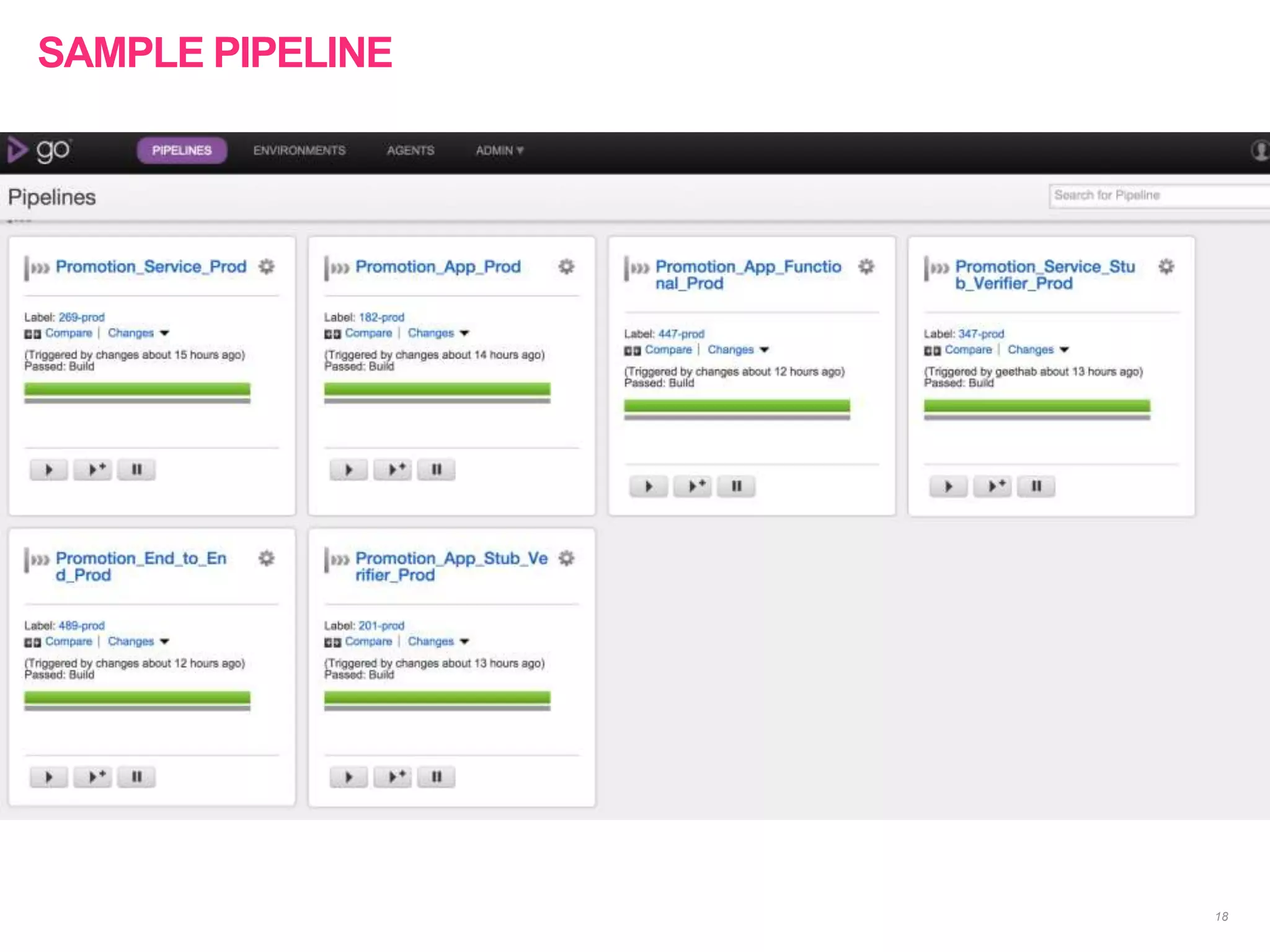
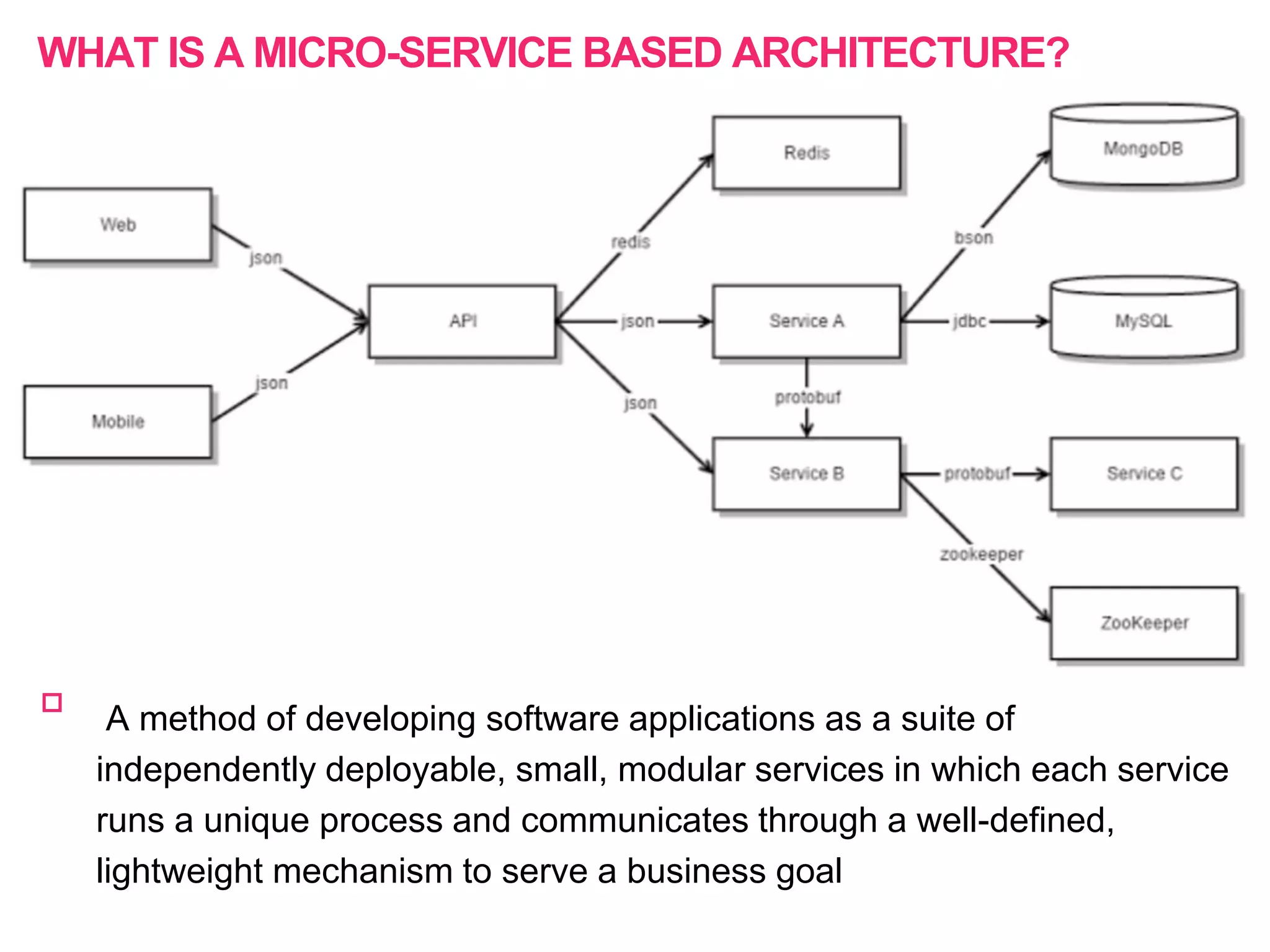
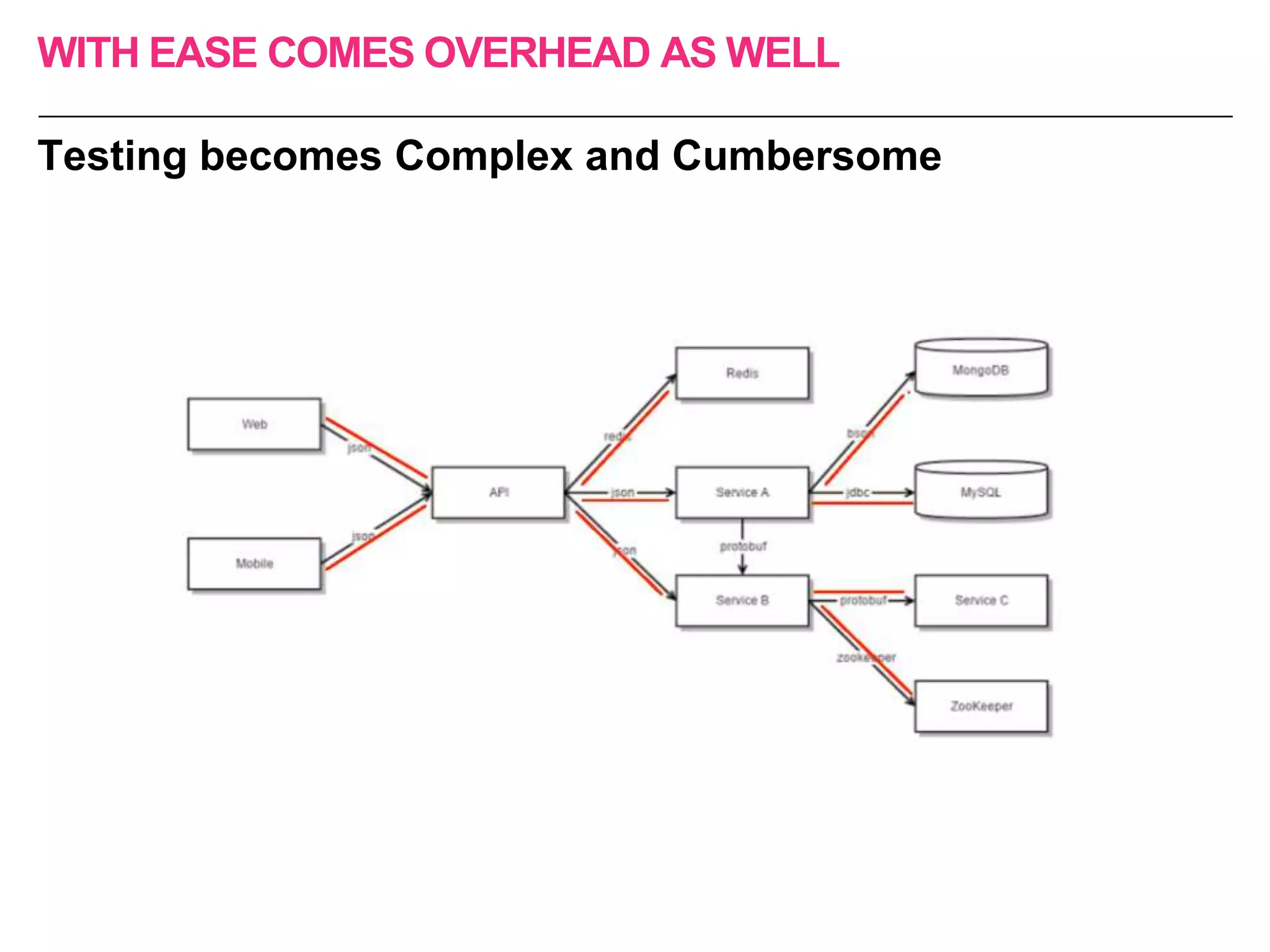
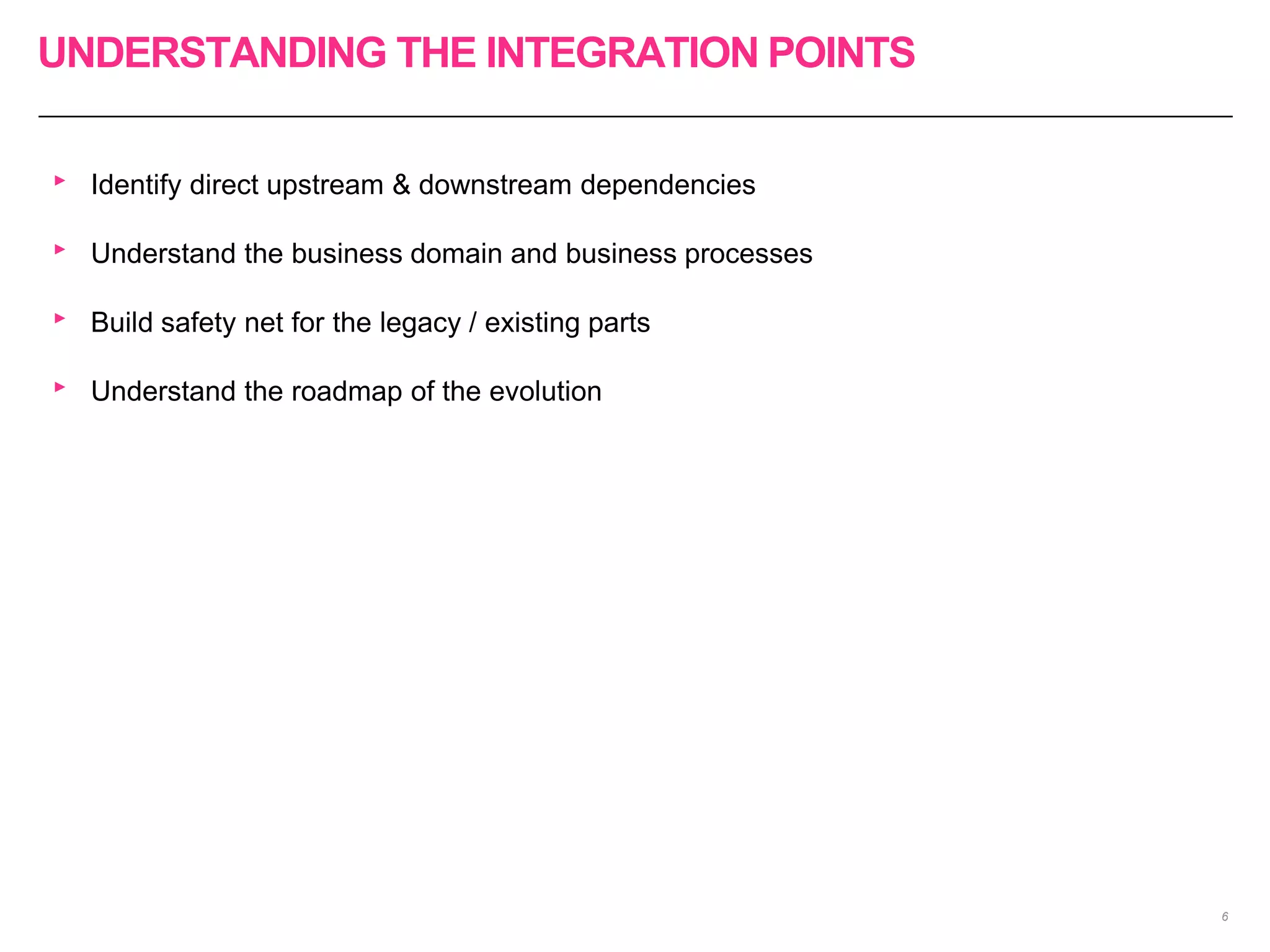
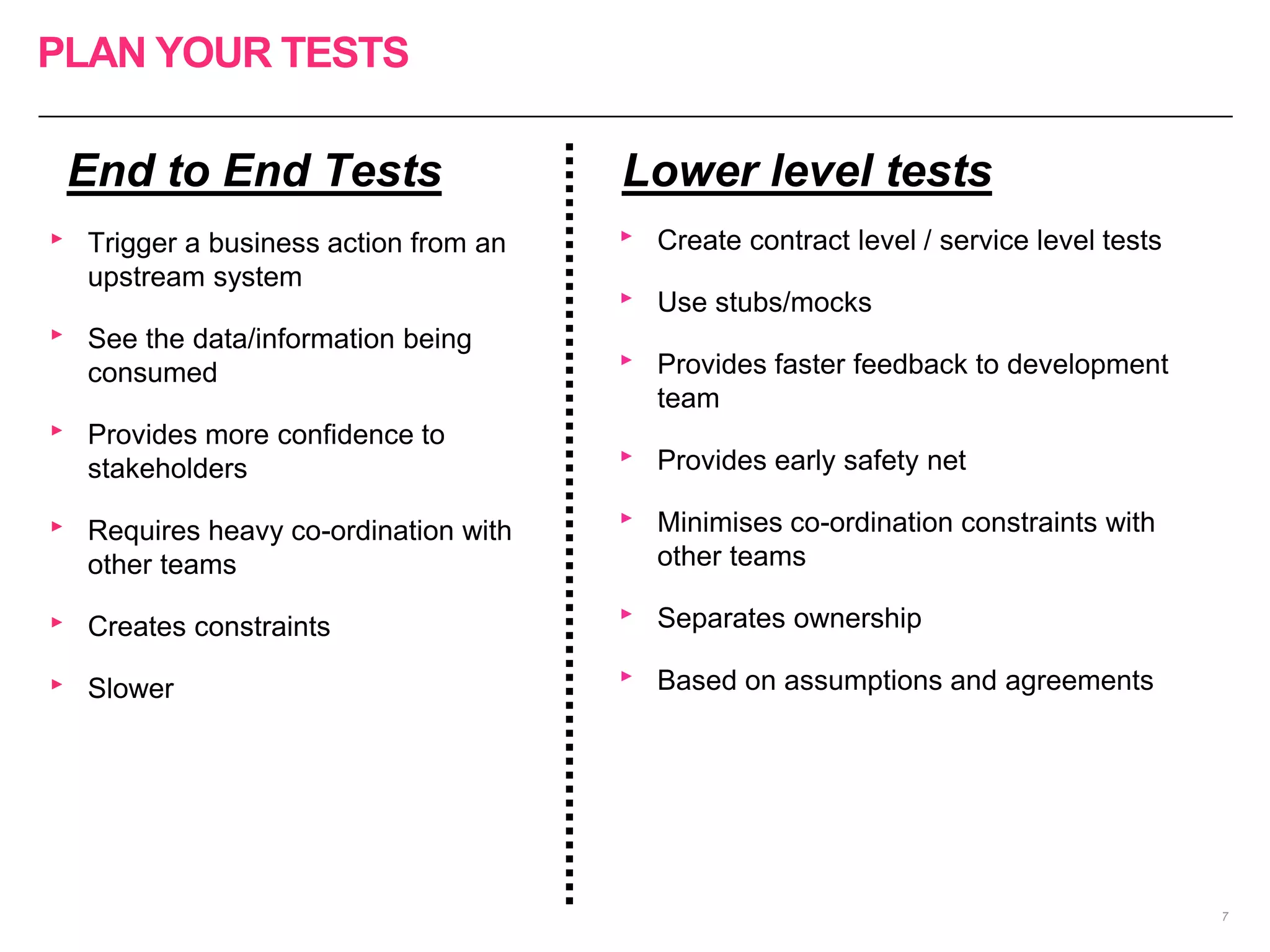
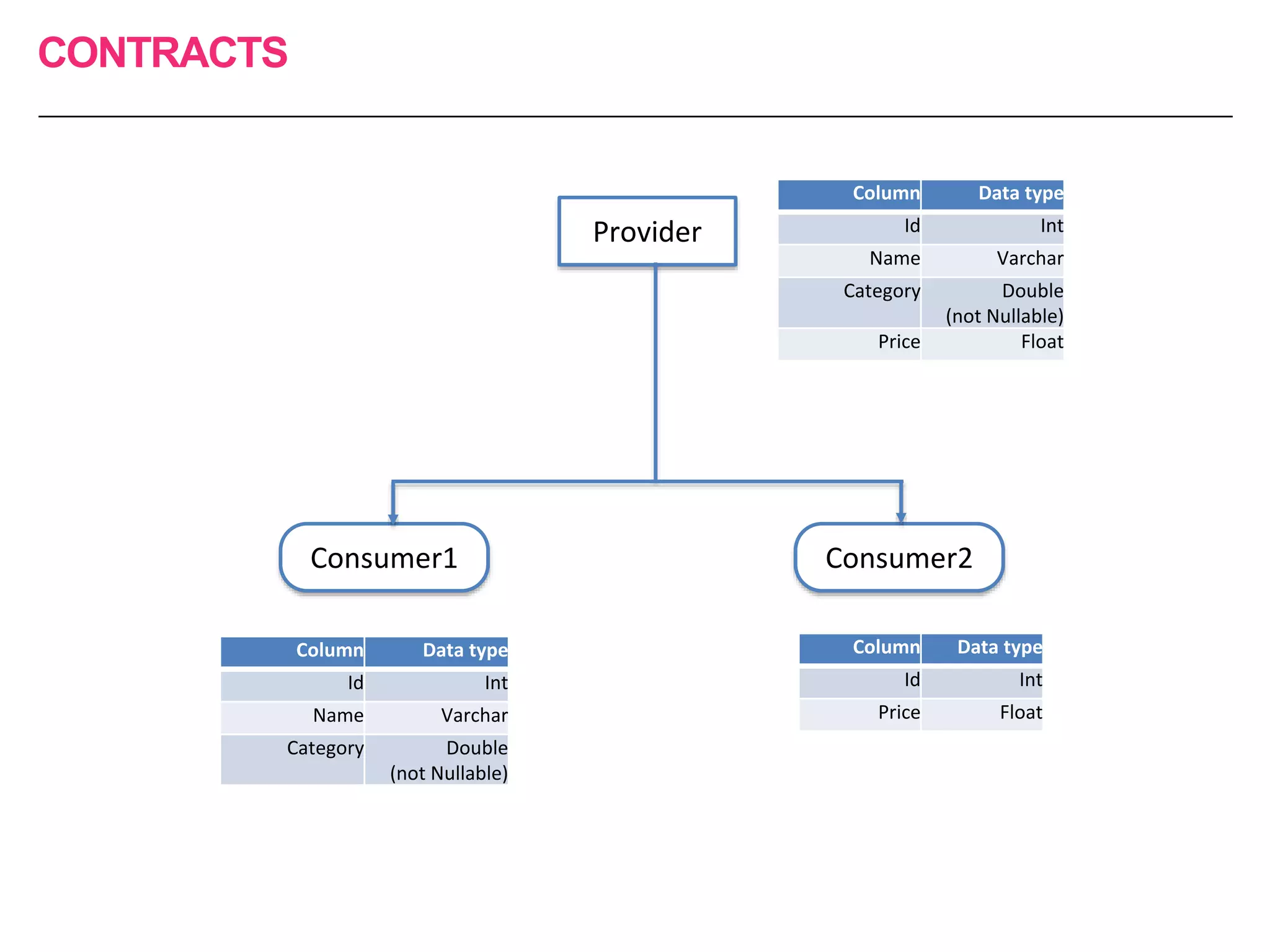
The document discusses the approach to re-engineering legacy applications