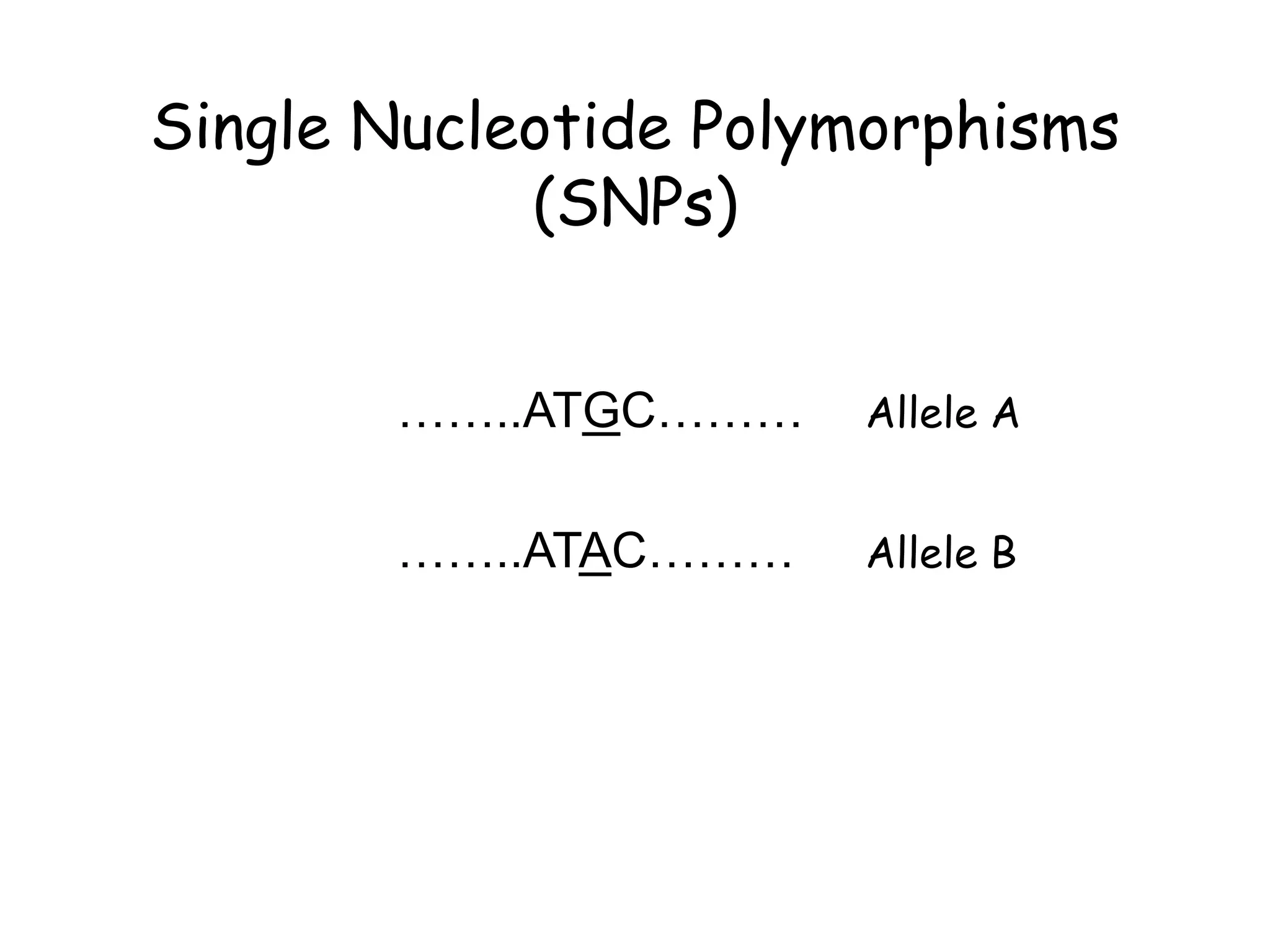
