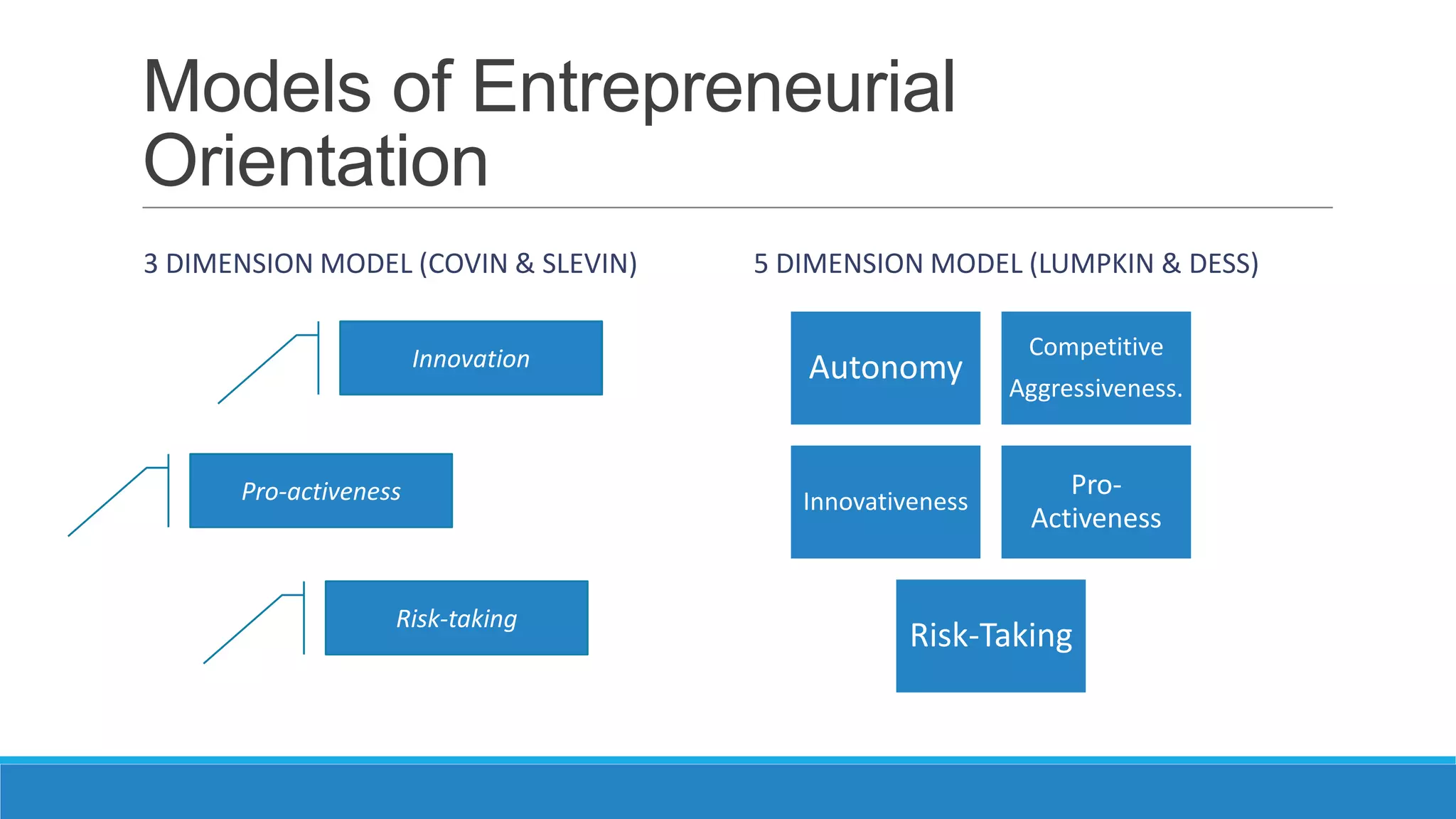
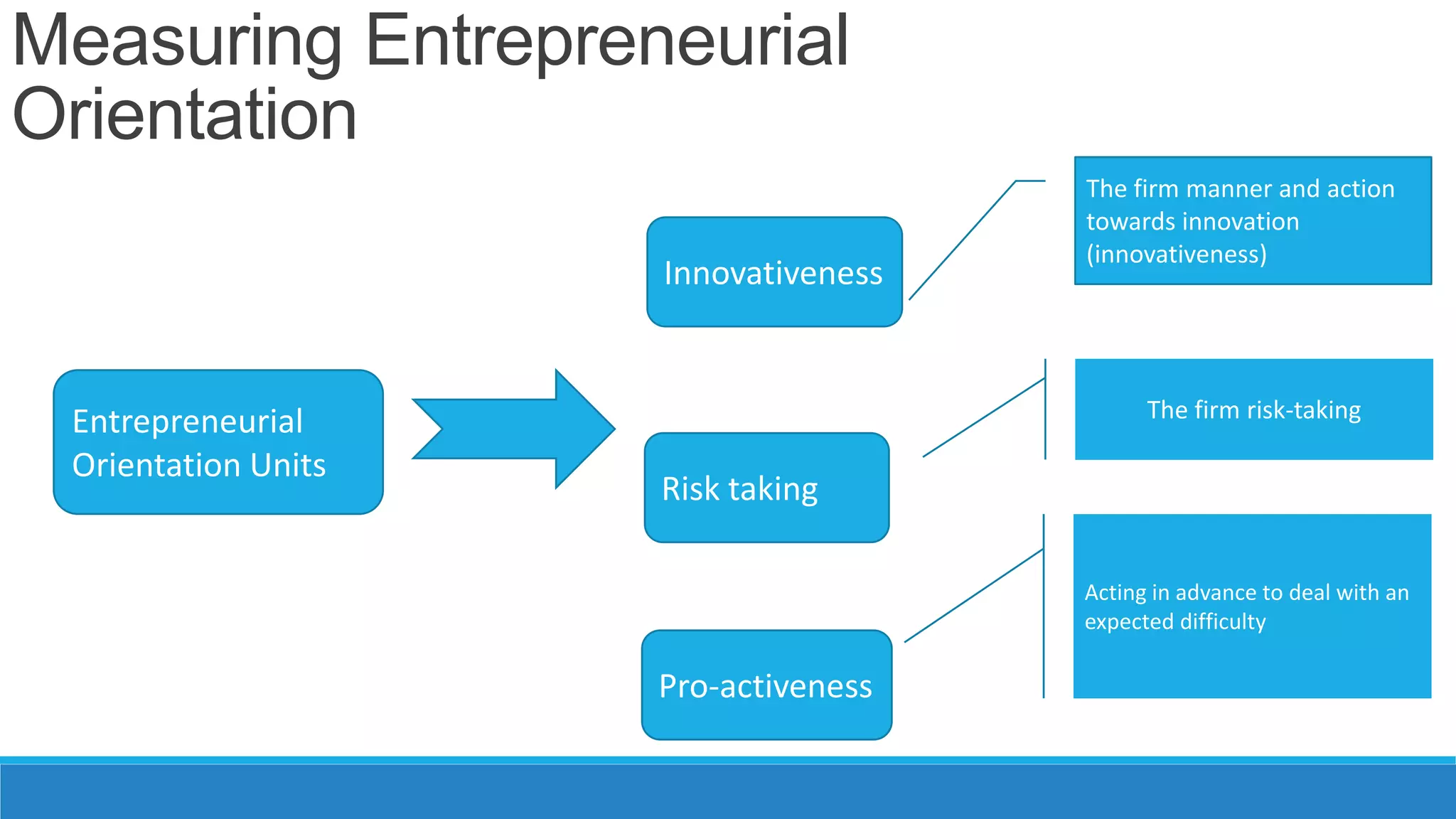
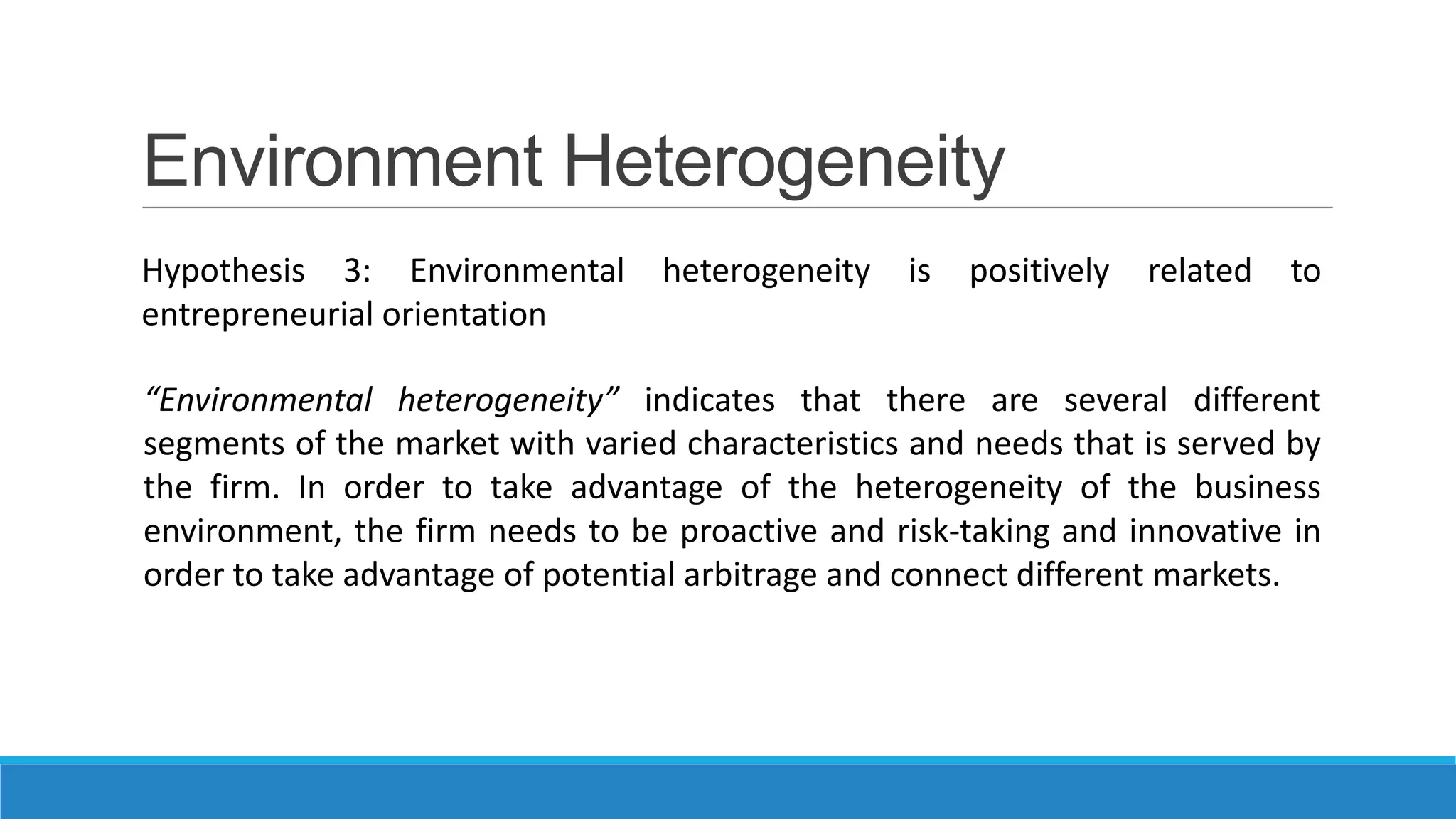
The document analyzes the relationship between a firm's entrepreneurial orientation and the perceived business environment. It presents four hypotheses about how dimensions of the business environment (dynamism, hostility, heterogeneity, munificence) relate to entrepreneurial orientation. The study assessed these relationships through a survey of small and medium enterprises. It found support for hypotheses that more dynamic and hostile environments increase proactiveness and risk-taking. However, dynamism decreased innovativeness while hostility did not affect it. The paper concludes that improving environmental conditions could enhance firms' entrepreneurial orientation and performance.