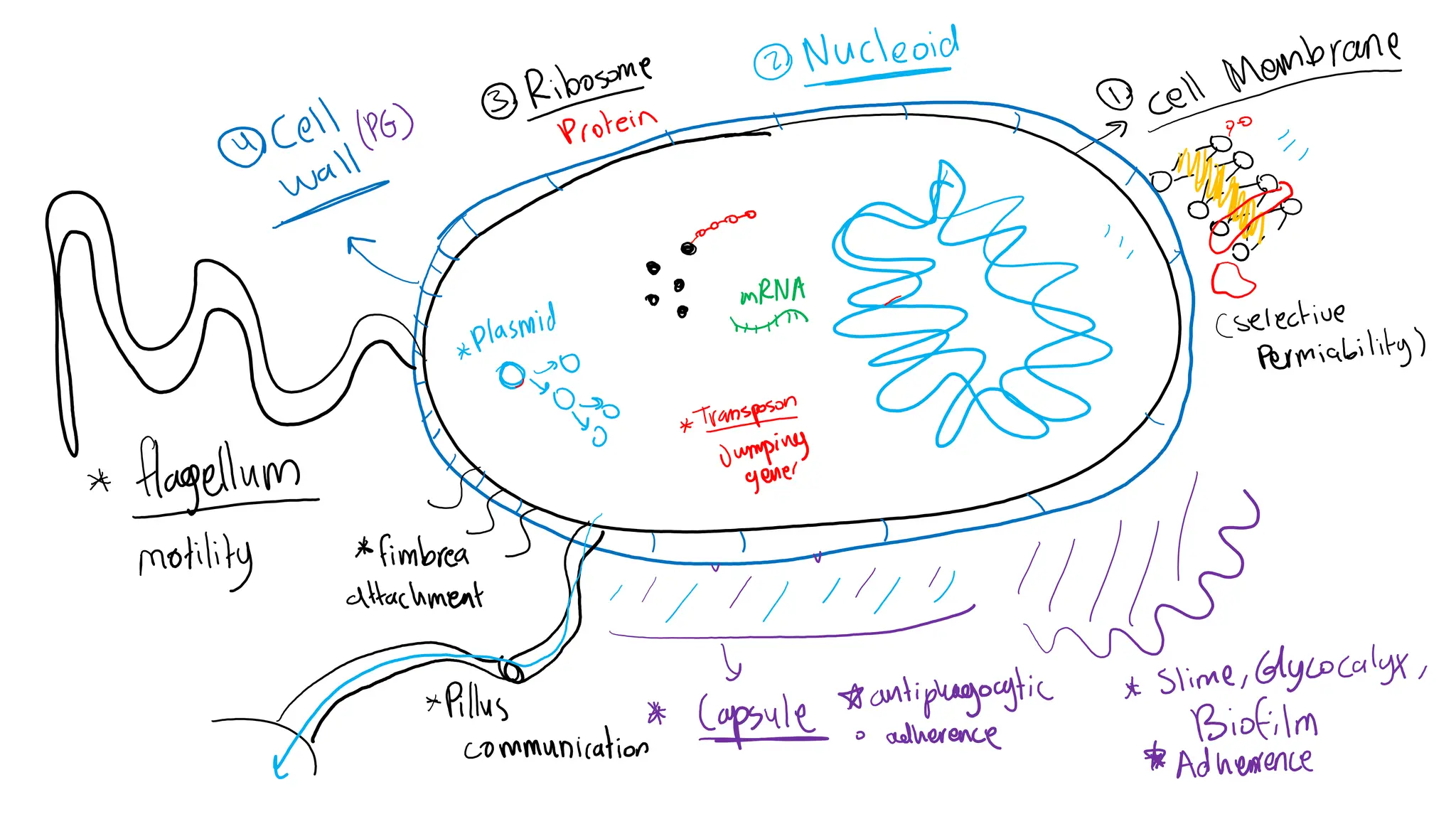
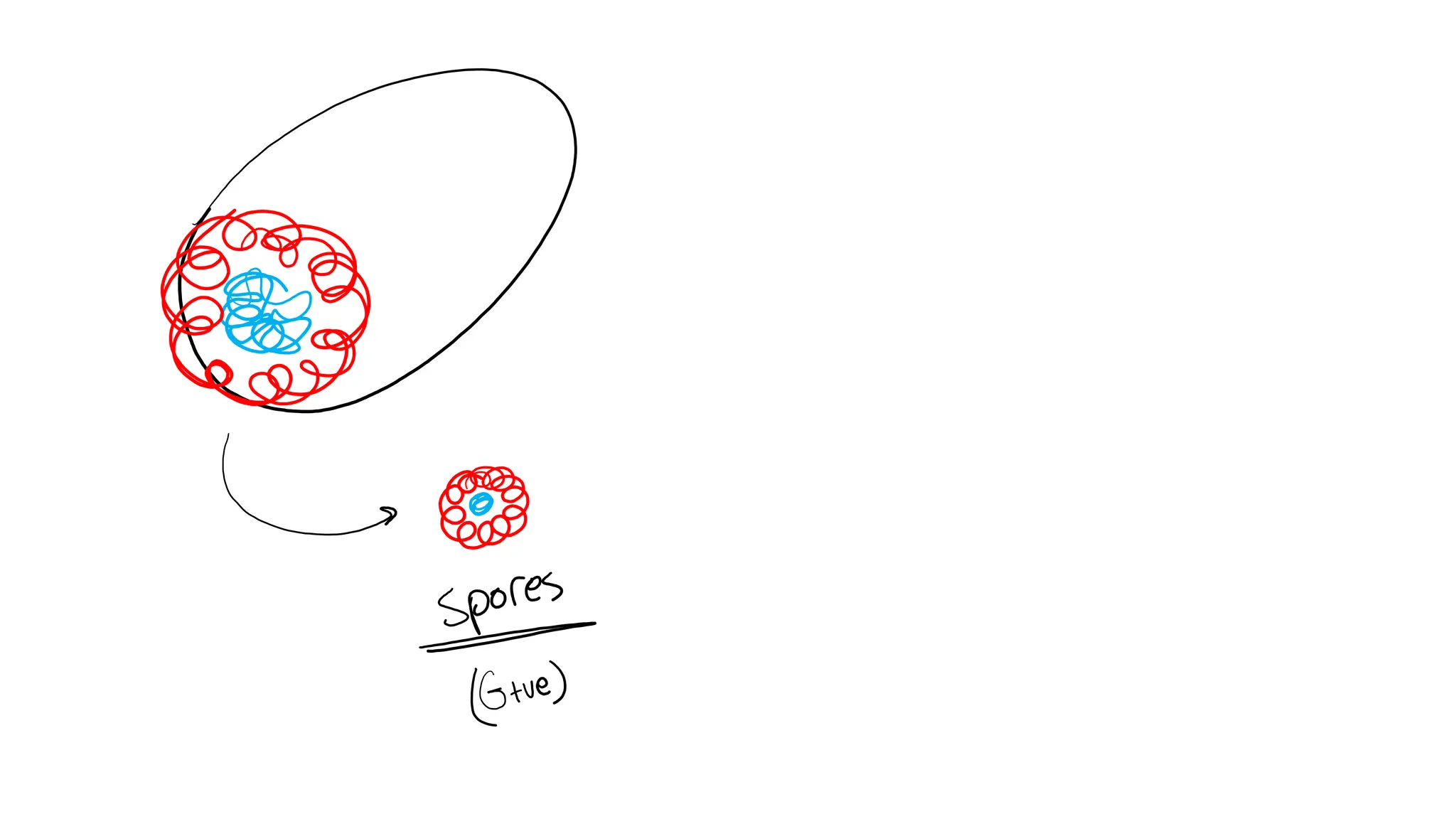
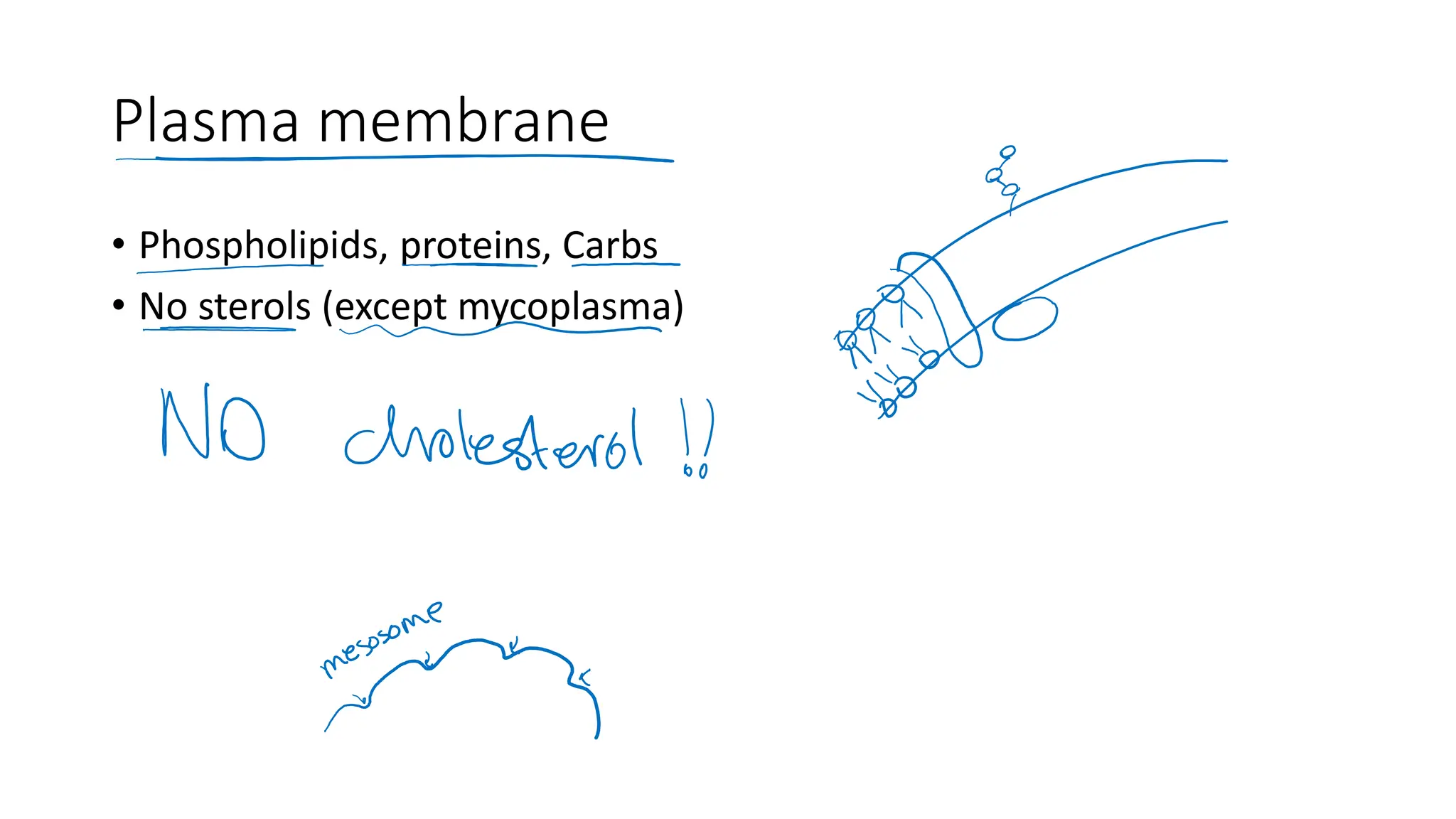
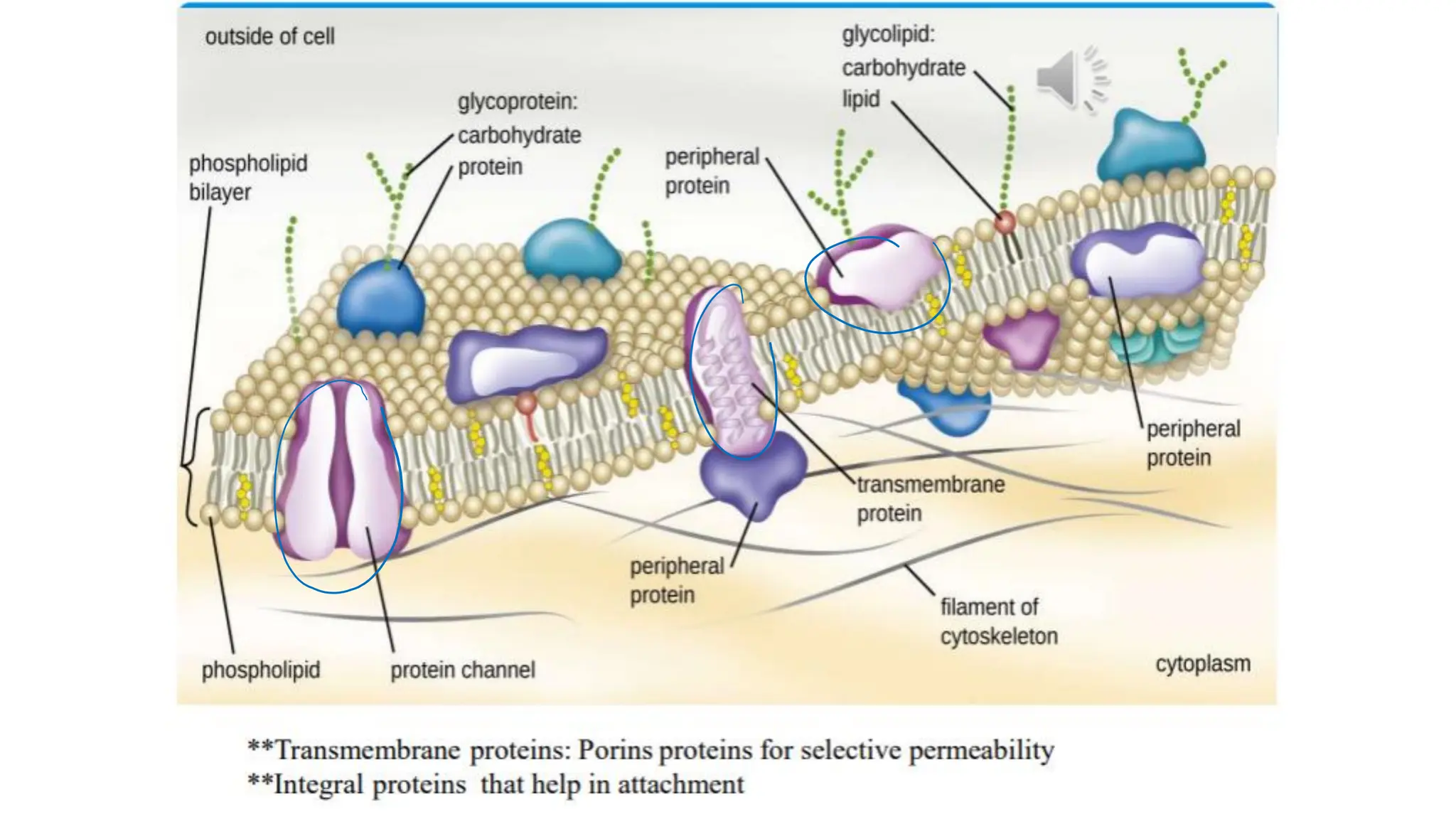