using micro-service architecture, emphasizing the development of independently deployable services. It highlights the complexities of testing within this framework, including the importance of comprehensive testing strategies and understanding upstream and downstream dependencies. The document also addresses challenges in maintaining effective testing practices amid evolving business processes.


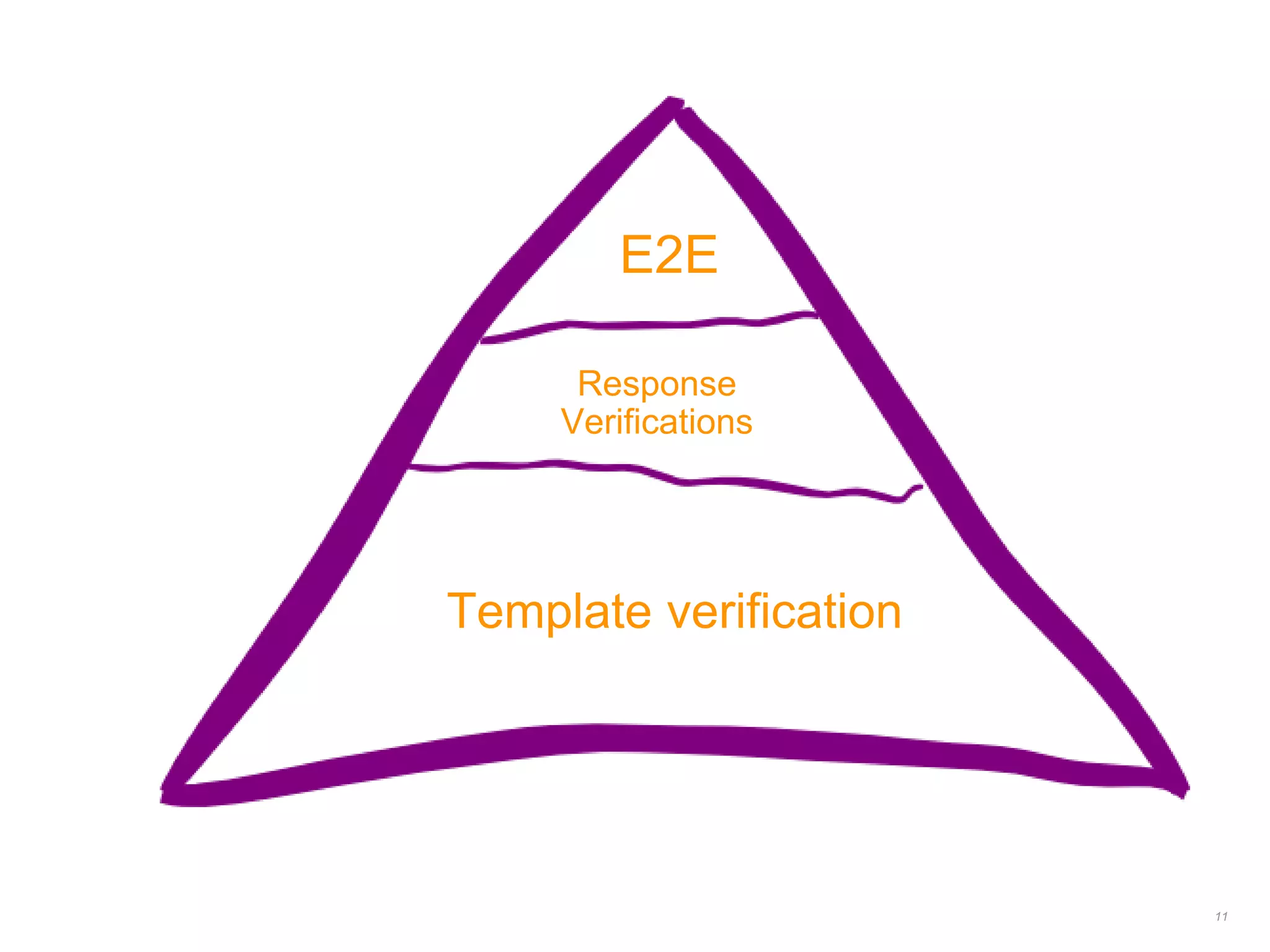
![TEMPLATE VERIFICATION
9
[
{
"article_unit": string,
"category": {
"id": integer,
"name": string
},
"sub_category": {
"id": integer,
"name": string
},
"article_weight": integer,
"name": string,
