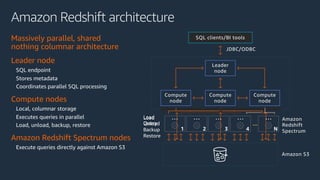
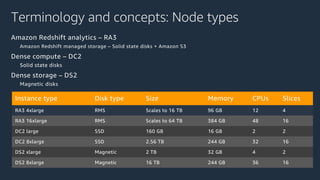
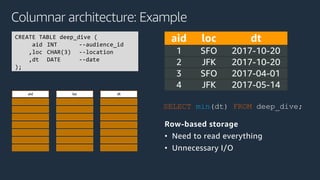
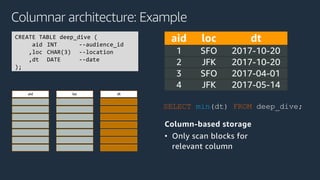
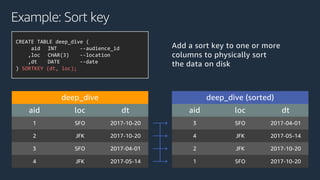
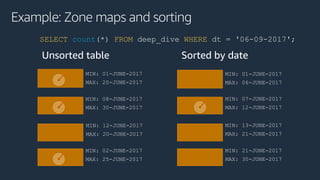
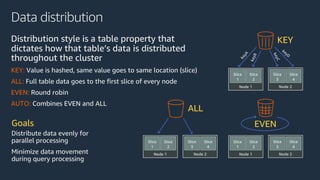
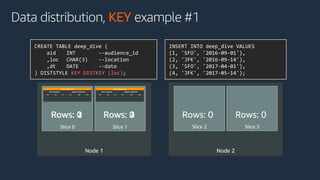
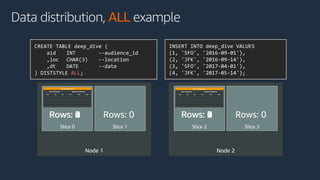
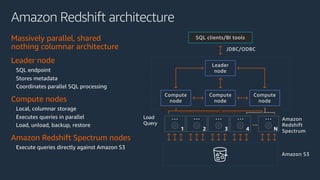
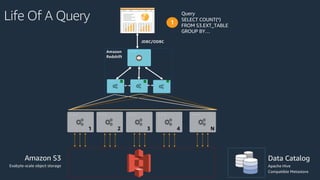
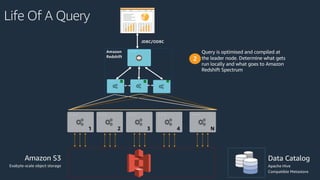
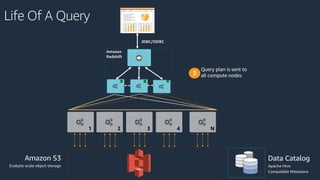
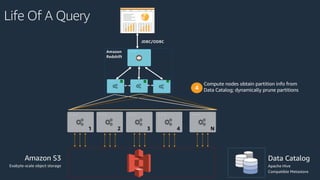
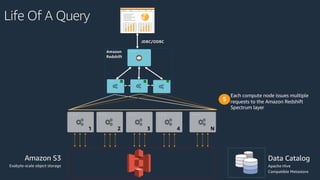
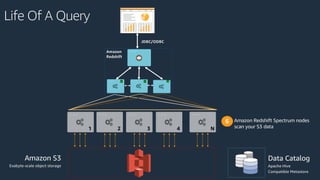
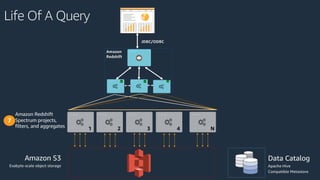
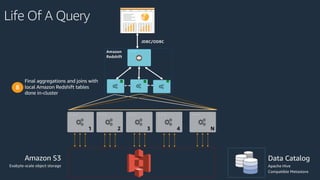
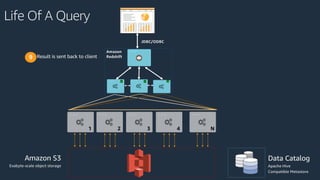
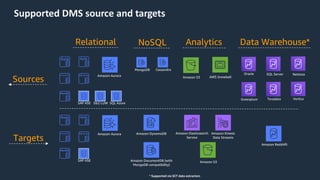
The document is a presentation on Amazon Redshift, focusing on its architecture, features, and data handling capabilities. It highlights the benefits of using a columnar data storage format for analytics, discusses data distribution methods, and outlines the process of querying data directly from Amazon S3. Additionally, the document covers the functionality of Amazon Redshift Spectrum for integrating data lakes with traditional data warehouses.