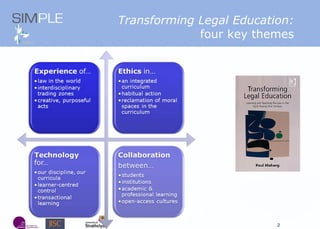
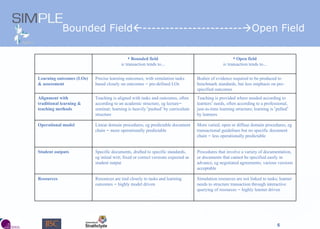
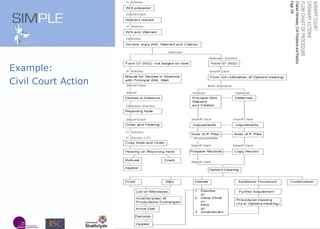
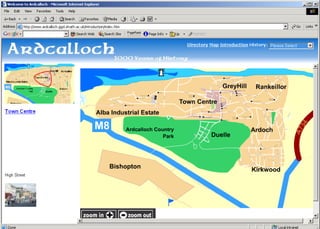
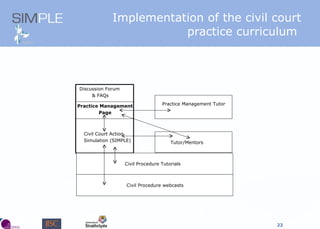
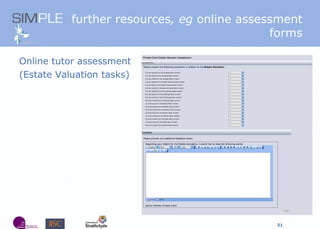
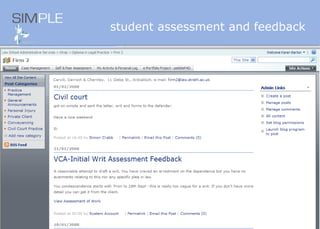
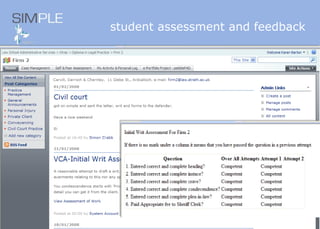
The document discusses the integration of authentic assessments in legal education through simulation-based learning, emphasizing active and collaborative learning approaches. It presents a framework for assessing students' legal skills and knowledge by using realistic tasks that reflect professional practices while fostering critical thinking and client care. The feedback from students highlights the importance of practical assignments and their contribution to effective learning and skill development in a legal context.



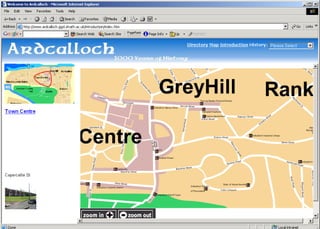
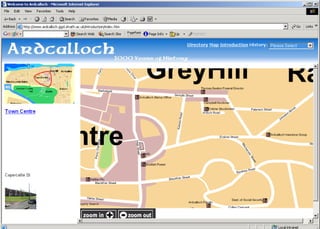
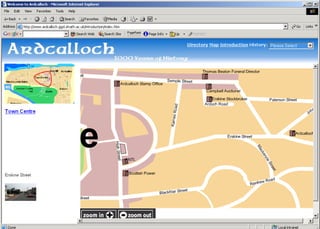
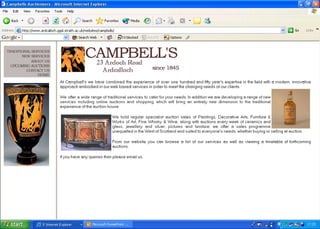
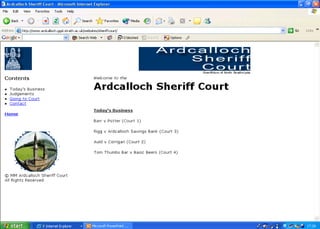
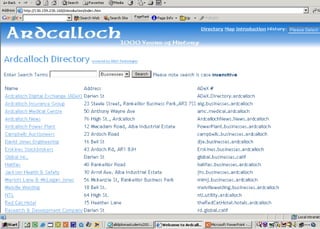
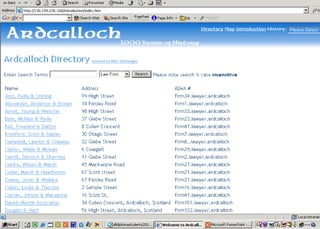
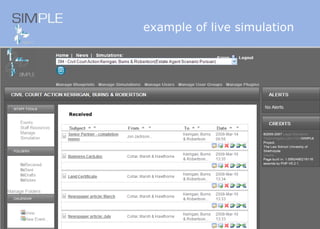
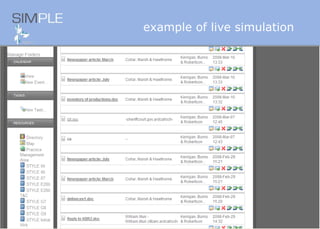
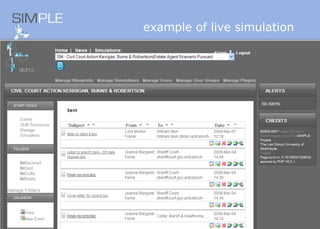
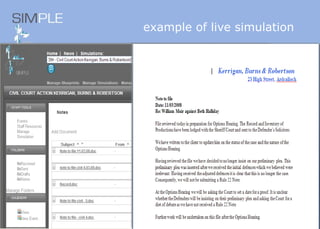
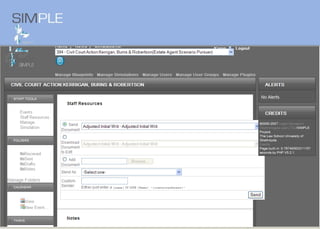









![feedback on learning… “… working in the virtual environment has also helped me focus on the concepts of individual and collective responsibility” “… our projects were quite clearly not completed in isolation…it was therefore vital to prioritize our workloads” “… the [Project] really emphasized the importance of client care…this aspect was vital to the successful completion of the project (as well as any future transaction in my traineeship).”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jisce-assessmentconference2011karenbarton-110920060645-phpapp02/85/Authentic-Assessment-in-Law-SIMPLE-36-320.jpg)



