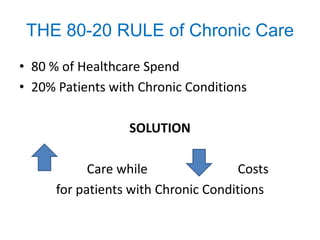
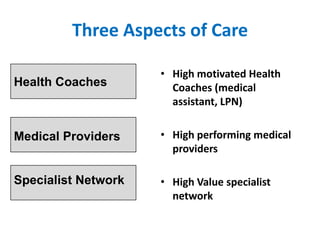
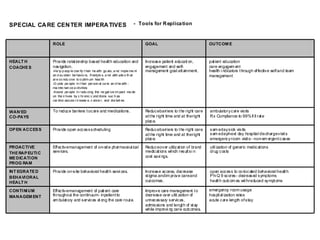
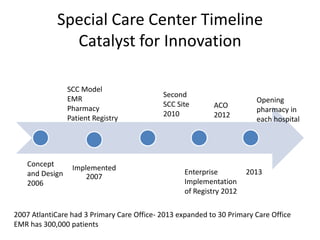
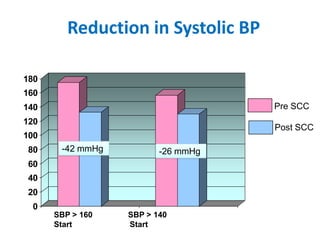
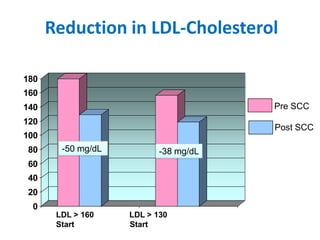
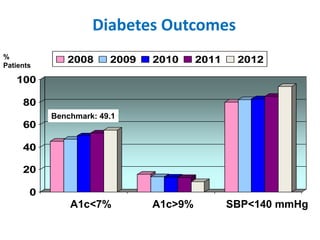
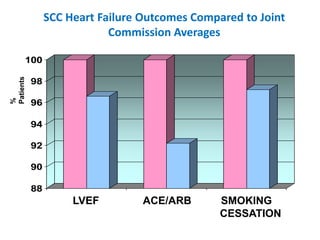
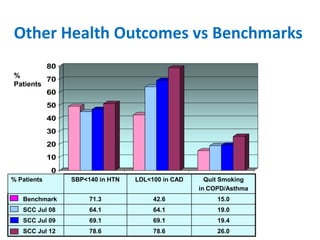
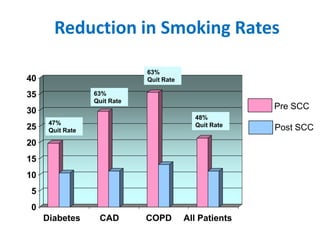
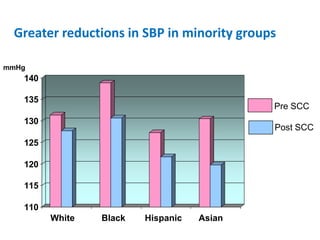
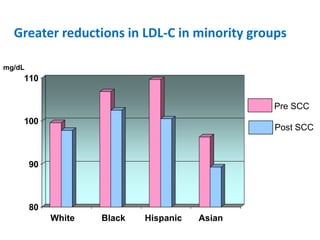
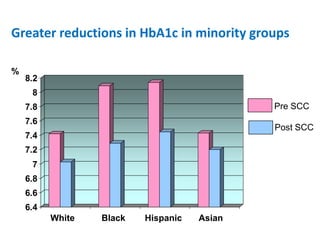
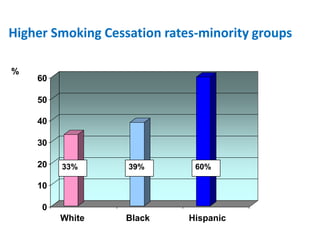
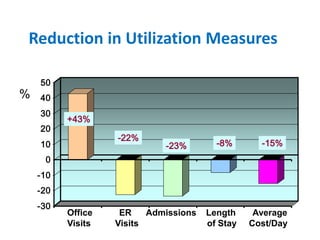
The document summarizes the Special Care Center, a service created by AtlantiCare to provide coordinated care for patients with chronic conditions. The Special Care Center aims to (1) manage chronic conditions effectively through a patient-centered medical home model, (2) reduce healthcare costs by focusing on preventative care and avoiding unnecessary emergency visits and hospitalizations, and (3) improve patient outcomes by providing integrated care, health coaching, open access to providers and services, and an emphasis on the patient experience. Since opening in 2007, the Special Care Center has expanded its services and grown to over 2,600 enrolled patients.