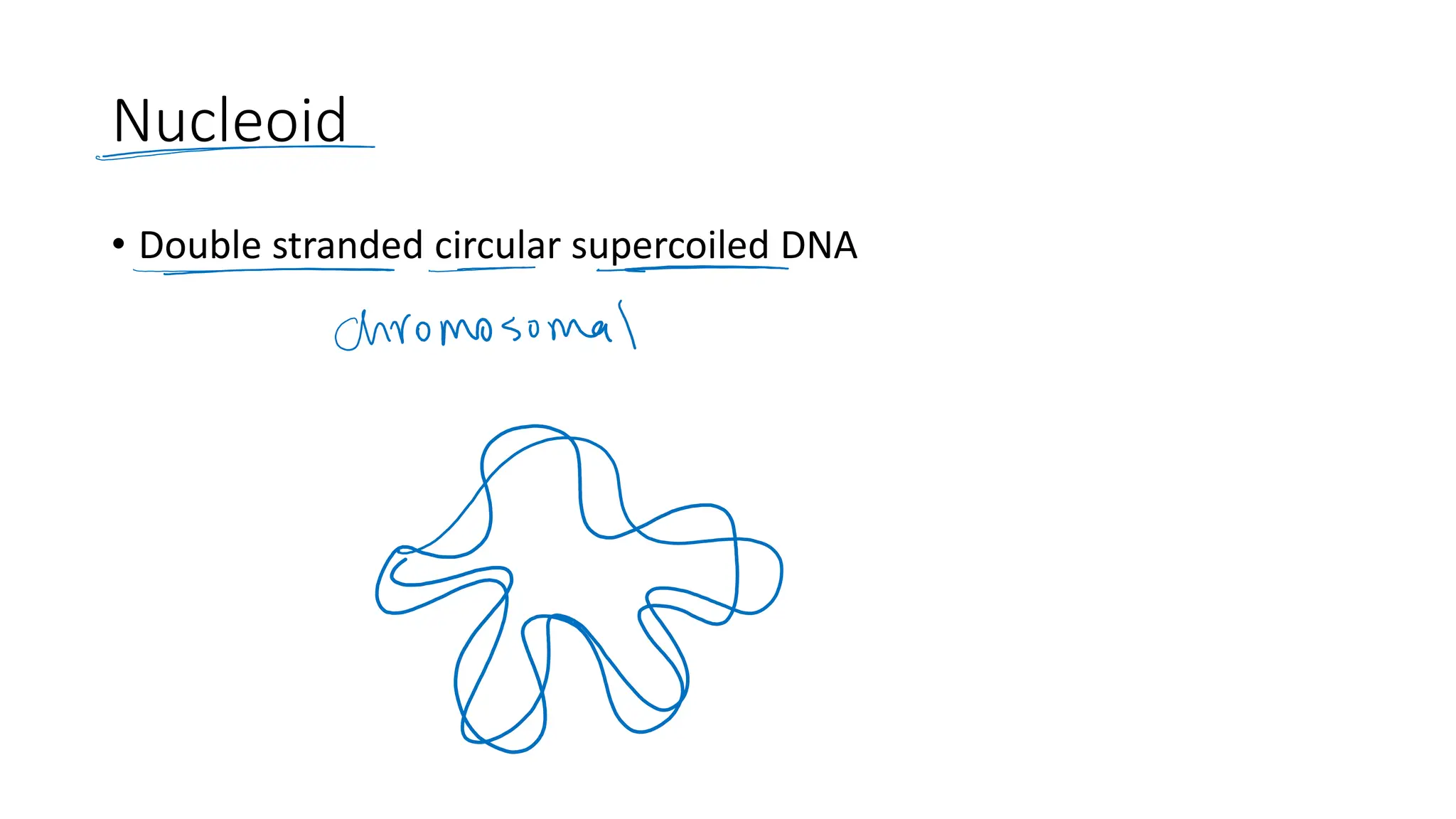
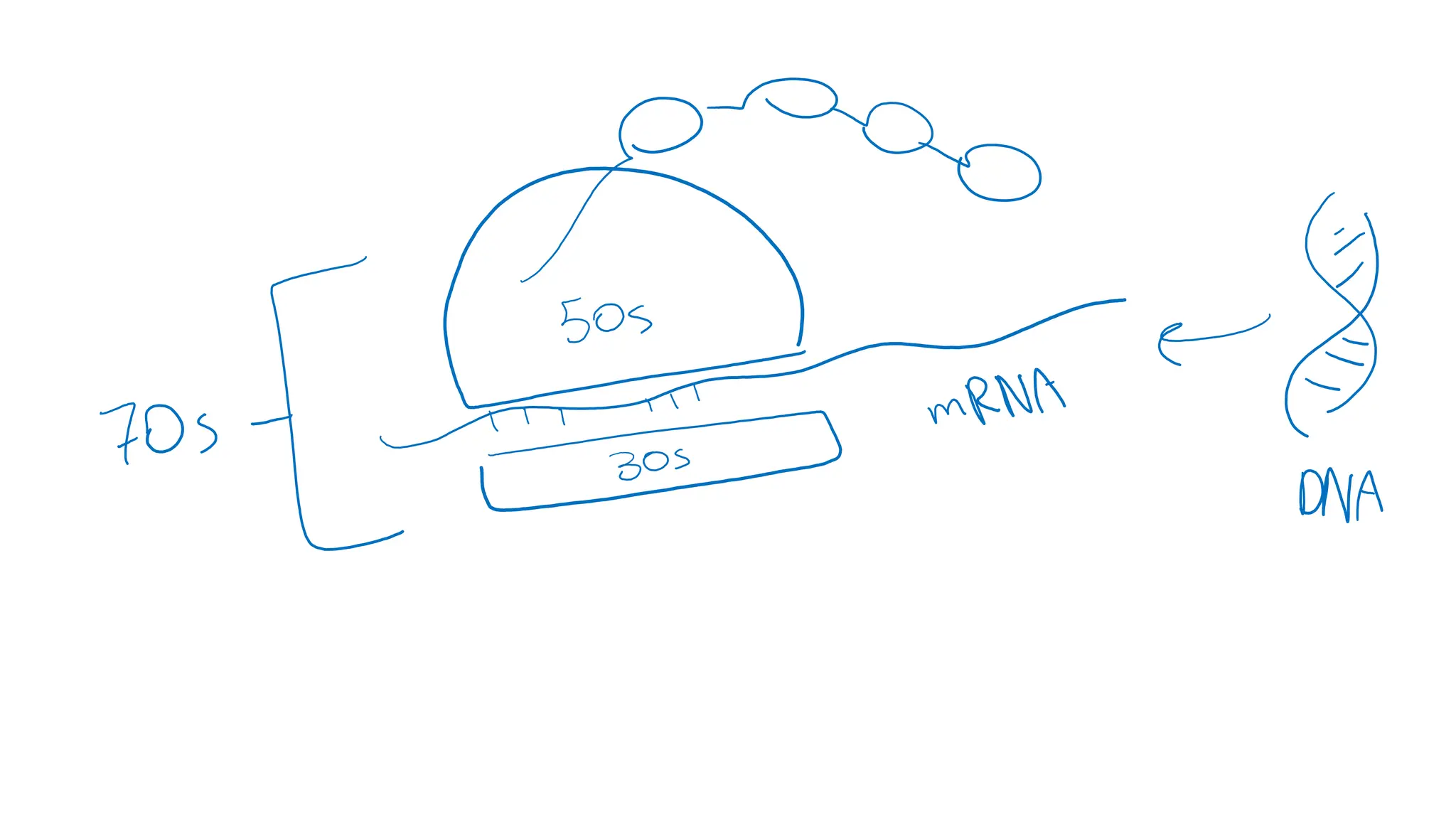
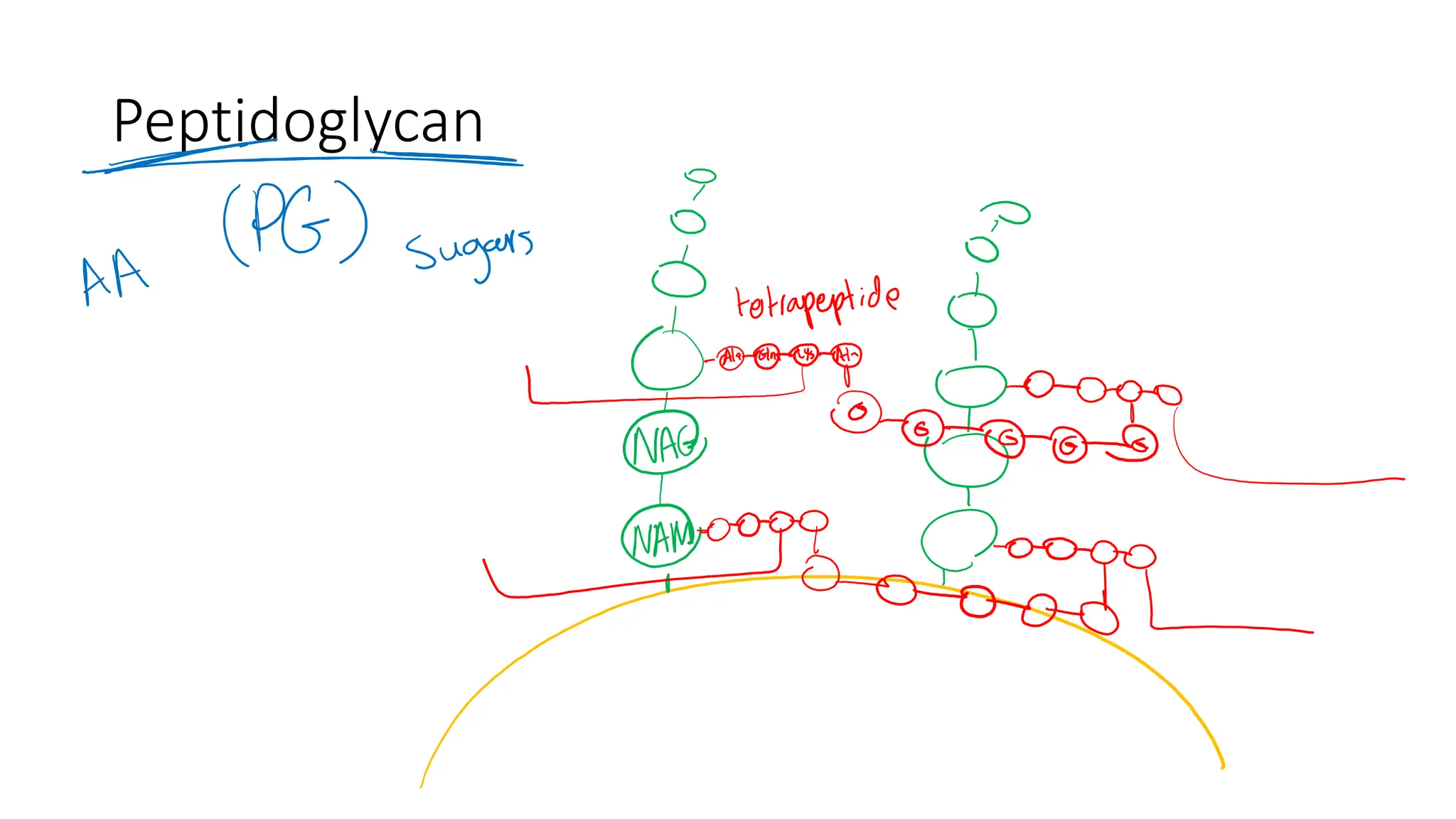
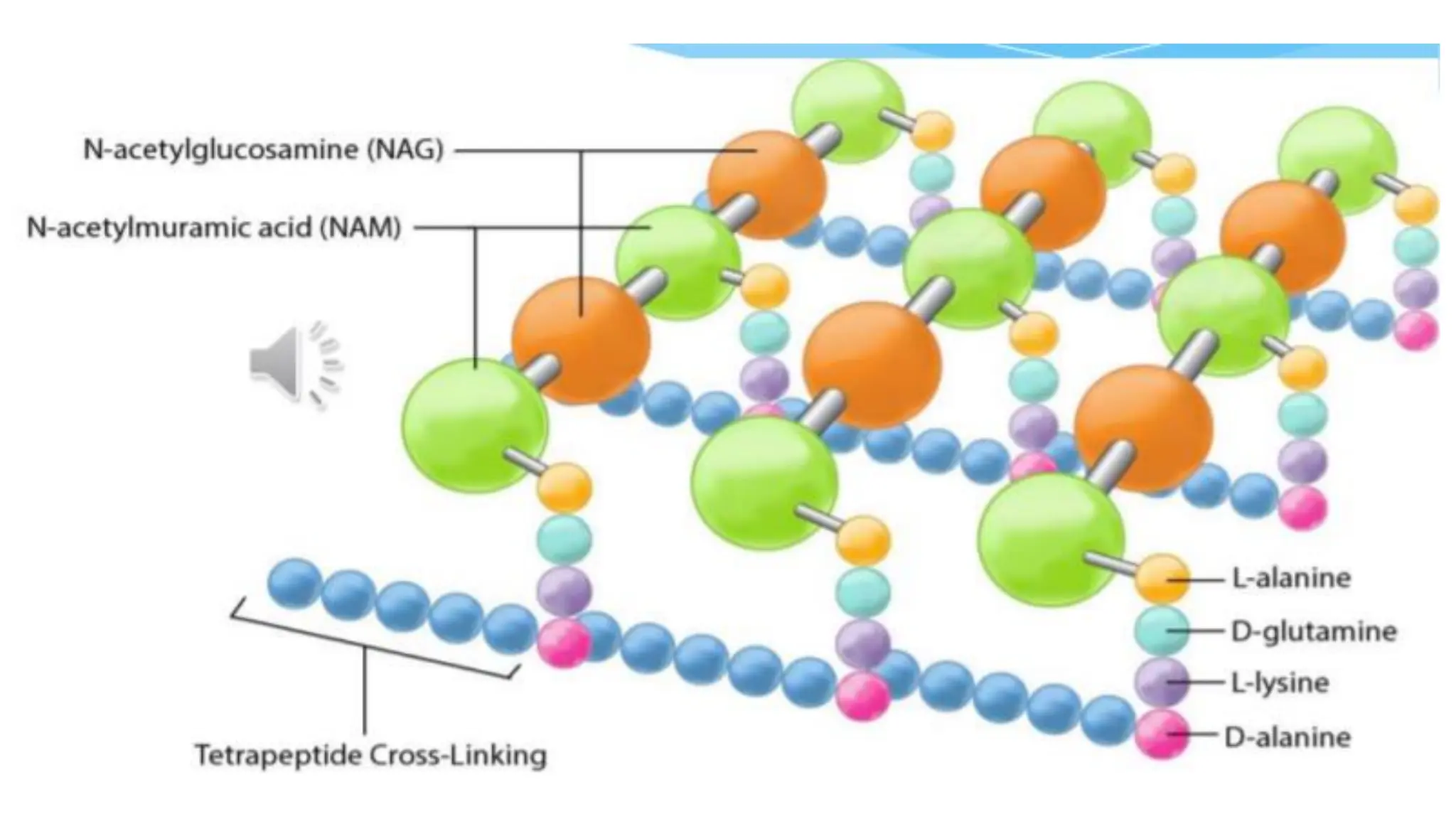
