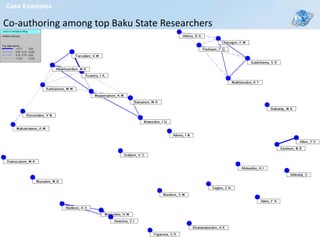
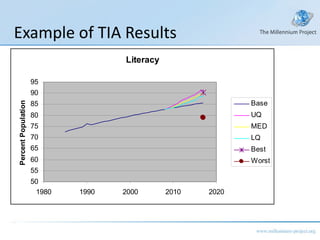
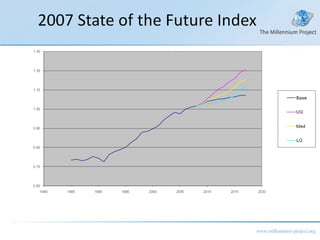
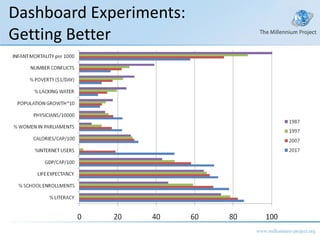
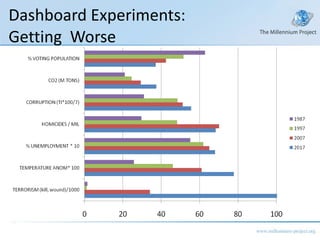
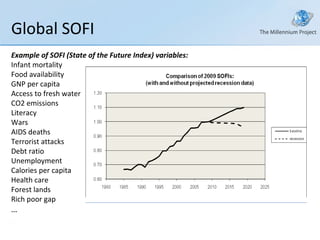
The document discusses a class on the State of the Future Index (SOFI) and text mining. It provides an overview of SOFI as a tool for policy analysis and education that combines weighted variables to measure if the future outlook is improving. It also discusses collecting expert judgments on variables, impacts, and future developments through techniques like the Real-Time Delphi to construct the SOFI. The document outlines sources and resources for more information on SOFI, text mining, and related topics.

















![Why Tech Mining? Welcome to the age of too much information. We need to treat: text as data to gain intelligence. Mine “ST&I” [Science, Technology & Innovation] information resources to answer technology management questions = Tech Mining. Enable Open Innovation © 2009 Search Technology, Inc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/azerbaijan2-2-3sofiandtextscanning-110303104341-phpapp02/85/Azerbaijan2-2-3-sofi-and-text-scanning-27-320.jpg)






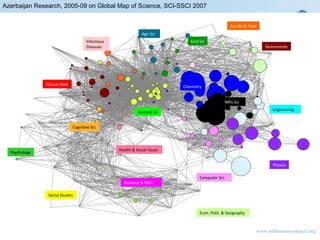
![Research Profile: Azerbaijan 2005-09 by Disciplines (top 5) Case Examples Macro-Discipline Author Affiliations Key Terms Authors Year Top 3 Top 5 Top 3 2008-09 Chemistry[475] Natl Acad Sci Azerbaijan [119] Baku State Univ [95] Azerbaijan Acad Sci [48] synthesis [72] thermodynamic properties [27] Density [24] Water [23] methanol [21] Abdulagatov, I M [25] Magerramov, A M [19] Chyragov, F M [18] 48% of 475 Materials Sci[382] Azerbaijan Acad Sci [95] Baku State Univ [66] Azerbaijan Natl Acad Sci [64] effect [29] TlInS2 [19] Incommensurate phase [17] CRYSTALS [17] SINGLE-CRYSTALS [14] Suleymanov, R A [16] Altindal, S [14] Tagiev, O B [13] Mammadov, T S [13] 51% of 382 Engineering[333] Natl Acad Sci Azerbaijan [83] Baku State Univ [74] Azerbaijan Acad Sci [38] methanol [14] Initial stresses [11] sufficient conditions [10] thermodynamic properties [10] approximation [10] boundedness [10] Akbarov, S D [22] Guliyev, V S [16] Khanmamedov, A K [9] Abdulagatov, I M [9] Nasibov, S M [9] 50% of 333 Physics[231] Azerbaijan Acad Sci [58] Baku State Univ [47] Azerbaijan Natl Acad Sci [35] MODEL [22] PHYSICS [12] SCATTERING [10] VARIABILITY [10] SYSTEMS [9] Shahverdiev, E M [13] Shore, K A [13] Aliev, T M [12] Sultansoy, S [12] 51% of 231 Biomed Sci[105] Baku State Univ [27] Azerbaijan Med Univ [9] Azerbaijan Acad Sci [7] EFFICIENCY [10] sturgeons [8] diencephalon [7] CYTOARCHITECTONIC ANALYSIS [7] Azerbaijan [7] EXPRESSION [7] organization [7] Zeynalov, R [9] Musayev, I [9] Rustamov, E K [8] Dadasheva, N [8] 39% of 105](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/azerbaijan2-2-3sofiandtextscanning-110303104341-phpapp02/85/Azerbaijan2-2-3-sofi-and-text-scanning-41-320.jpg)
![Research Profile: Baku State University – 5 Researchers Case Examples Authors Subject Category Key Terms Authors Year Top 5 Items Top 5 Items Top 5 Items 2008-09 Magerramov, A M[19] Chemistry, Applied [8] Chemistry, Organic [7] Chemistry, Physical [3] Materials Science, Multidisciplinary [2] Optics [2] reaction [9] synthesis [9] DERIVATIVES [4] reactions [3] formation [3] Magerramov, A M [19] Allakhverdiev, M A [9] Mamedov, I G [5] Bairamov, M R [5] Farzaliev, V M [4] Rzaeva, I A [4] 68% of 19 Chyragov, F M[18] Chemistry, Analytical [14] Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear [4] complexation [15] photometric determination [11] stability constants [8] Chyragov, F M [18] Gadzhieva, S R [12] Makhmudov, K T [6] Alieva, R A [5] Guseinov, F E [4] 17% of 18 Allakhverdiev, M A[14] Chemistry, Applied [8] Chemistry, Organic [5] Chemistry, Physical [3] Energy & Fuels [2] Engineering, Chemical [2] Engineering, Petroleum [2] synthesis [8] reaction [6] antioxidant activity [3] cumene [3] Allakhverdiev, M A [14] Magerramov, A M [9] Farzaliev, V M [6] Rzaeva, I A [6] Guseinova, A T [4] 79% of 14 Gadzhieva, S R[14] Chemistry, Analytical [9] Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear [5] complexation [11] photometric determination [8] stability constants [6] Gadzhieva, S R [14] Chyragov, F M [12] Makhmudov, K T [6] Guseinov, F E [4] Pashaev, F G [3] 29% of 14 Babanly, M B[12] Materials Science, Multidisciplinary [8] Electrochemistry [2] Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear [2] X-ray diffraction [7] thermodynamic properties [6] differential thermal analysis [6] standard entropies [5] Babanly, M B [12] Babanly, N B [2] Sadygov, F M [2] Shykhyev, Y M [2] Imamalieva, S Z [2] Yusibov, Y A [2] 100% of 12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/azerbaijan2-2-3sofiandtextscanning-110303104341-phpapp02/85/Azerbaijan2-2-3-sofi-and-text-scanning-42-320.jpg)