbonamide
- 41. By-products of wheat milling • Bran from the break system • Shorts from the residue system; small particle size bran pieces • Red dog from low grade system; flour rich bran particles • Low grade flour from low grade system; flour sized particles from last grinding step • Germ from sizing system