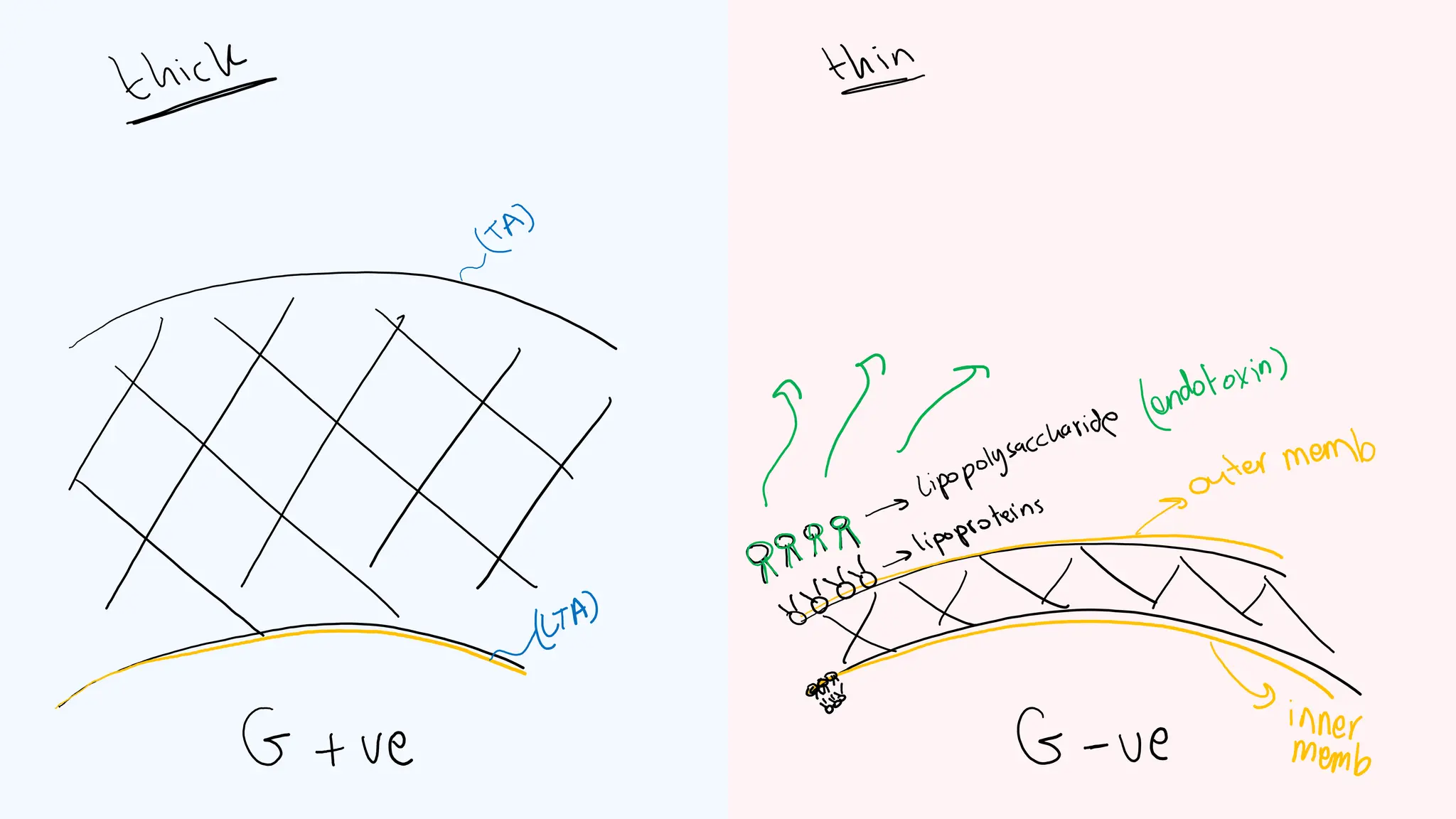
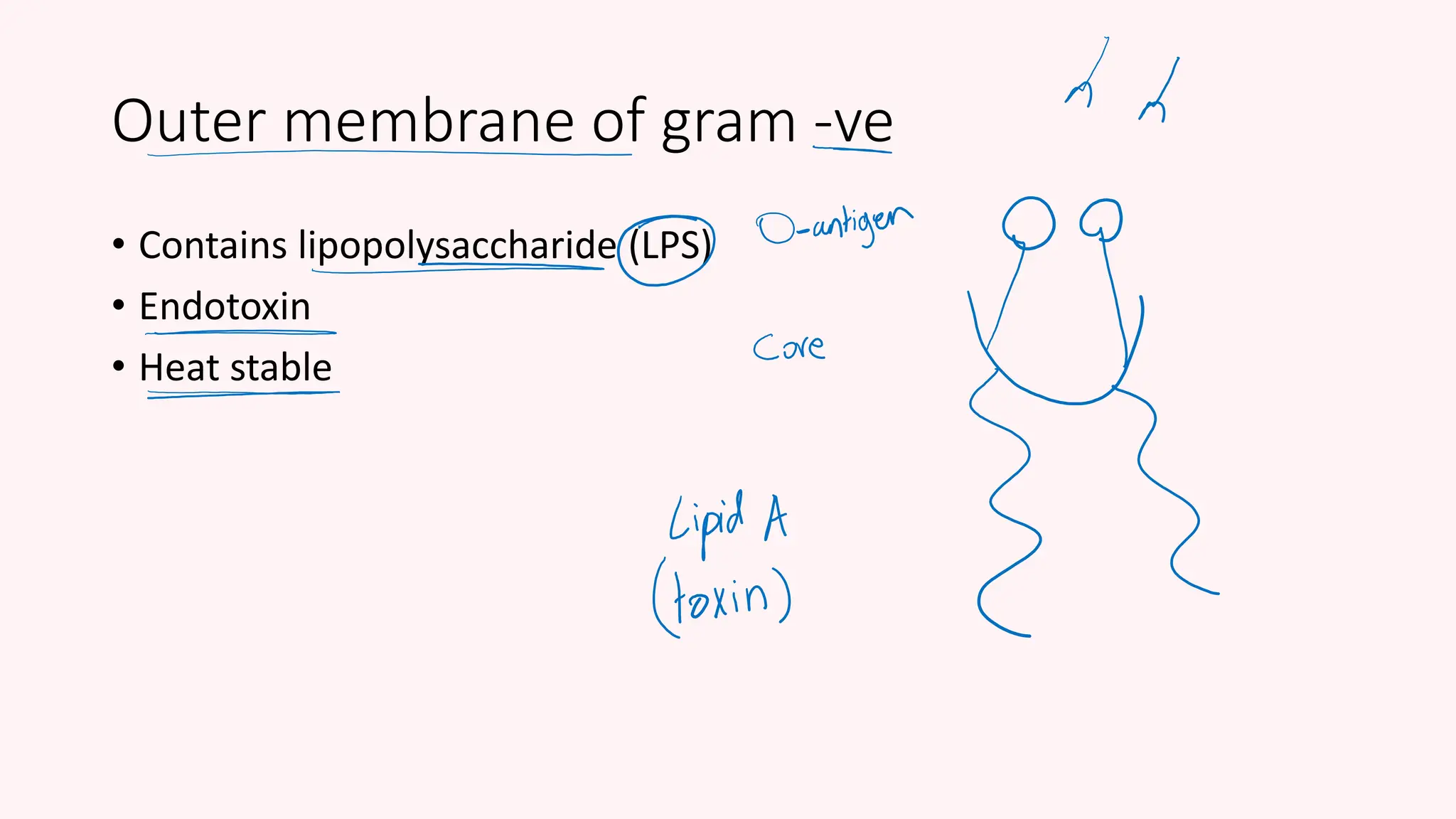
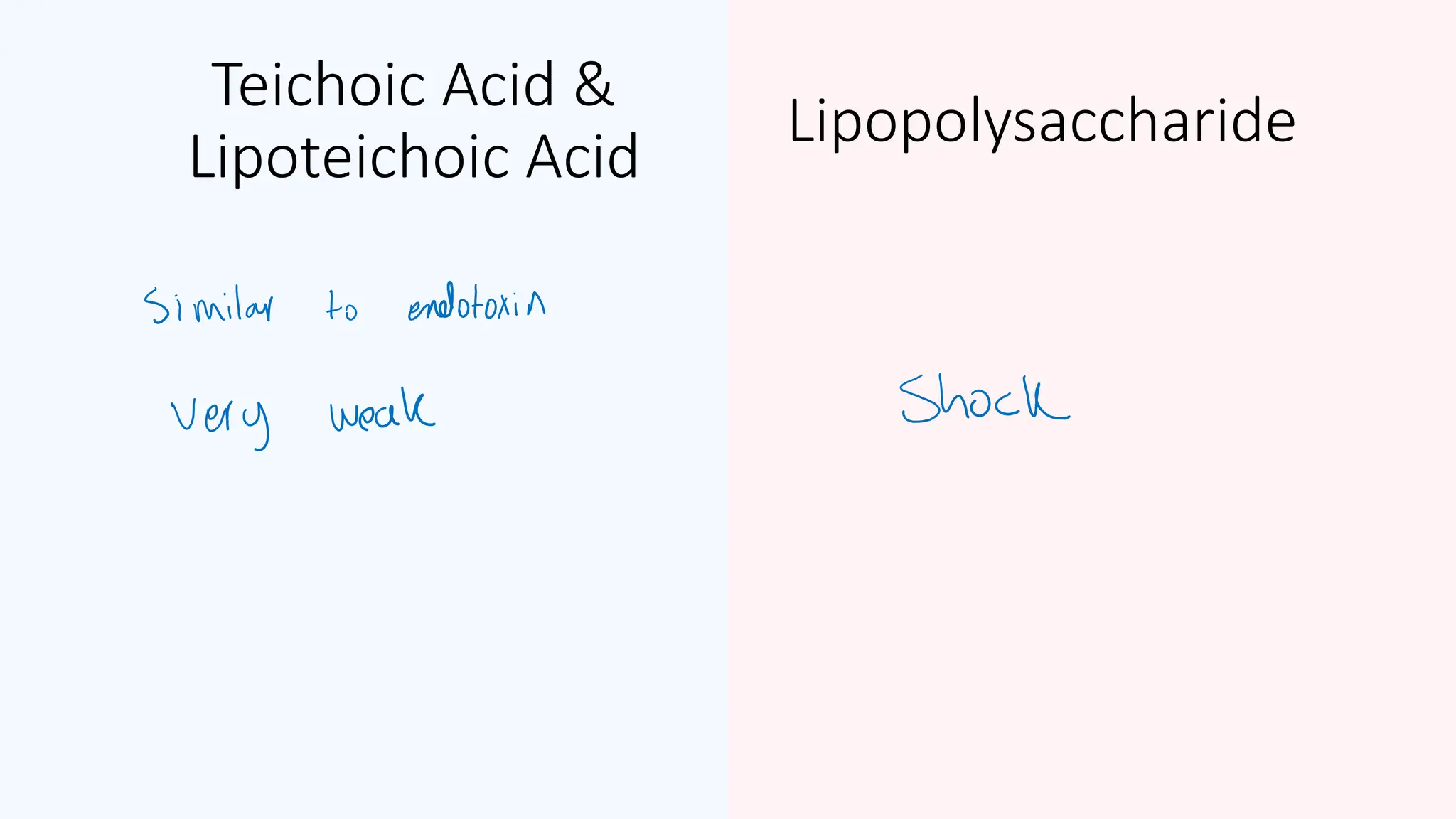
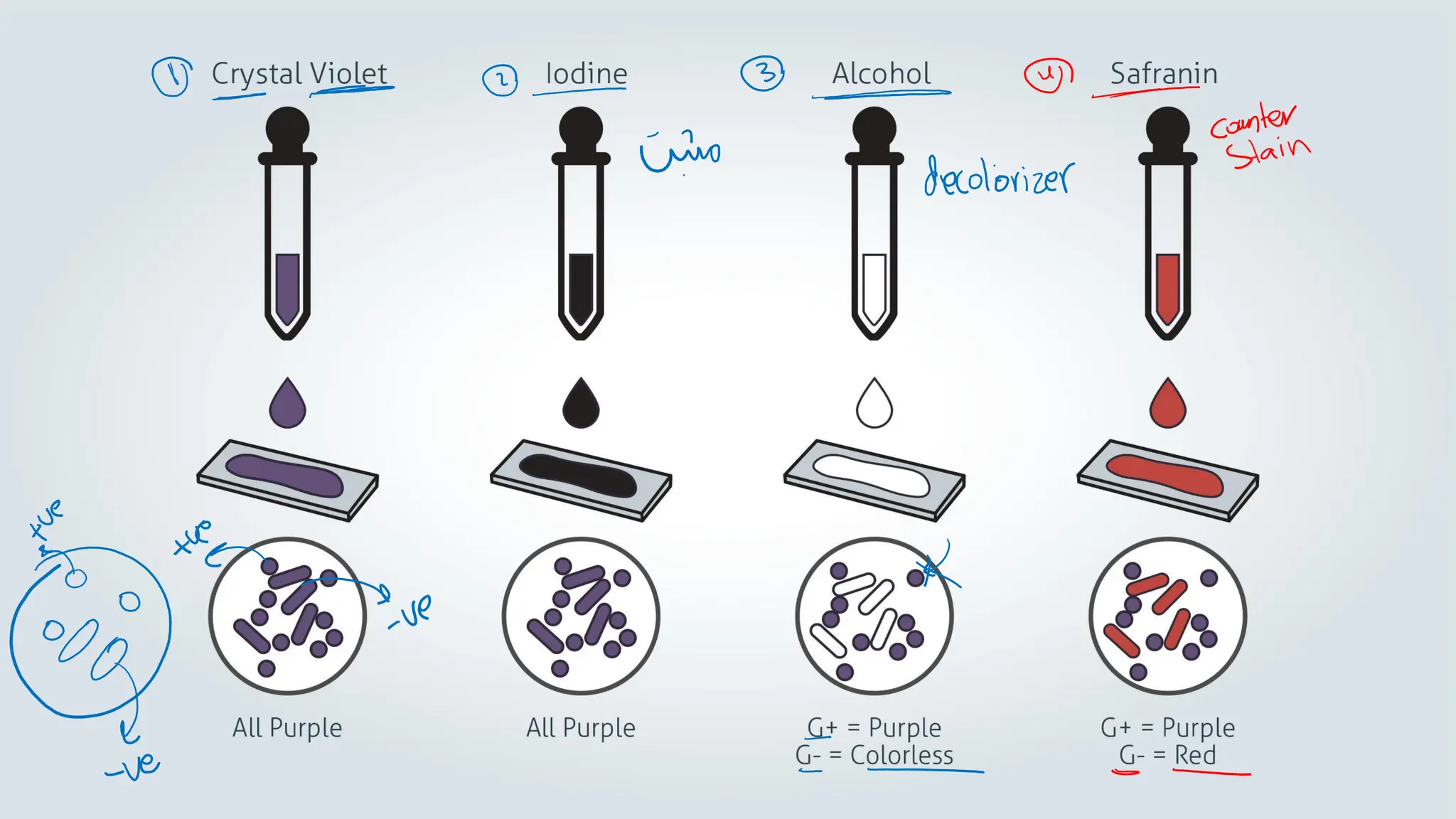
