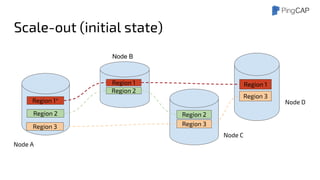
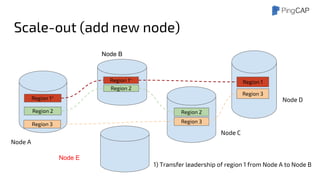
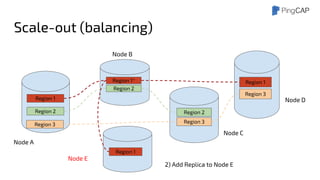
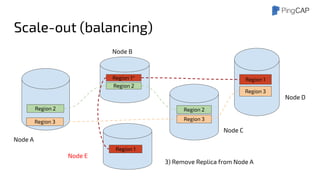
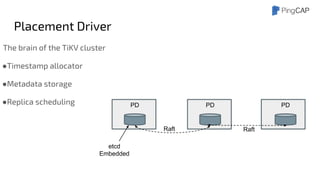
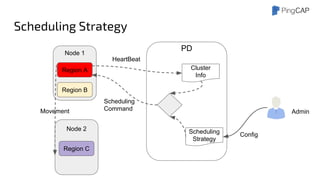
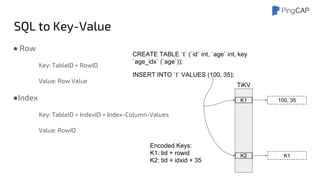
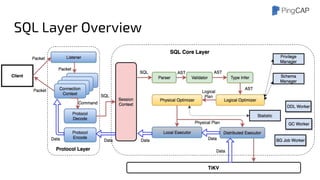
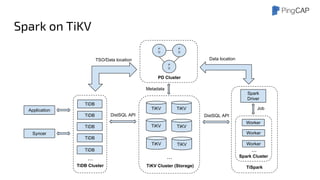
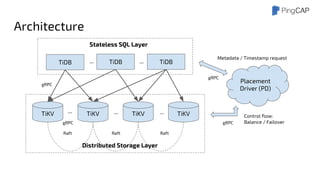
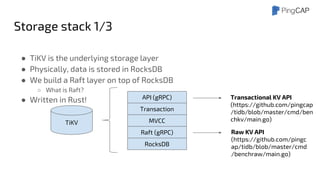
This document outlines the motivations, architecture, and future plans for TiDB, a NewSQL database by PingCAP aimed at overcoming limitations of traditional RDBMS. TiDB provides transparent sharding, ACID transactions, high availability through the Raft consensus algorithm, and is MySQL compatible, while also incorporating advanced tools like Spark for analytical processing. The company is expanding with a new office in the Bay Area and aims for a smoother transition to GA with enhancements to its optimizer and scheduling mechanisms.





![RocksDB
Instance
Region 1:[a-e]
Region 3:[k-o]
Region 5:[u-z]
...
Region 4:[p-t]
RocksDB
Instance
Region 1:[a-e]
Region 2:[f-j]
Region 4:[p-t]
...
Region 3:[k-o]
RocksDB
Instance
Region 2:[f-j]
Region 5:[u-z]
Region 3:[k-o]
... RocksDB
Instance
Region 1:[a-e]
Region 2:[f-j]
Region 5:[u-z]
...
Region 4:[p-t]
Raft group
Storage stack 3/3
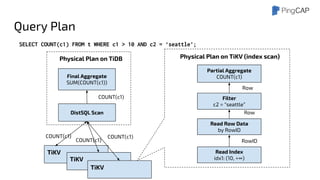
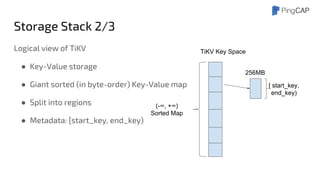
● Data is organized by Regions
● Region: a set of continuous Key-Value pairs
RPC (gRPC)
Transaction
MVCC
Raft
RocksDB
···](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalerelationaldatabasewithnewsql-171031082237/85/Scale-Relational-Database-with-NewSQL-9-320.jpg)
![Dynamic Multi-Raft
● What’s DynamicMulti-Raft?
○ Dynamic split / merge
● Safe split / merge
Region 1:[a-e]
split Region 1.1:[a-c]
Region 1.2:[d-e]split](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalerelationaldatabasewithnewsql-171031082237/85/Scale-Relational-Database-with-NewSQL-10-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 1/4
TiKV1
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV2
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV3
Region 1:[a-e]
raft raft
Leader Follower Follower
Raft group](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalerelationaldatabasewithnewsql-171031082237/85/Scale-Relational-Database-with-NewSQL-11-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 2/4
TiKV2
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV3
Region 1:[a-e]
raft raft
Leader
Follower Follower
TiKV1
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Region 1.2:[d-e]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalerelationaldatabasewithnewsql-171031082237/85/Scale-Relational-Database-with-NewSQL-12-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 3/4
TiKV1
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Region 1.2:[d-e]
Leader
Follower Follower
Split log (replicated by Raft)
Split log
TiKV2
Region 1:[a-e]
TiKV3
Region 1:[a-e]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalerelationaldatabasewithnewsql-171031082237/85/Scale-Relational-Database-with-NewSQL-13-320.jpg)
![Safe Split: 4/4
TiKV1
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Leader
Region 1.2:[d-e]
TiKV2
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Follower
Region 1.2:[d-e]
TiKV3
Region 1.1:[a-c]
Follower
Region 1.2:[d-e]
raft
raft
raft
raft](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/scalerelationaldatabasewithnewsql-171031082237/85/Scale-Relational-Database-with-NewSQL-14-320.jpg)