This document provides information on balance sheets and income statements for farms. It includes:
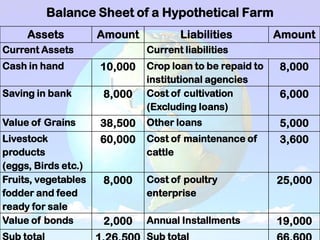
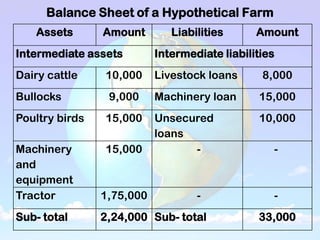
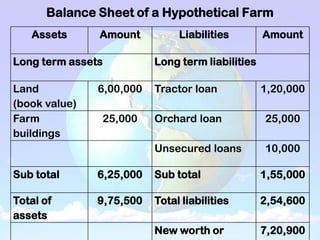
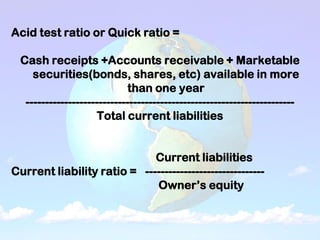
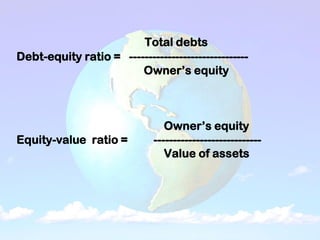
1) A balance sheet shows a farm's financial position at a point in time by listing assets owned and liabilities owed. Assets include current assets (cash, crops), intermediate assets (machinery, livestock), and long-term assets (land, buildings). Liabilities include current (short-term loans), intermediate, and long-term debts.
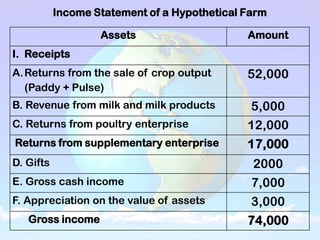
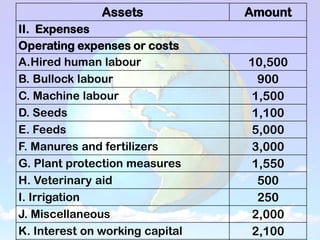
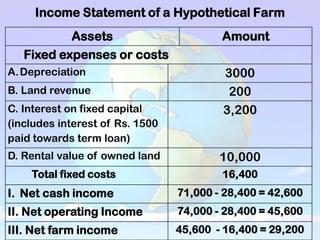
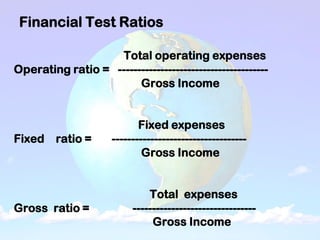
2) An income statement reports a farm's receipts, expenses, and profits over a period of time. Receipts come from crop and livestock sales. Expenses include operating costs and fixed costs like depreciation. Profits are calculated as net cash income, net