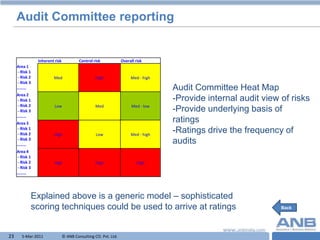
The document discusses audit, risk management, and the role of the audit committee. It provides definitions of risk, audit, and the audit committee. It outlines the classification of risks into strategic, operational, and compliance risks. It describes the expectations from effective risk management, including avoiding surprises, protecting reputation, and informed decision making. It summarizes the role of the audit committee in overseeing financial reporting, internal controls, and risk management policies.