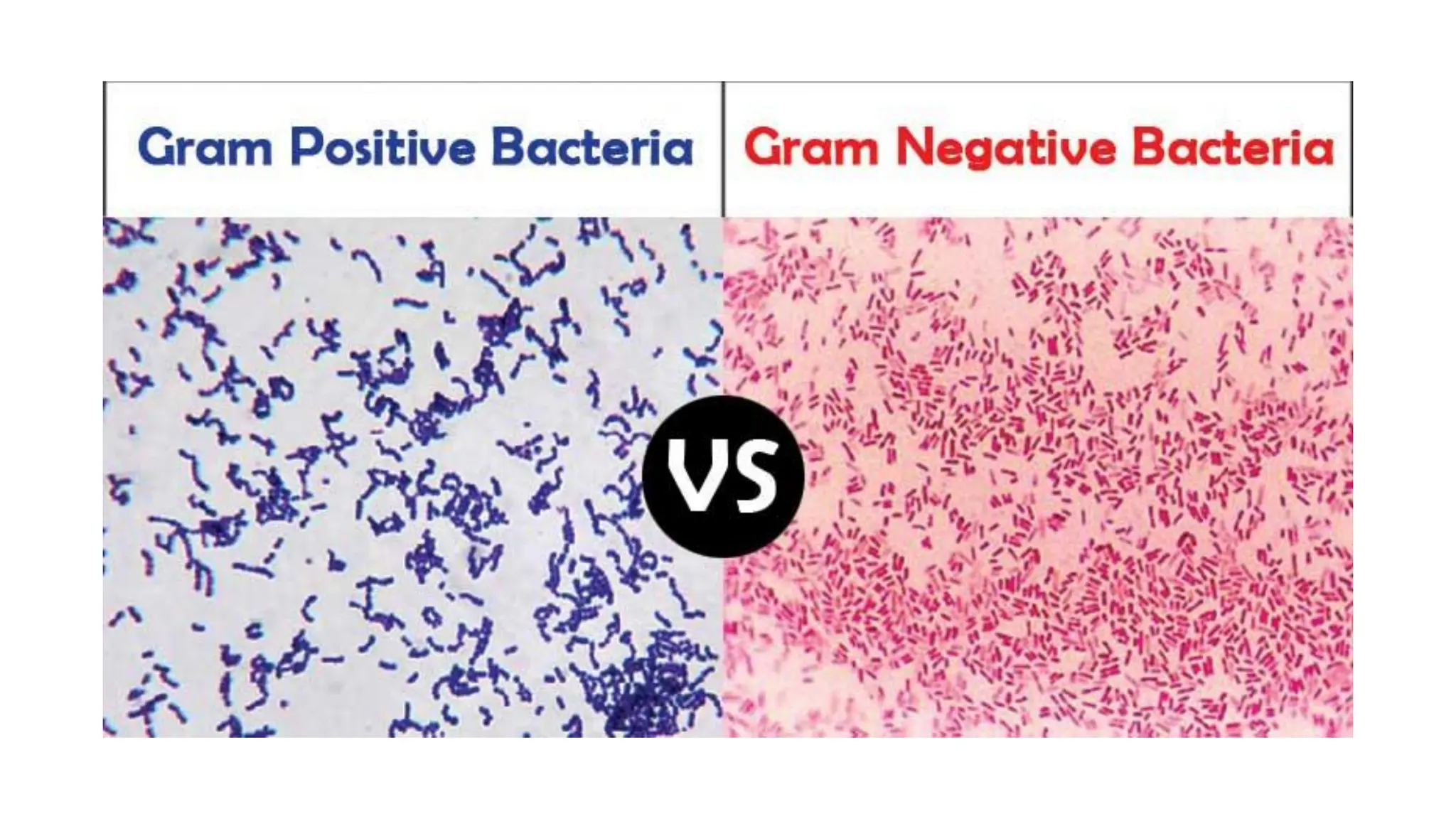
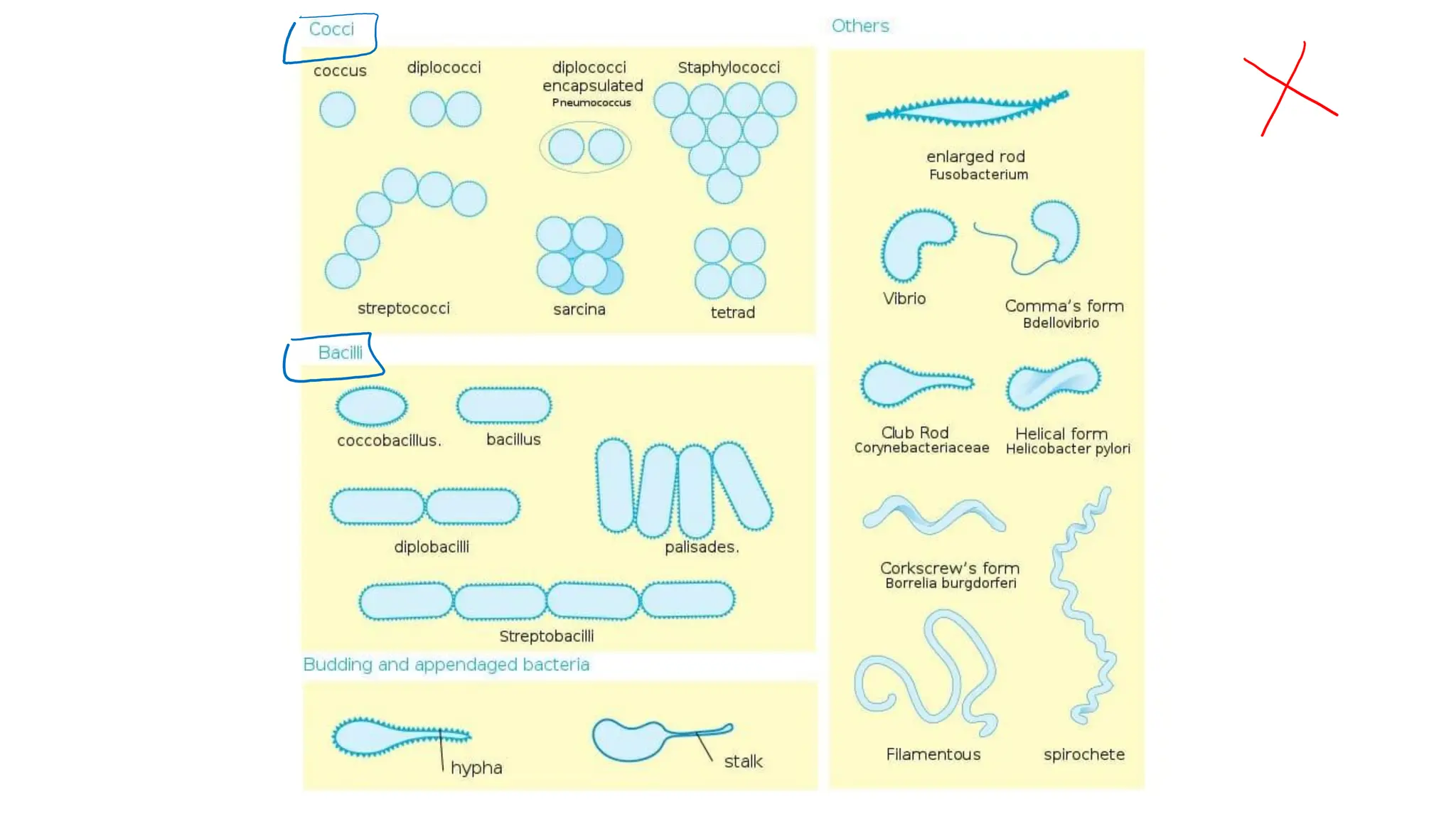
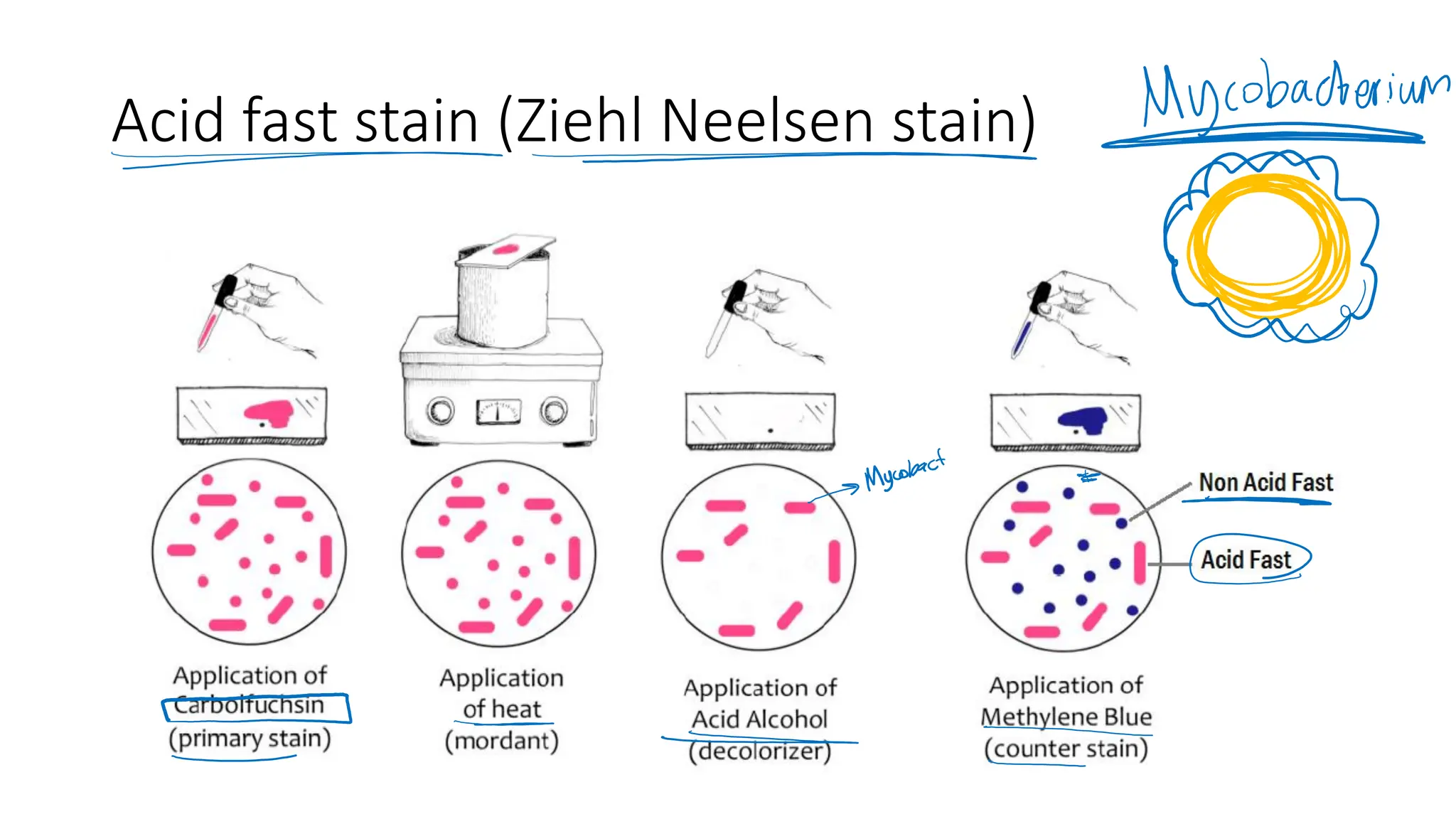
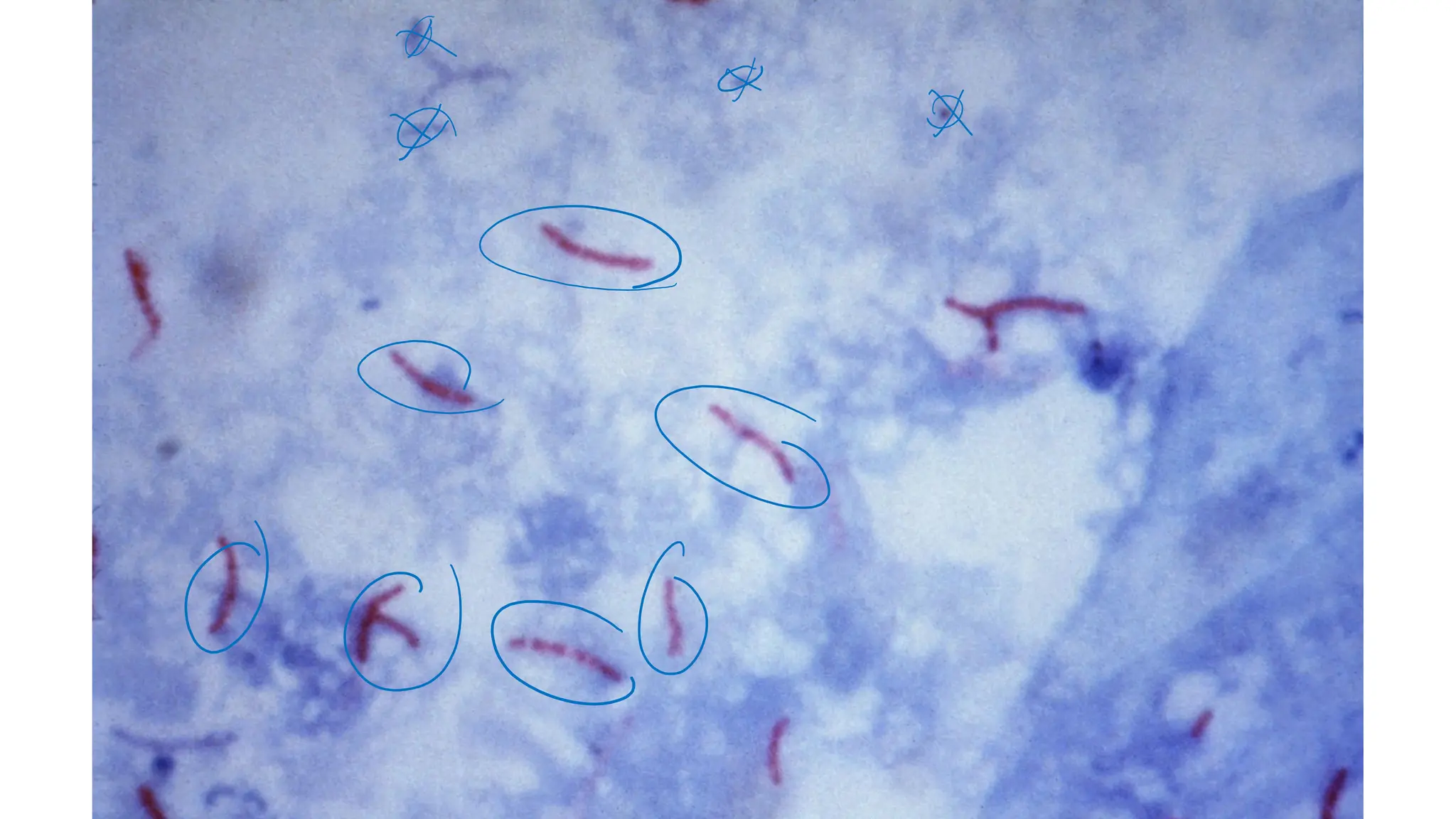
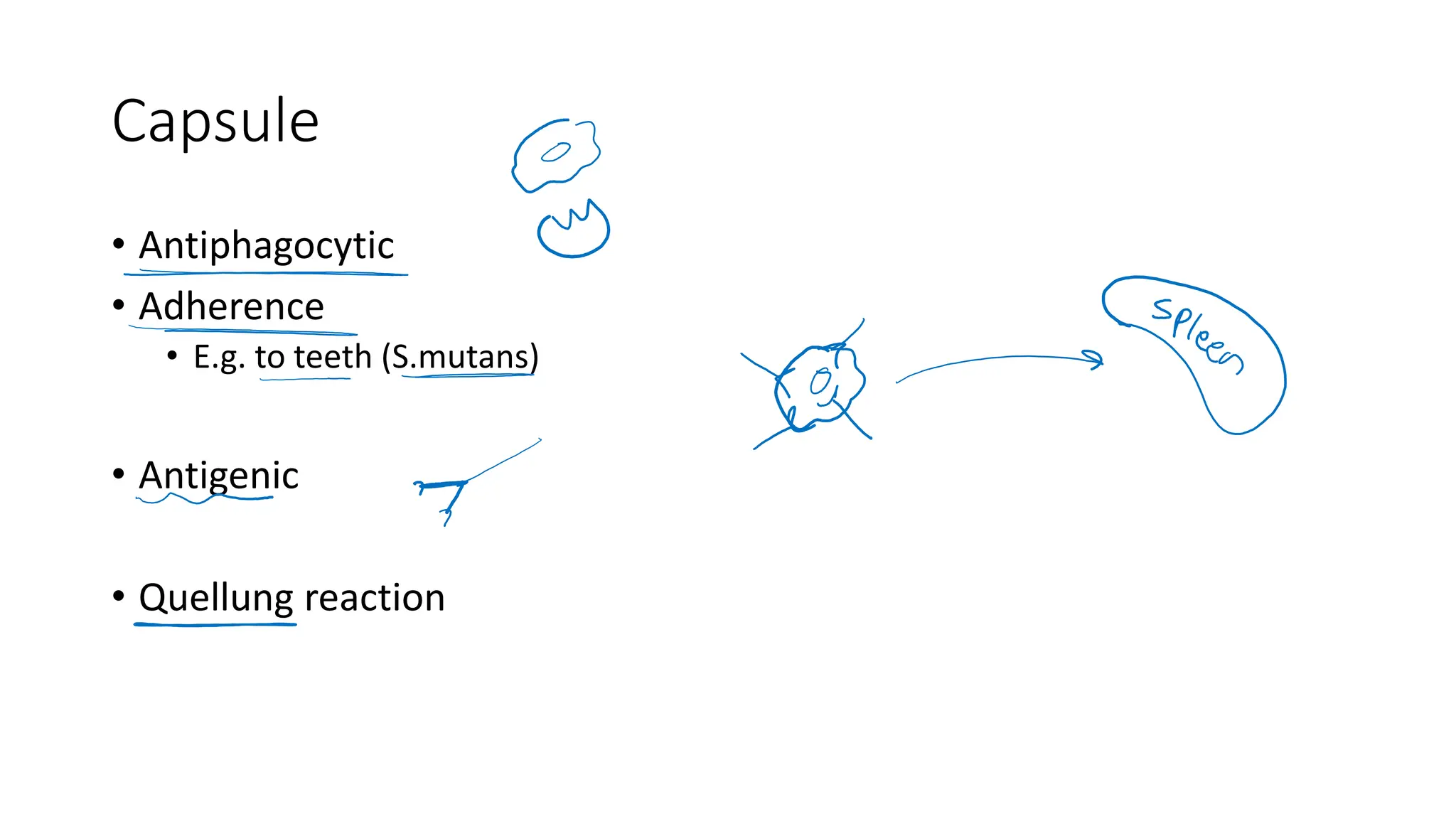