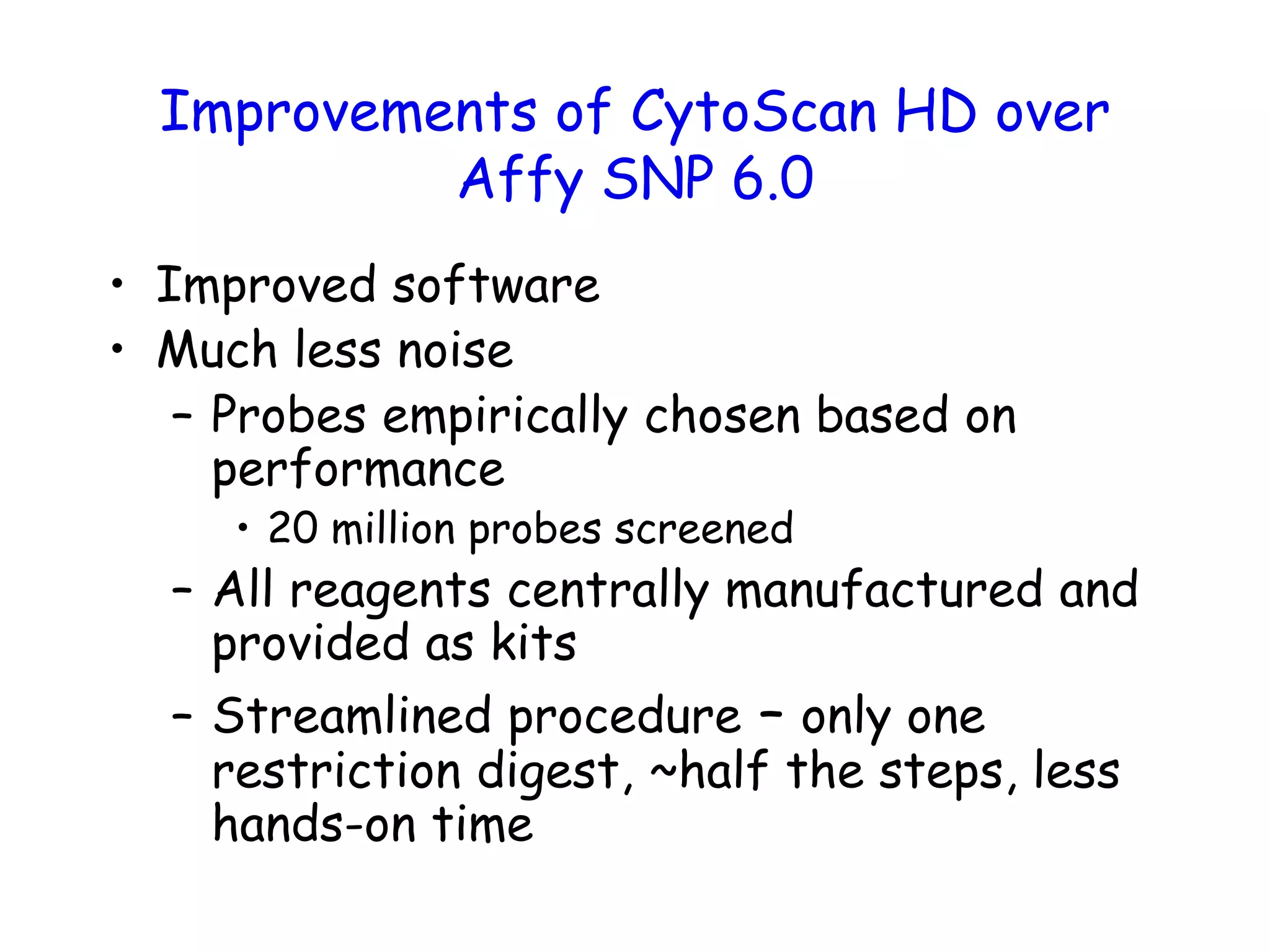
