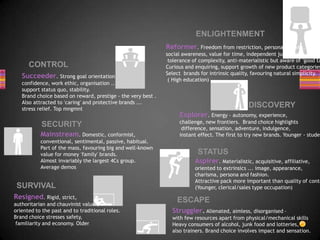
This document discusses audience research methods for media producers. It defines audiences as groups that receive and make sense of media texts. Producers must understand their target audiences. Common research methods include demographics, which categorizes people by occupation; psychographics, which examines personality traits and behaviors; and research organizations that provide industry data. Psychographic models segment audiences based on needs and interests, like Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs. Effective audience research combines both primary sources like surveys and secondary sources from various media to gain audience insights.