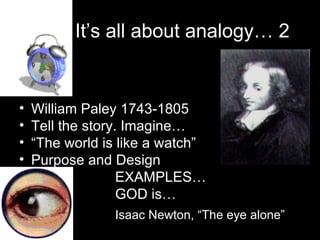
The document discusses teleological arguments for the existence of God based on apparent order and purpose in the world. It outlines the design arguments put forward by philosophers like Aquinas, Paley, and Swinburne, noting they observe design and purpose in nature and conclude a creator God must exist. However, the document also explains challenges to these arguments from David Hume and developments in science like Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection, which provide alternative explanations for order and complexity without needing to invoke God.