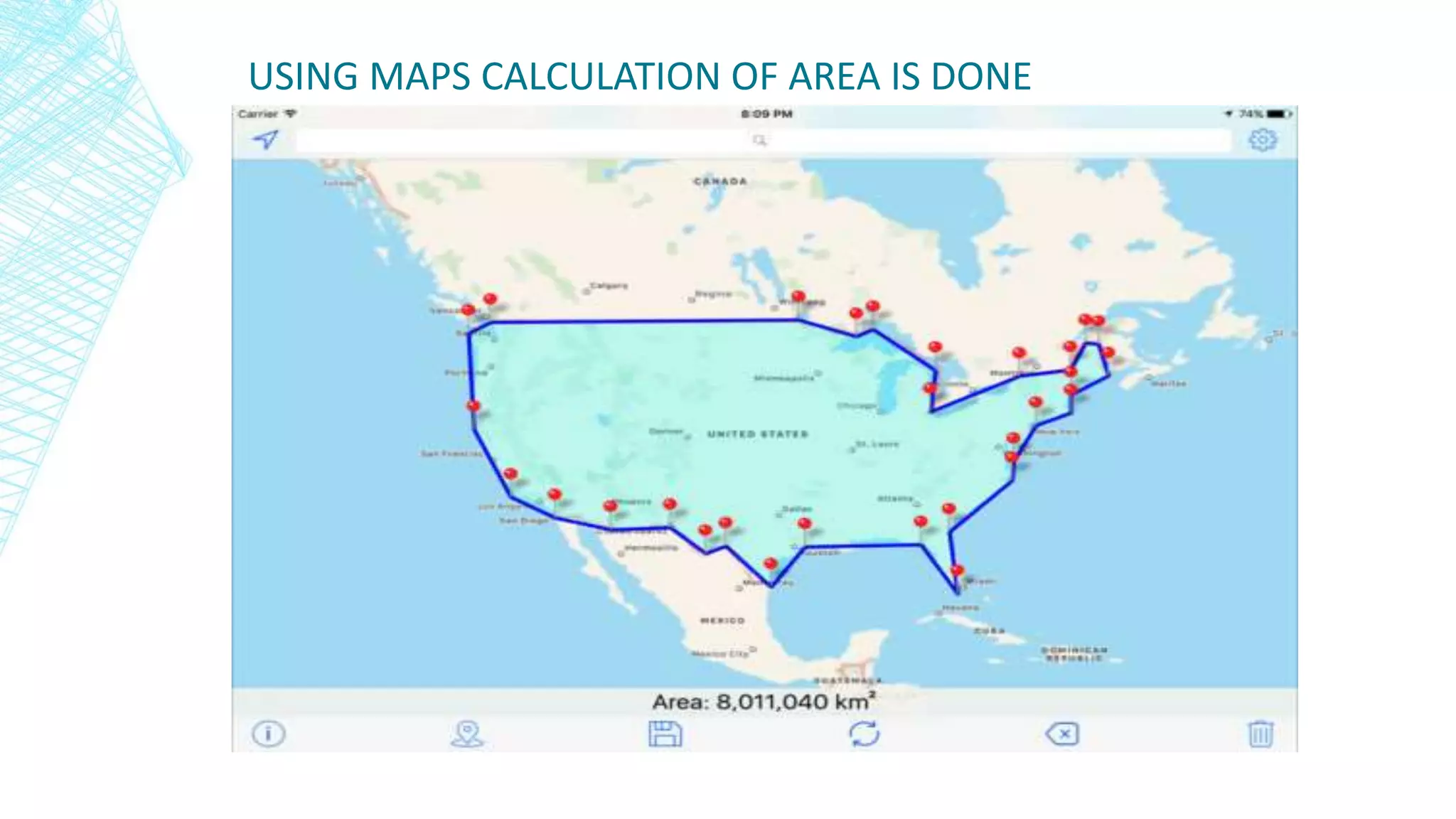
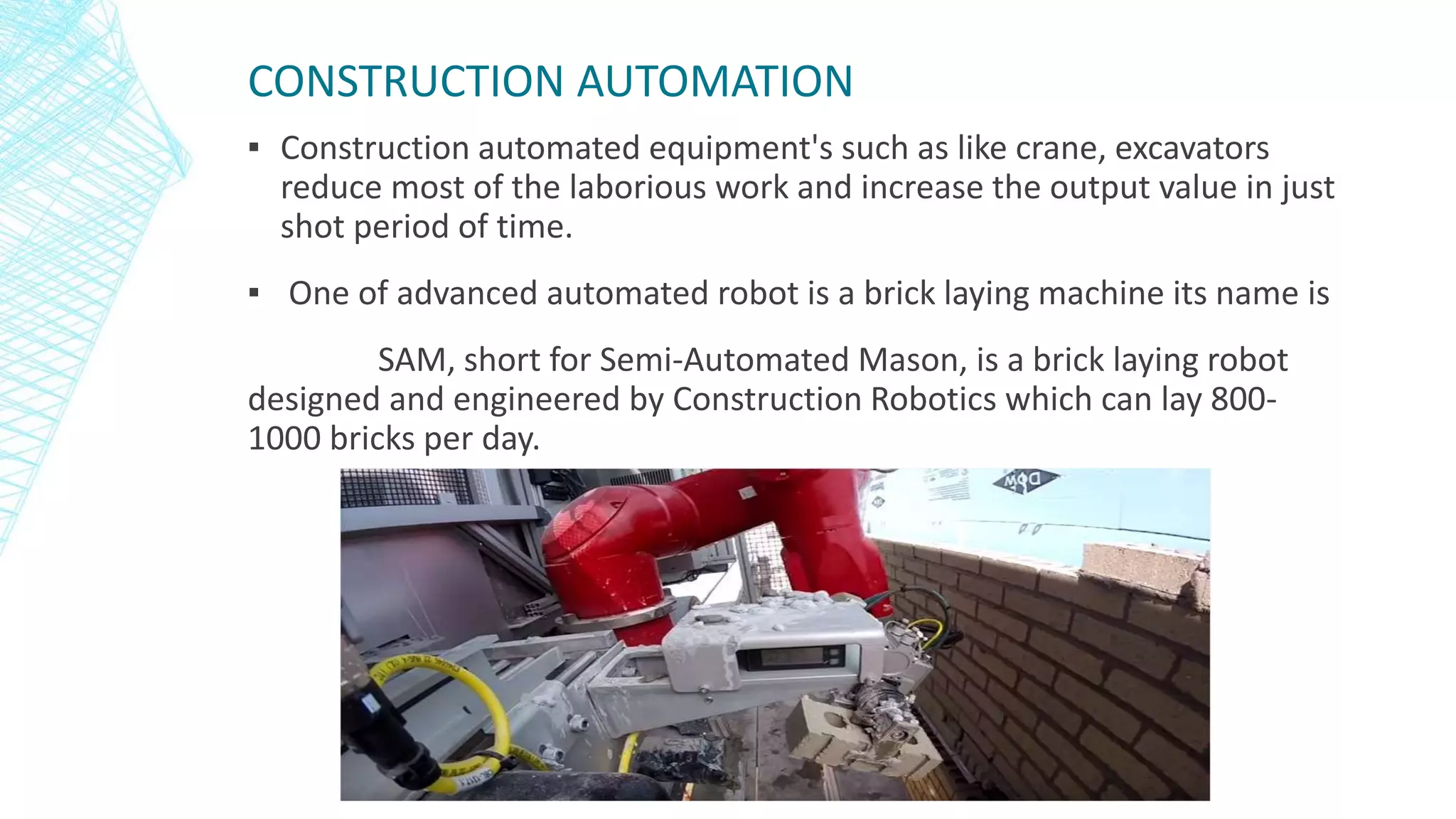
Automation in civil engineering can improve productivity and safety. It is necessary in developing countries like India due to labor shortages and dangerous working conditions. Areas of automation include surveying using tools like laser scanners, designing using software like AutoCAD, and construction using robots and equipment like cranes. Automation increases accuracy, efficiency and reduces costs but requires large initial investments and maintenance. It also risks job losses and potential errors if not implemented carefully.