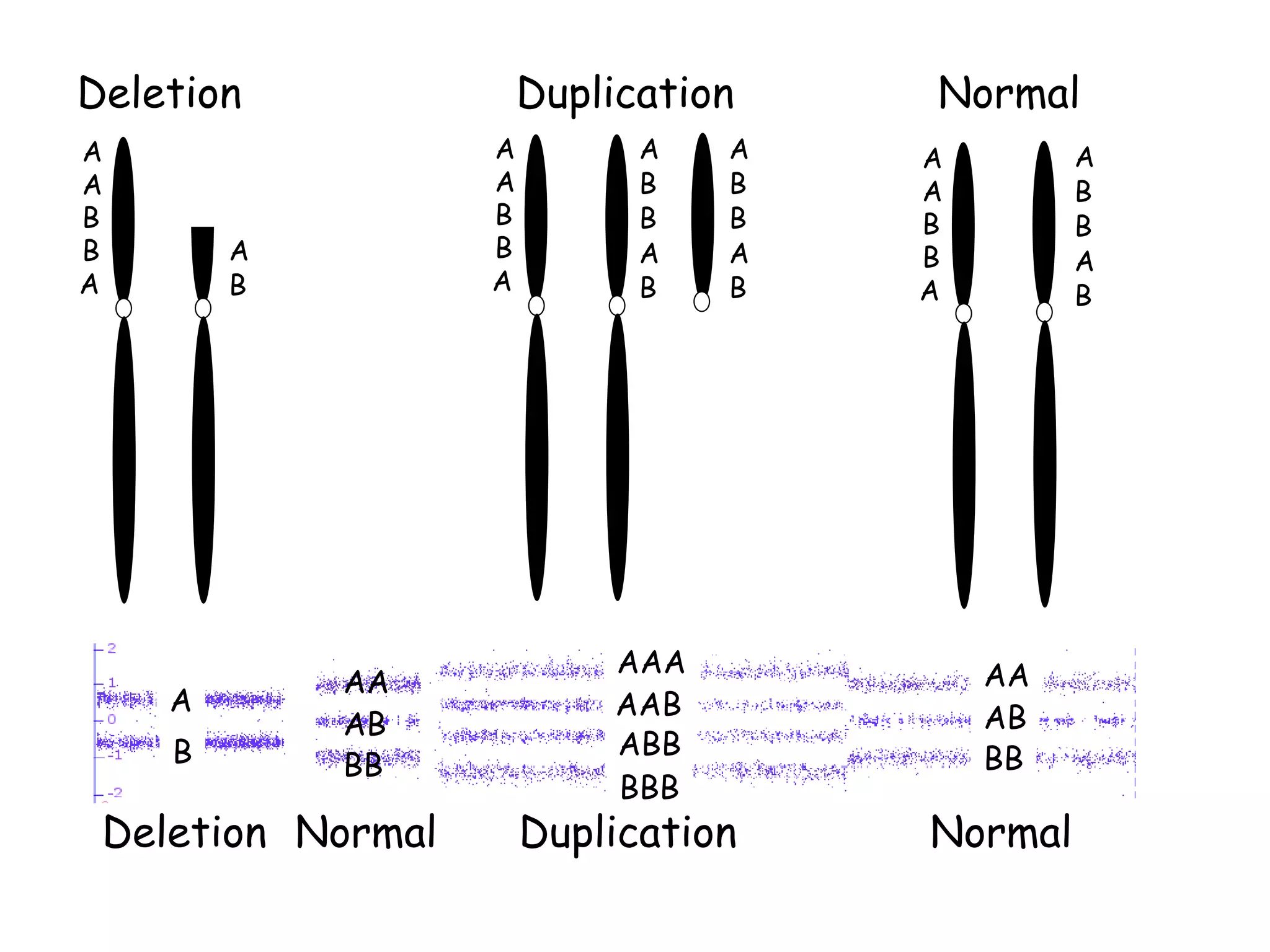