"id": integer,
“frozen”: boolean
}
]
End Point Provides
[
{
"category": {
"id": integer,
"name": string
},
"sub_category": {
"id": integer,
"name": string
},
"name": string,
"id": integer,
“frozen”: boolean
}
]
Consumer Requires](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atagtr2017testapproachforreengineeringlegacyapplicationsbasedonmicro-servicearchitecturefinalpptx-170320090215/75/ATAGTR2017-Test-Approach-for-Re-engineering-Legacy-Applications-based-on-Micro-service-Architecture-9-2048.jpg)
![RESPONSE VERIFICATION
10
[
{
"article_unit": "C",
"category": {
"id": 1,
"name": "SALMON"
},
"article_weight": 500,
“brand_name": "SALMON",
"id": 123,
“frozen”: true
}
]
- request:
url: /articles/123.json
method: GET
file: articles/GET_articleId.json
- request:
url: /articles/456.json
method: GET
file: articles/GET_articleId.json
[
{
"article_unit": "X",
"category": {
"id": 456,
"name": "CHOCOLATE"
},
“article_weight": ,
“brand_name": "CADBURY",
"id": 456,
“frozen”: false
}
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/atagtr2017testapproachforreengineeringlegacyapplicationsbasedonmicro-servicearchitecturefinalpptx-170320090215/75/ATAGTR2017-Test-Approach-for-Re-engineering-Legacy-Applications-based-on-Micro-service-Architecture-10-2048.jpg)