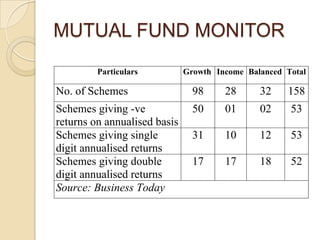
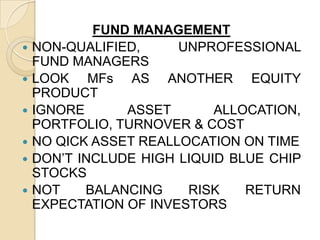
This document provides information on mutual funds, including their definition and types. It discusses the different categories of mutual funds according to ownership, scheme of operation, portfolio, and location. Specific mutual fund schemes are also described such as SBI funds, ULIPs, Dhanraksha, and Dhanshree. Performance issues facing mutual funds are outlined. In conclusion, it is noted that mutual funds are subject to market risk and there are no guarantees of achieving objectives or positive returns.