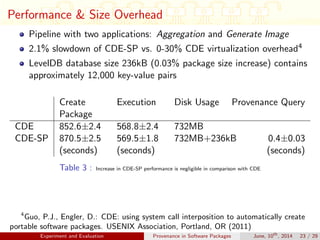
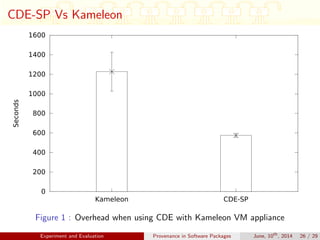
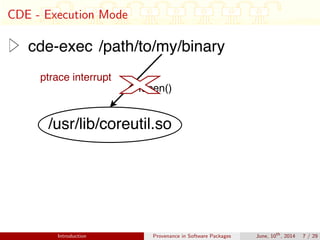
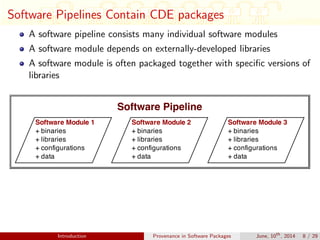
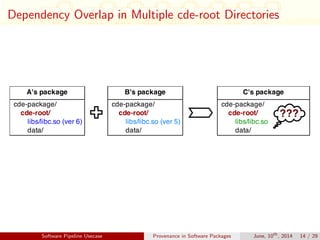
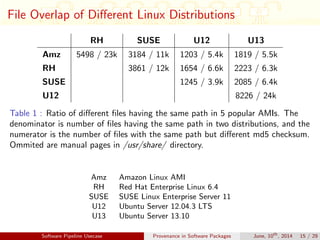
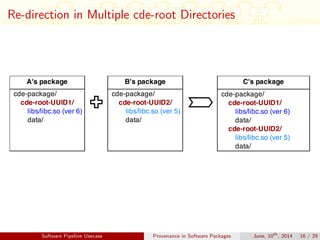
This document discusses auditing and maintaining provenance in software packages. It presents CDE-SP, an enhancement to the CDE system that captures additional details about software dependencies to enable attribution of authorship as software packages are combined and merged into pipelines. CDE-SP uses a lightweight key-value storage system to store provenance data within packages and allows provenance queries to determine package dependencies and validate authorship as packages are combined. Experiments show the overhead of CDE-SP is negligible for audit performance, storage size, and execution compared to the original CDE system.
















![B’s Experiment & Package
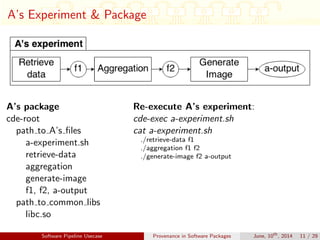
B’s package
cde-root
path to A’s files
[...]
path to B’s files
b-experiment.sh
analysis
b-output
path to common libs
libc.so
Re-execute B’s experiment:
cde-exec b-experiment.sh
cat b-experiment.sh
cd path to A’s experiment
cde-exec a-experiment.sh
cd path to B’s files
./analysis path to A’s files/a-output b-output
Software Pipeline Usecase Provenance in Software Packages June, 10th
, 2014 12 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipaw14quanppresentation-151027164935-lva1-app6891/85/Auditing-and-Maintaining-Provenance-in-Software-Packages-23-320.jpg)
![C’s Experiment & Package
C’s package
cde-root
path to A’s files
[...]
path to B’s files
[...]
path to C’s files
c-experiment.sh
parallel-init
parallel-summary
c-output
path to common libs
libc.so
Re-execute C’s experiment:
cde-exec c-experiment.sh
cat c-experiment.sh
parallel-init path to A’s files/f4
cd path to A’s files
cde-exec ./aggregation f4 f5
cde-exec ./generate-image f5 f6
cd path to B’s files
cde-exec ./analysis path to A’s files/f6 f7
cd path to C’s files
./parallel-summary path to B’s files/f7 c-output
Software Pipeline Usecase Provenance in Software Packages June, 10th
, 2014 13 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipaw14quanppresentation-151027164935-lva1-app6891/85/Auditing-and-Maintaining-Provenance-in-Software-Packages-24-320.jpg)




![Storage
Store provenance within the package itself
Use LevelDB: a fast and light-weight key-value storage library
Encode in the key the UNIX process identifier along with spawn time
Key Value Explanation
pid.PID1.exec.TIME PID2 PID1 wasTriggeredBy PID2
pid.PID.[path, pwd, args] VALUES Other properties of PID
io.PID.action.IO.TIME FILE(PATH) PID wasGeneratedBy / wa-
sUsedBy FILE(PATH)
meta.agent USERNAME User information
meta.machine OSNAME operating system distribution
Table 2 : LevelDB key-value pairs that store file and process provenance. Capital letter words are arguments.
CDE-SP: Software Provenance in CDE Provenance in Software Packages June, 10th
, 2014 19 / 29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ipaw14quanppresentation-151027164935-lva1-app6891/85/Auditing-and-Maintaining-Provenance-in-Software-Packages-32-320.jpg)