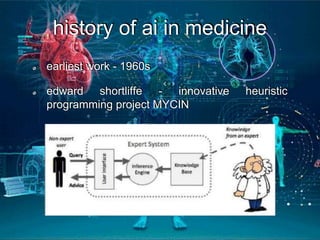
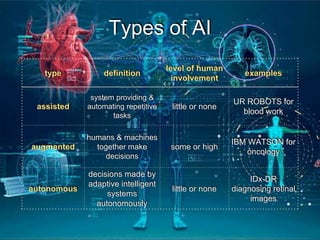
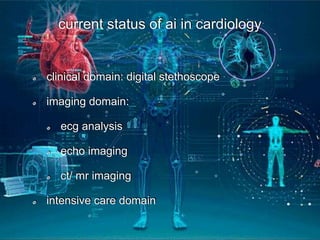
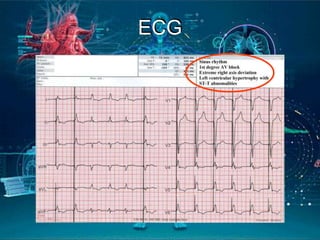
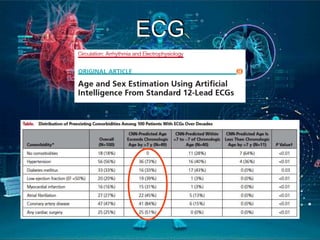
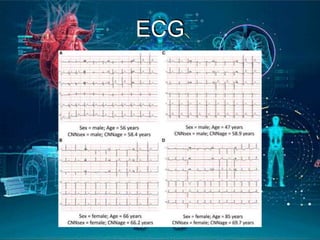
This document provides an introduction to artificial intelligence (AI). It discusses the history of AI, including its origins in the 1950s and important figures like Alan Turing. It also covers the history of AI in medicine, such as early work in the 1960s and IBM's Deep Blue defeating Gary Kasparov in 1997. The document defines different types of AI systems and provides examples. It discusses the current applications of AI in cardiology, such as digital stethoscopes, ECG and echo image analysis, and AI use in intensive care. In conclusion, it states that AI is already here and will significantly impact fields involving imaging and data, while creating innovations that need to be adopted early in clinical practice.