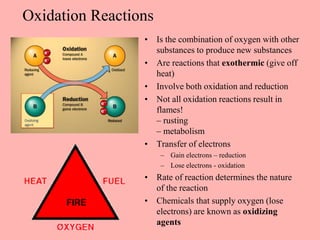
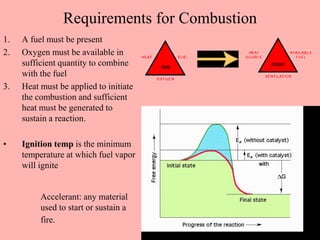
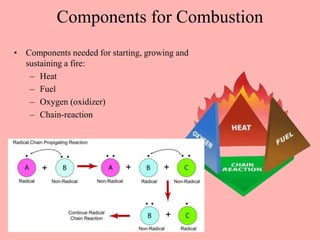
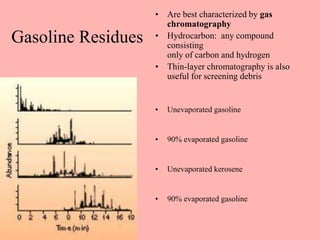
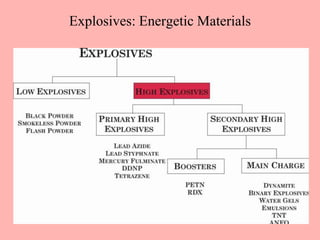
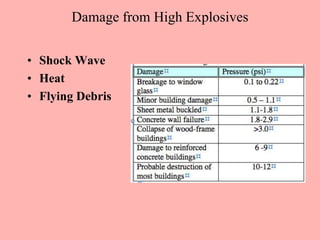
This document discusses arson and explosives. It defines fire, combustion, and oxidation reactions. The three requirements for combustion are a fuel, oxygen, and heat. An accelerant is any material used to start or sustain a fire. Arson investigations examine fire patterns, debris, and evidence of accelerants. Explosives are energetic materials that produce heat, light, and expanding gases rapidly through chemical reactions. They are classified as low or high explosives based on their reaction rates. Primary explosives are highly sensitive initiators used in detonators.