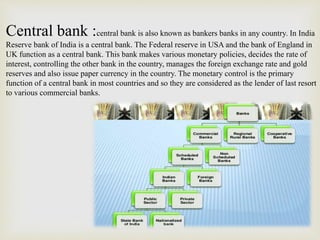
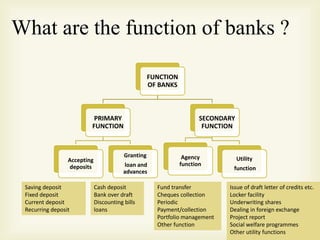
Banks provide essential financial services and fall into several categories. Commercial banks accept deposits from customers and use those funds to issue loans to individuals and businesses. They can be public sector banks owned by the government, private sector banks operated by private entities, or foreign banks with branches in India. Cooperative banks provide lower-interest financing to farmers, small businesses, and salaried individuals. Specialized banks focus on unique services like foreign exchange, while investment banks help raise capital and provide financial advice. Central banks like India's Reserve Bank make monetary policy and ensure stability of the overall banking system.