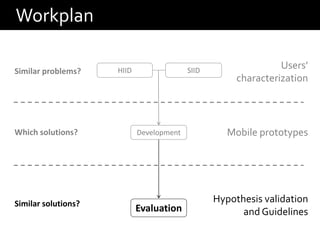
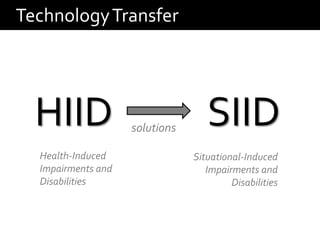
This document discusses bridging the gap between solutions for health-induced impairments and disabilities (HIID) and solutions for situational-induced impairments and disabilities (SIID). It hypothesizes that HIID solutions can be applied to SIID to improve user performance by characterizing users' capabilities in different mobile contexts. The approach involves characterizing problems in HIID and SIID, developing mobile prototypes using text-entry solutions from both domains, and evaluating the solutions to validate the hypothesis and provide guidelines for transferring technologies between user groups. The expected results are relationships between physical and situational impairments, guidelines for transferring solutions, and a transferability index.












![Leading to …
Situationally-Induced Impairments and Disabilities [Sears, 2003]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcpresentation-111111095252-phpapp02/85/ASSETS-11-Doctoral-Consortium-14-320.jpg)



![Do they share …
Similar problems?
[Yesilada et al., 2010]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcpresentation-111111095252-phpapp02/85/ASSETS-11-Doctoral-Consortium-18-320.jpg)









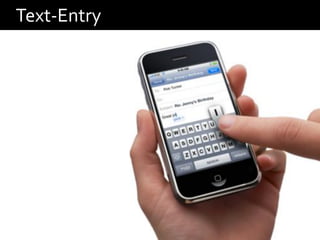




![Text-entry Solutions
Filters e.g. [Trewin, 2002]
Orthographic correctors e.g. [Kane et al., 2008]
Adaptive keyboards e.g. [Merlin and Raynal, 2010]
Alternative techniques e.g. [Wobbrock et al., 2003]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dcpresentation-111111095252-phpapp02/85/ASSETS-11-Doctoral-Consortium-38-320.jpg)