Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times

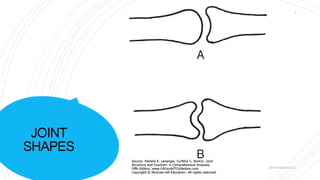
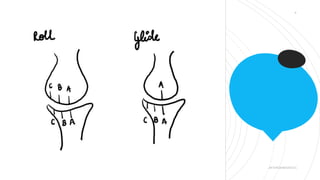
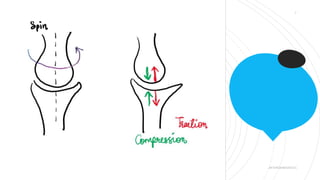
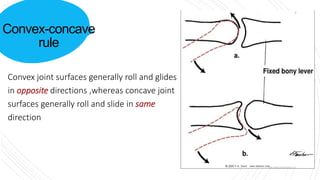




This document discusses arthrokinematics, or accessory motions that occur between adjacent joint surfaces. It defines the main types of motions as roll, slide, spin, compression, and traction. A key concept covered is the convex-concave rule, which states that convex joint surfaces generally roll and glide in opposite directions, while concave surfaces roll and slide in the same direction. The document also addresses joint play and how it allows for freedom of movement between articular surfaces.