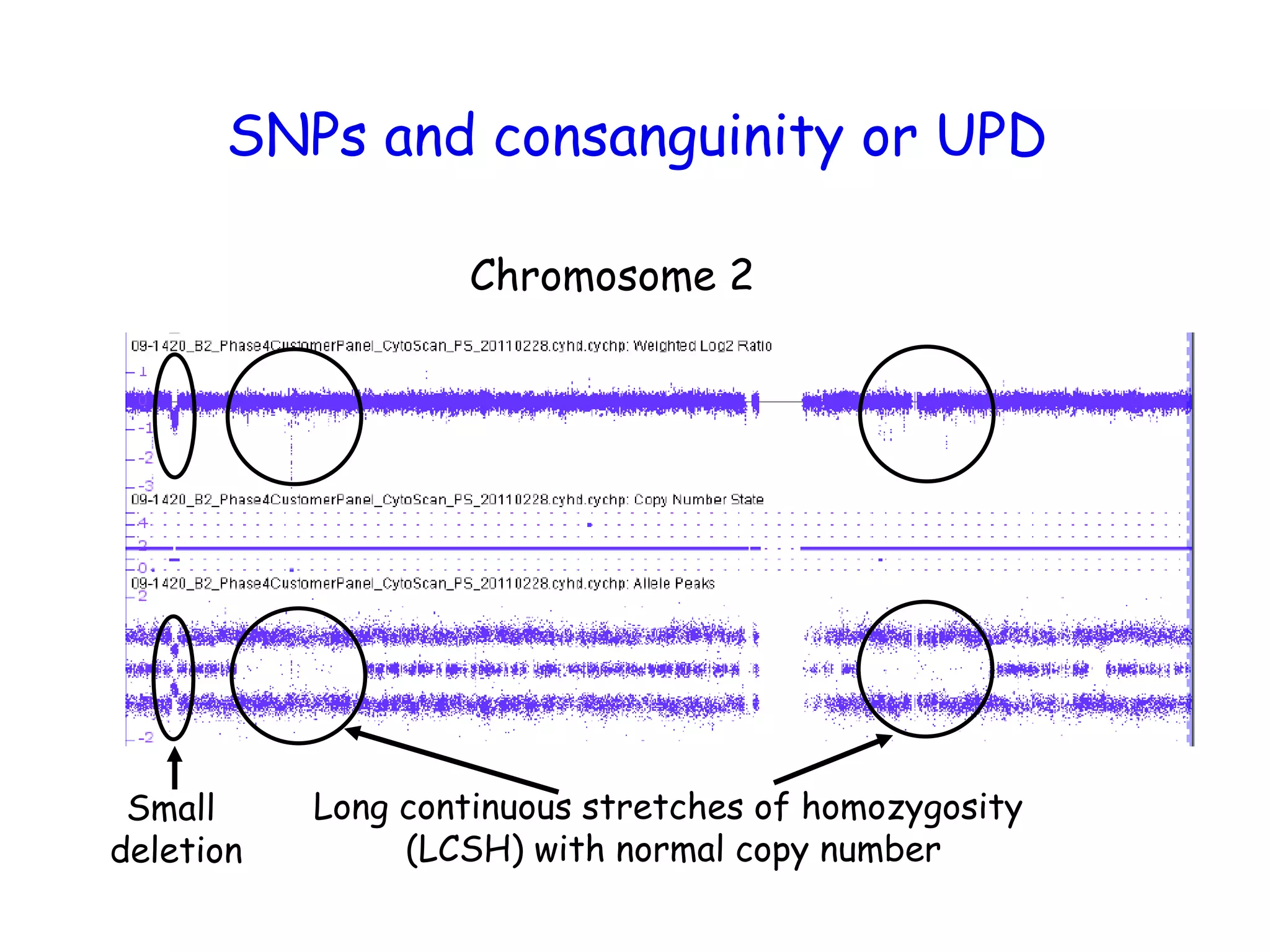
