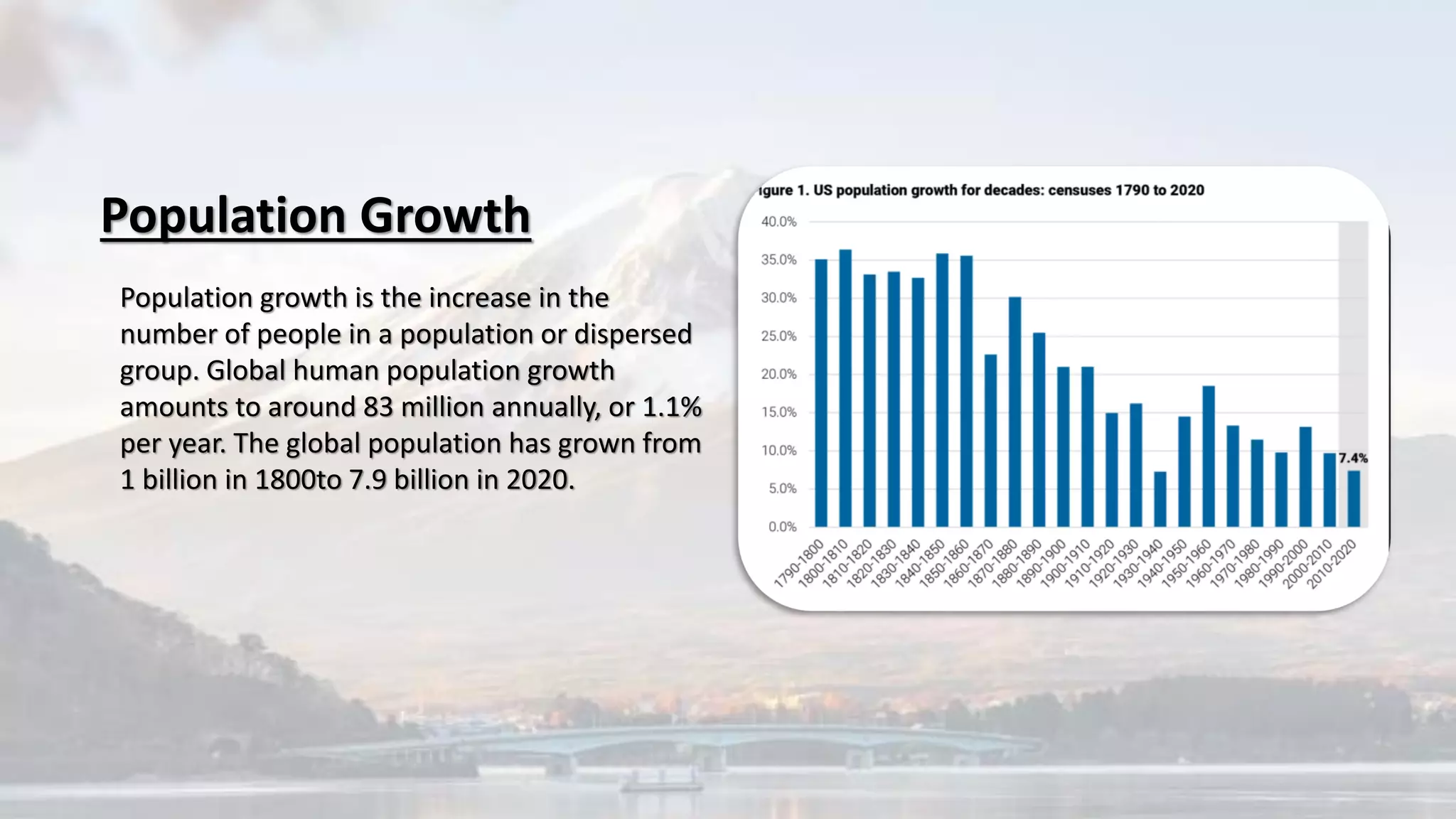
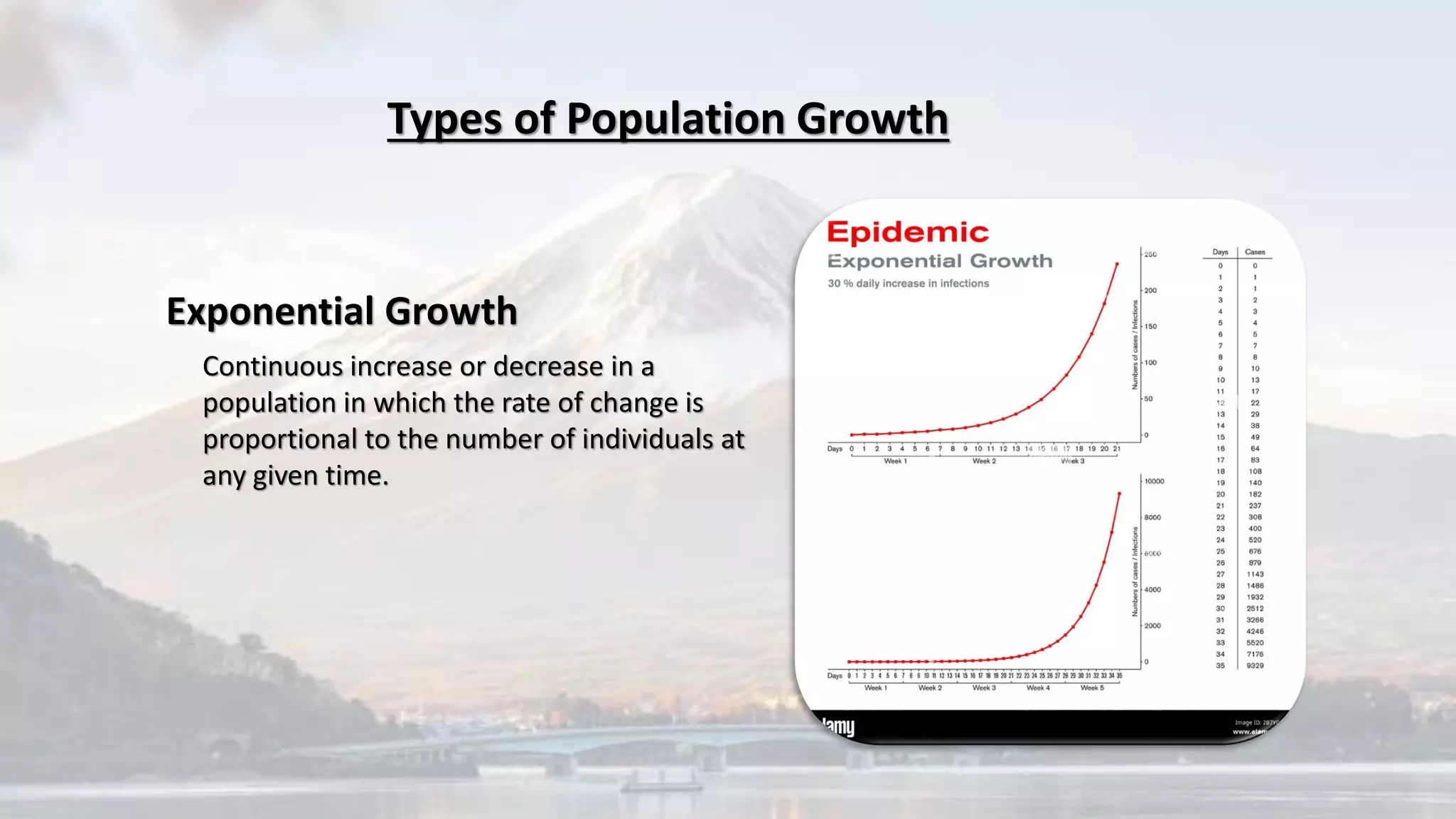
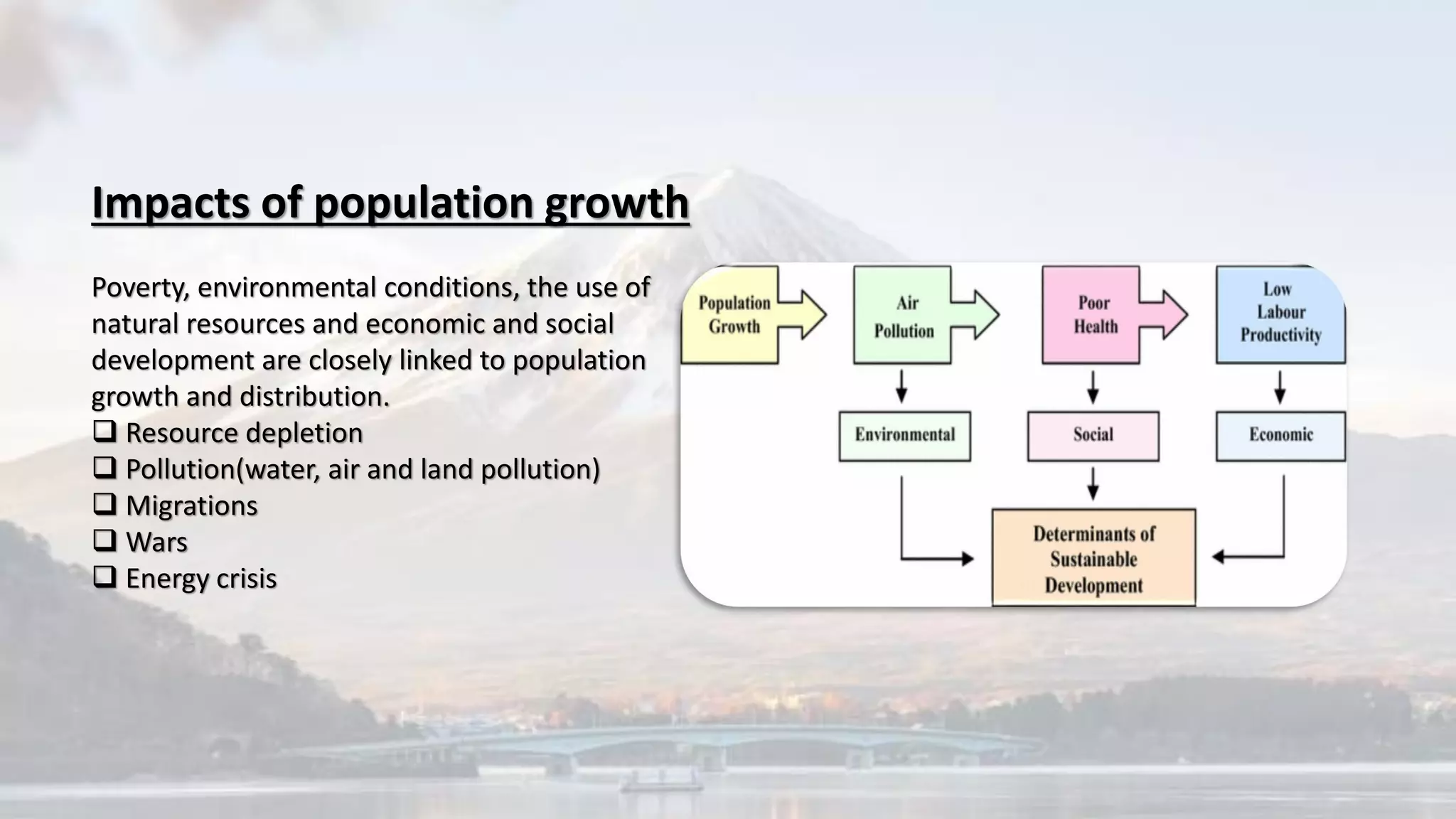
The document discusses various environmental challenges and their causes. It covers topics like deforestation, air pollution, land pollution, greenhouse effect, sustainable development, population growth, and the impacts of population growth. It provides examples and definitions for key terms. Population growth contributes to issues like increased demand for resources, climate change, and degradation of the environment over coming decades. The rapid growth affects sustainability objectives and causes problems related to resources, pollution, migrations, and conflicts.