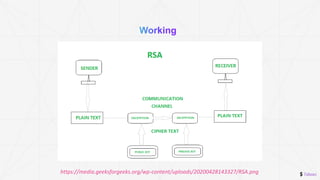
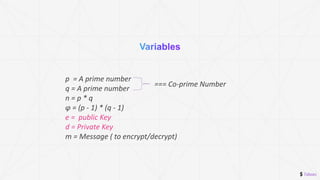
The document discusses the RSA encryption algorithm. It begins by explaining asymmetric cryptography and how it uses public and private key pairs. It then walks through the RSA encryption process step-by-step, including generating the public and private keys from prime numbers, encrypting a message with the public key, and decrypting it with the private key. Finally, it reiterates that asymmetric encryption is more secure than symmetric encryption.










![$ 7absec
• A number that is less than phi, and coprime to both n
and phi.
• The key should be greater than 2 and less than phi
(2<e<phi)
• n = 143
• phi = 120
• possible_bup_keys = []
• for i in range(2, phi):
• if gcd(n, i) == 1 and gcd (phi, i) == 1:
• possible_bup_keys.append(i)
• Print(possible_bup_keys)
Walk Through
1: Prime Number
2: Coprime Number
3: Assigning values of p & q
4: Calculating n and phi
5: Progress upto this
7: Finding “d”
8: Progress upto this
9: Asymmetric Keys
10: Encryption & Decryption](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asmtrc-enc-rsa-211223055710/85/Asymmetric-Encryption-with-RSA-13-320.jpg)
![$ 7absec
• A number that is grater than phi
• d*e mod phi = 1 or d*e % phi = 1
• phi = 120
• e = 7
• possible_pvt_keys = []
• for i in range(phi + 1, phi + 1000):
• if i * e % phi == 1:
• possible_pvt_keys.append(i)
• Print(possible_pvt_keys)
Walk Through
1: Prime Number
2: Coprime Number
3: Assigning values of p & q
4: Calculating n and phi
5: Progress upto this
6: Finding “e”
8: Progress upto this
9: Asymmetric Keys
10: Encryption & Decryption](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asmtrc-enc-rsa-211223055710/85/Asymmetric-Encryption-with-RSA-14-320.jpg)




