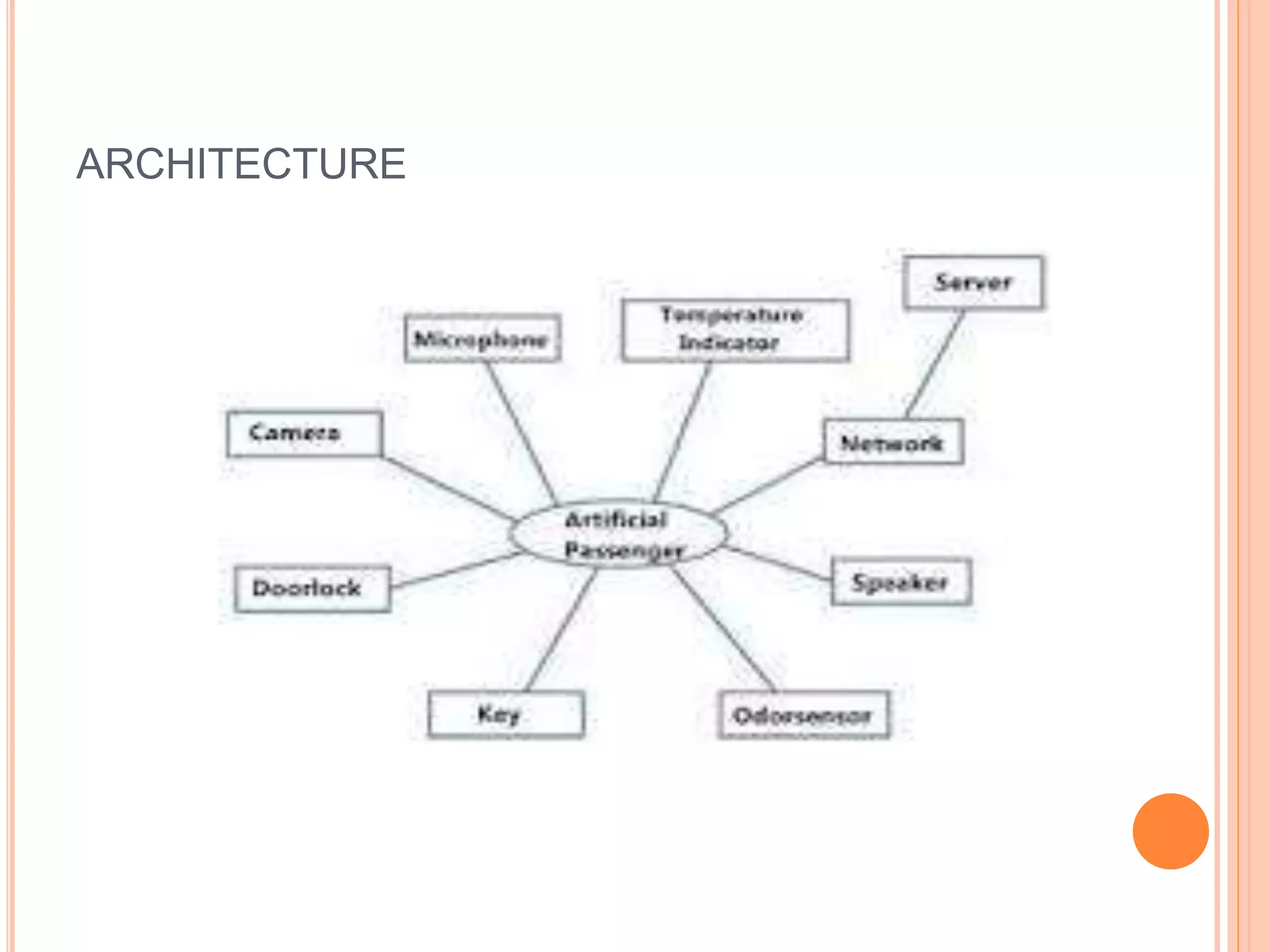
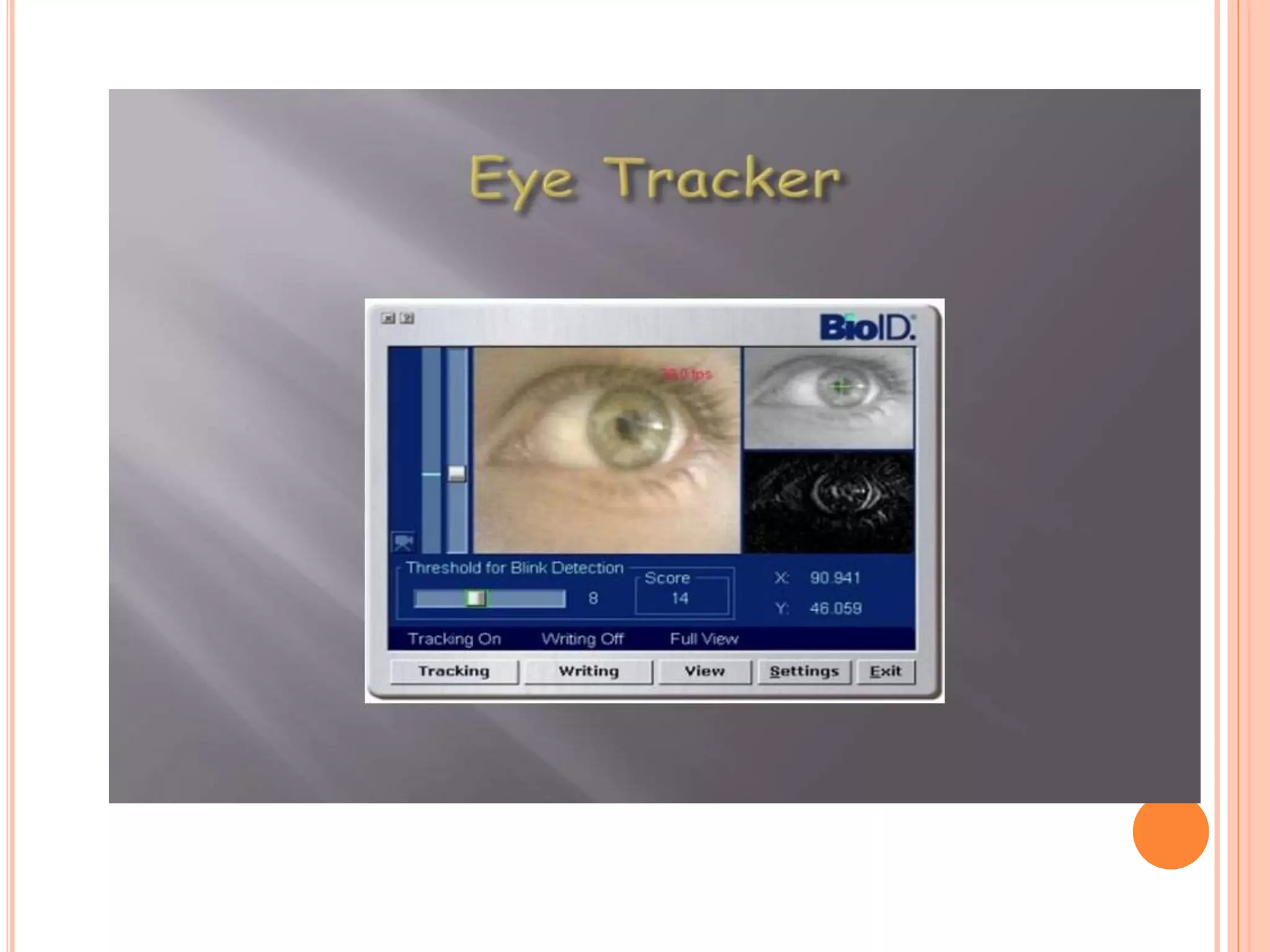
The document describes an artificial passenger system that uses sensors and AI to monitor drivers for drowsiness and prevent accidents. It detects drowsiness through analysis of eye movement, blinking, yawning and other biometrics. When drowsiness is detected, it uses speech and other alerts to engage the driver. The system aims to provide conversation and entertainment to help drivers stay alert during long solo trips. It has potential to prevent accidents and be used to ensure alertness in other safety-critical roles.