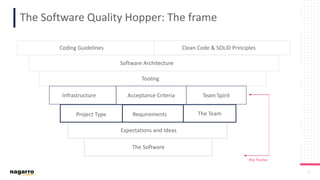
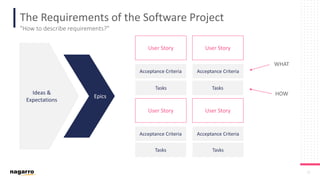
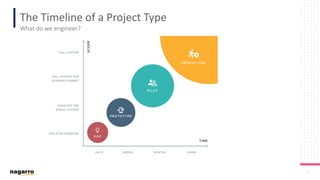
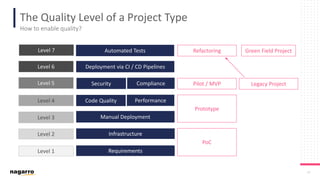
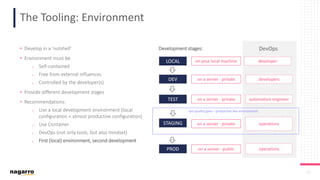
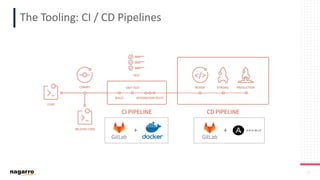
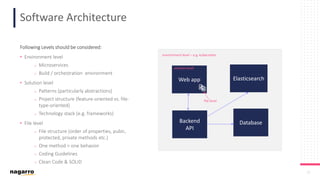
The document discusses the complexities and subjective nature of software quality, emphasizing the importance of team collaboration and proper metrics to define and assess quality. It highlights that quality can be influenced by factors such as project type, coding standards, and development environments, while also cautioning against the false security that certain metrics may provide. Ultimately, it stresses the need for a collective mindset towards quality within teams to ensure effective software delivery.