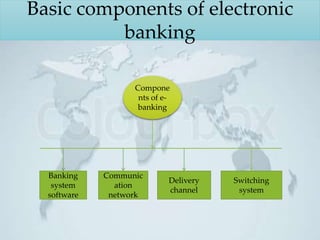
This document provides an overview of electronic banking (e-banking) in Bangladesh. It discusses the objectives and basic components of e-banking from both the bankers' and clients' point of view. Specific components covered include automated teller machines (ATMs), debit cards, credit cards, point of sale (POS) services, and mobile and internet banking. The document also outlines some functions of ATMs, advantages of debit cards, and risks associated with e-banking. It concludes by identifying some problems with e-banking in Bangladesh and providing recommendations to improve its implementation.