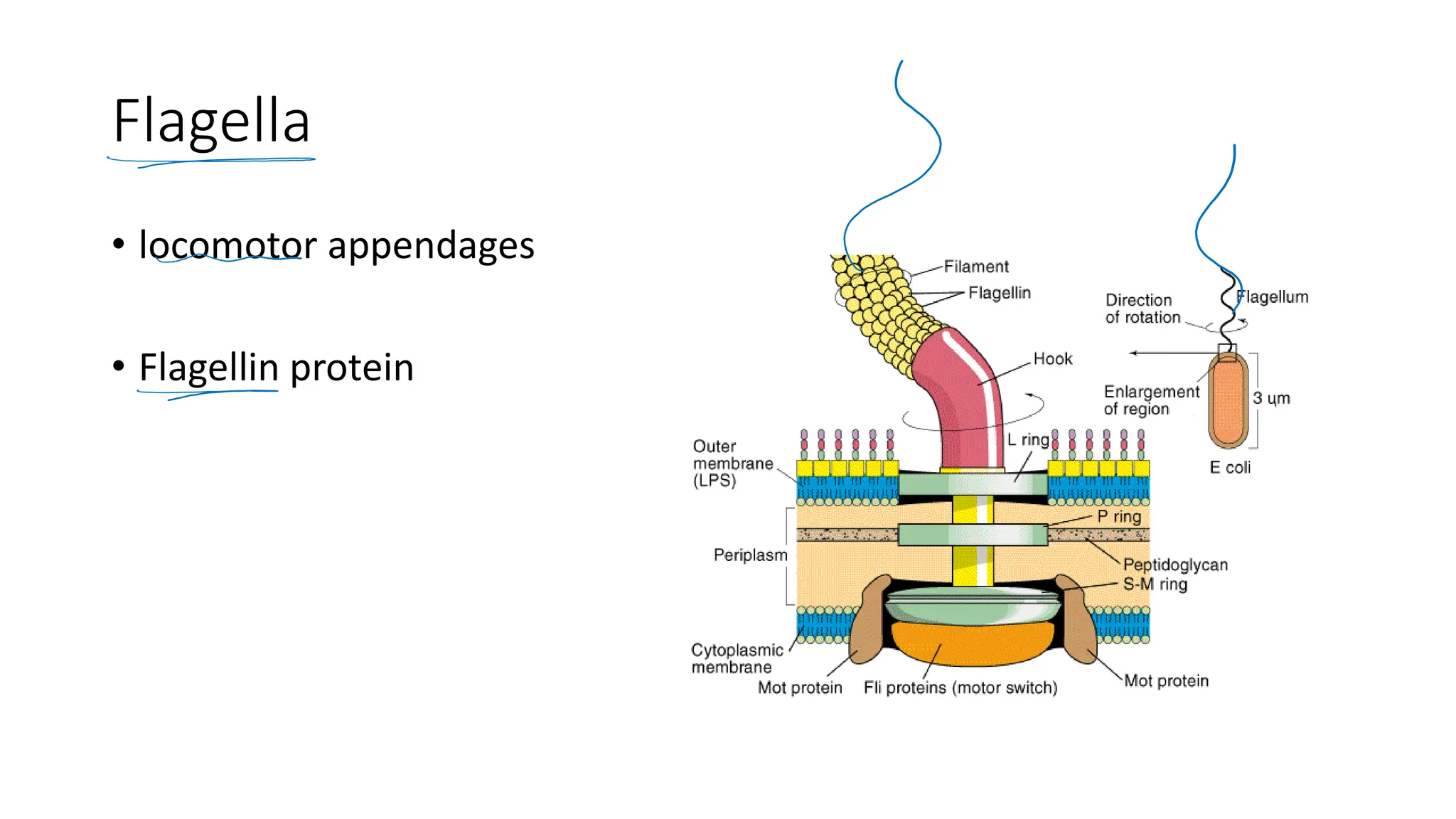
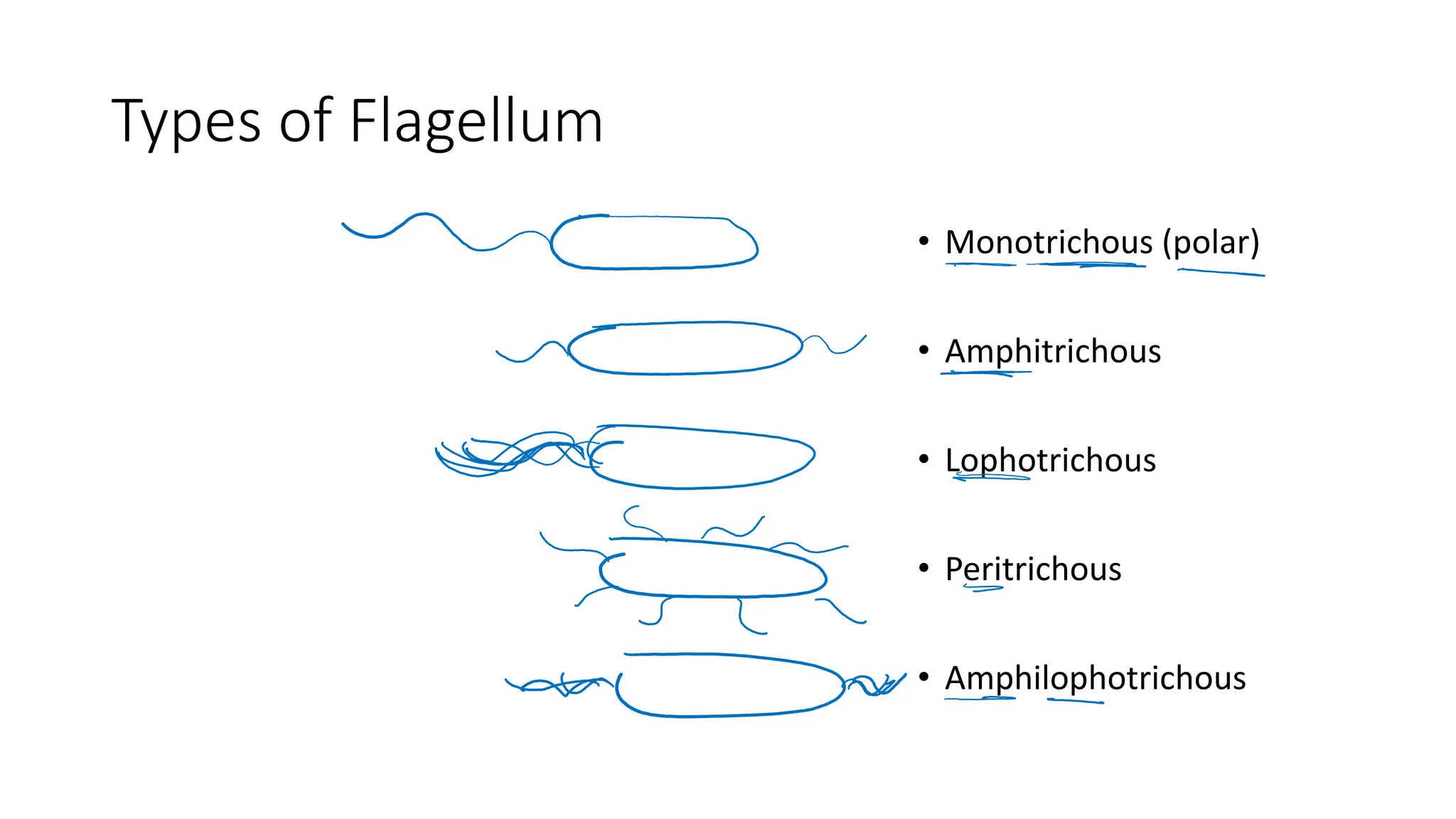
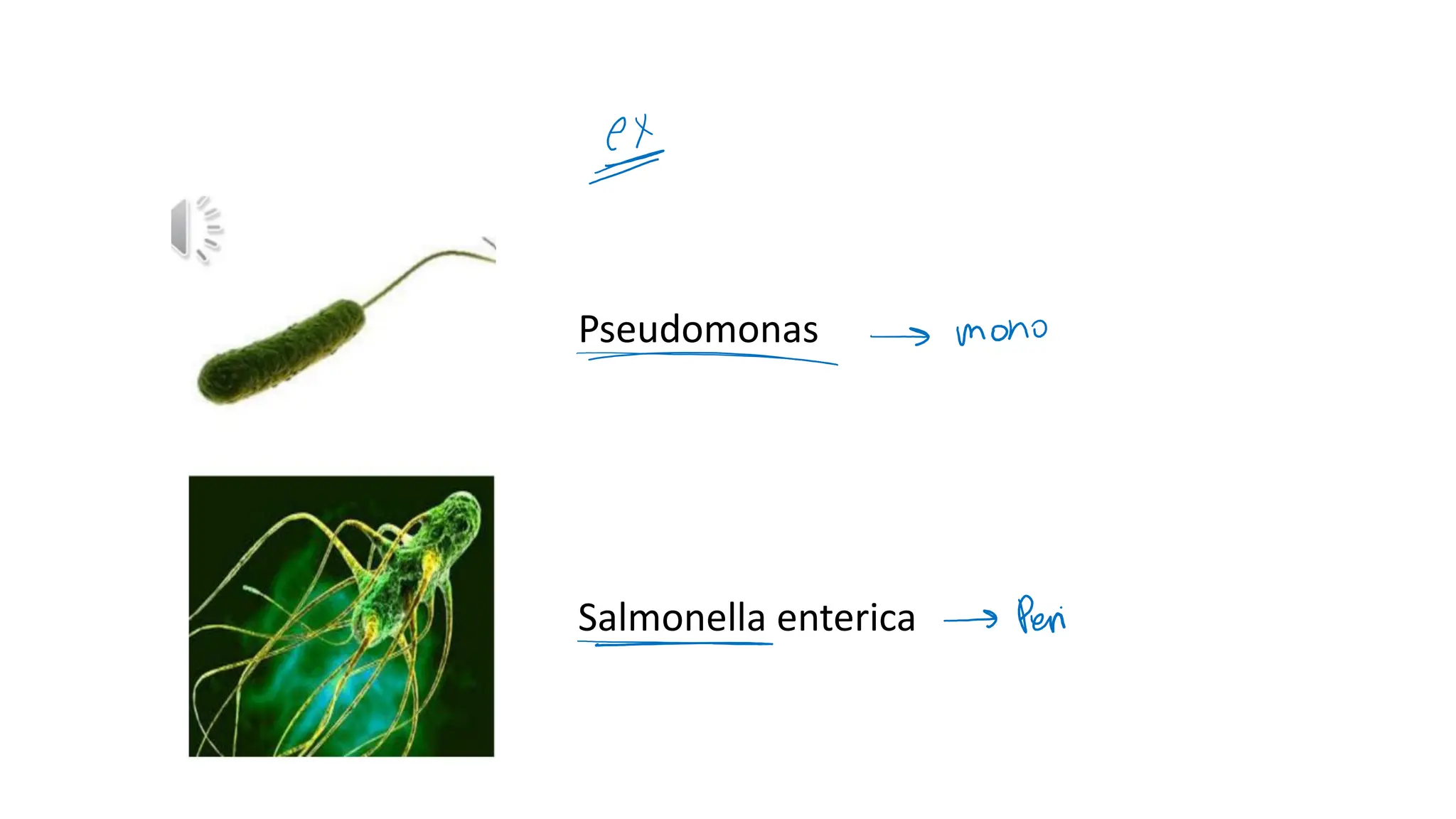
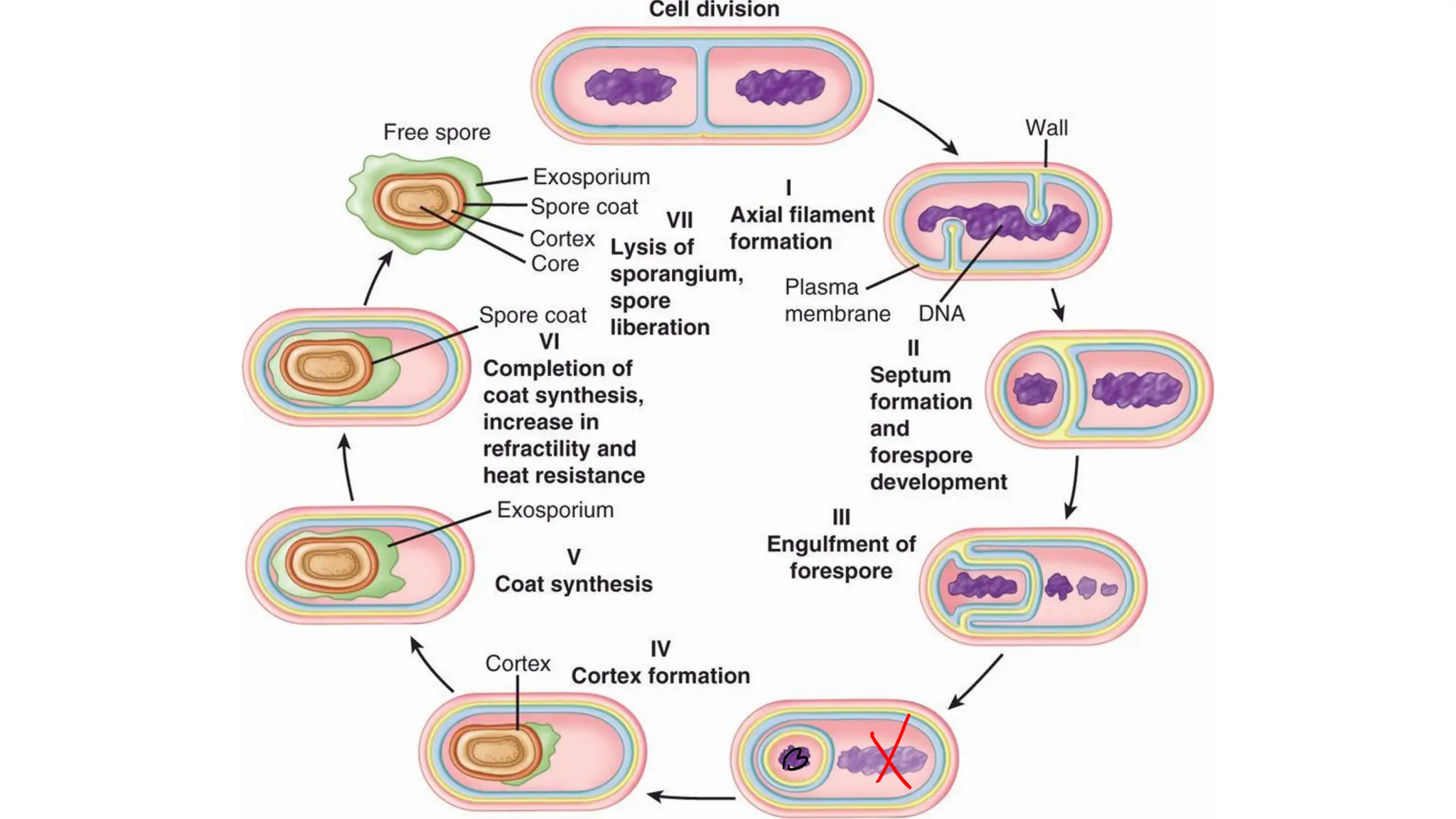
The document provides a comprehensive overview of bacterial structure, highlighting essential components like the cell wall, plasma membrane, and nucleoid, as well as accessory features such as capsules, flagella, and plasmids. It details various characteristics of bacteria, their growth, physiology, metabolism, and the significance of these structures in identification and pathogenicity. Additionally, the document discusses topics like sterilization, disinfection, and genetics related to bacteria.