Embed presentation
Download to read offline

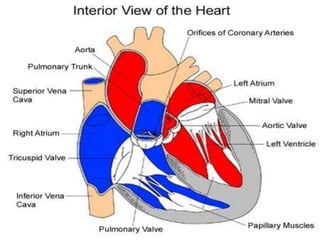

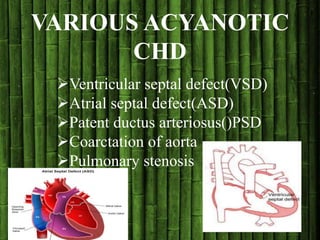

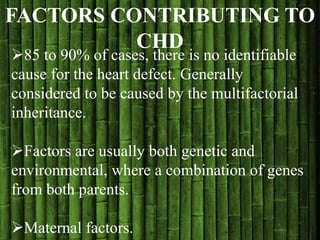


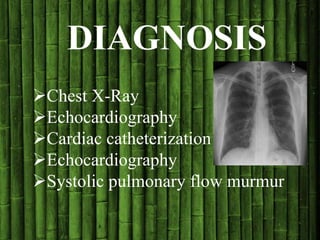



Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a structural heart defect present at birth, affecting up to 9 in every 1,000 babies. CHD is classified into acyanotic and cyanotic types, with various conditions under each category, and its causes are often multifactorial, involving both genetic and environmental factors. Treatment options vary based on the type of CHD and may include observation, surgery, medical management, or cardiac transplantation.











