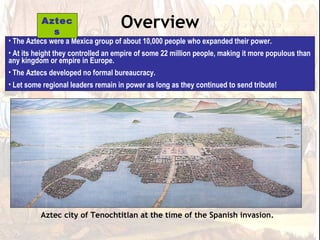
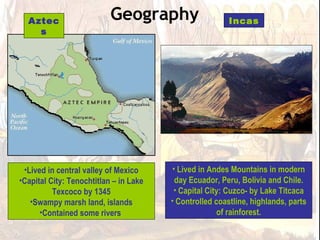
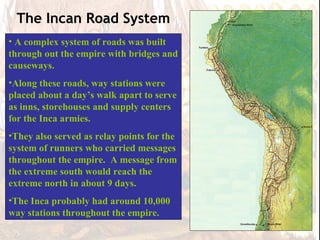
The Aztec Empire controlled most of central Mexico by the 15th century, with their capital at Tenochtitlan located on an island in Lake Texcoco. At its height, the Aztec Empire had over 22 million subjects, making it larger than any European kingdom at the time. The Aztecs developed no formal bureaucracy and instead allowed regional kings to remain in power as long as they continued to pay tribute. Religion played a key role in Aztec rule, especially human sacrifice which was believed to nourish the gods.