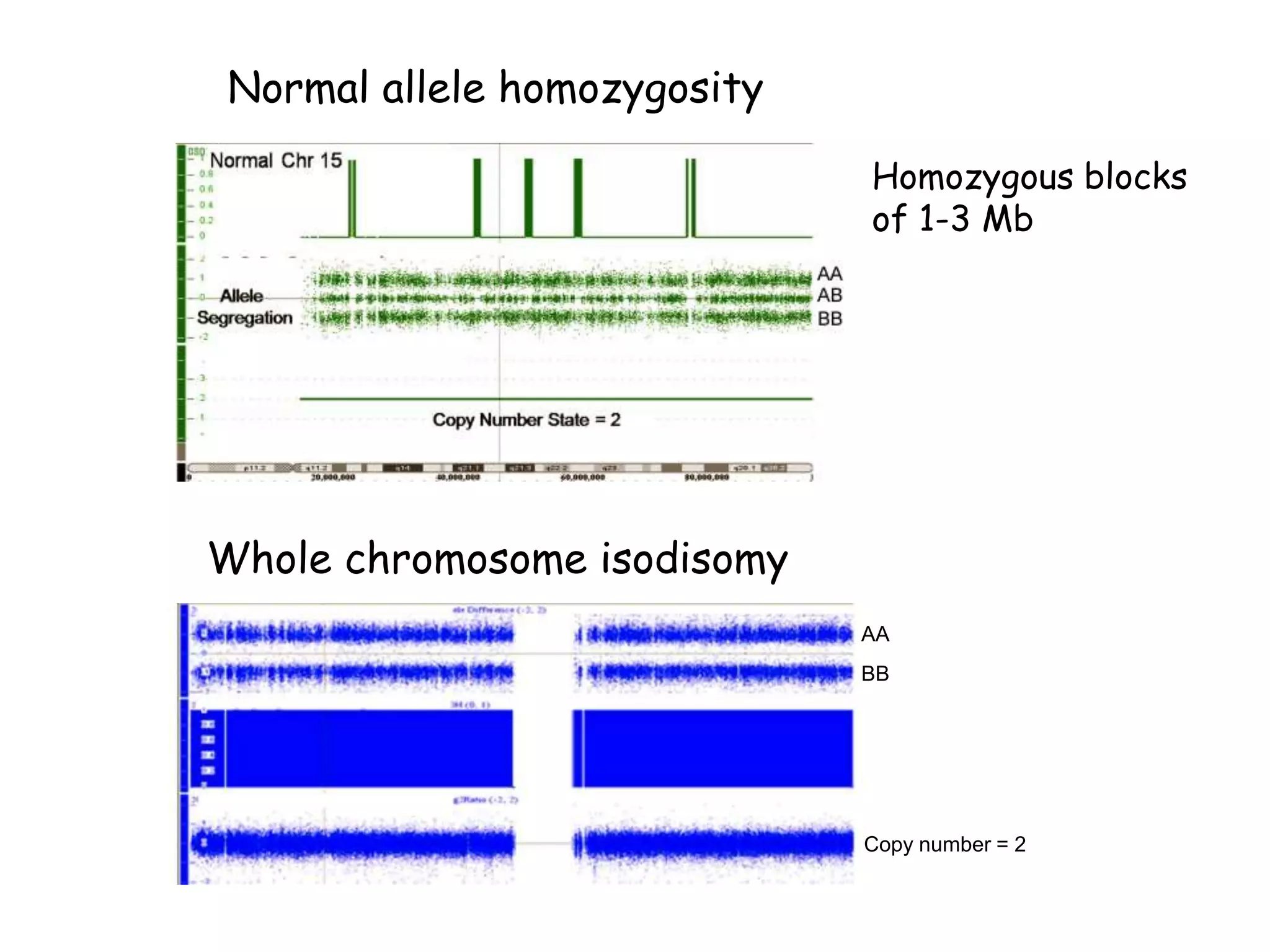
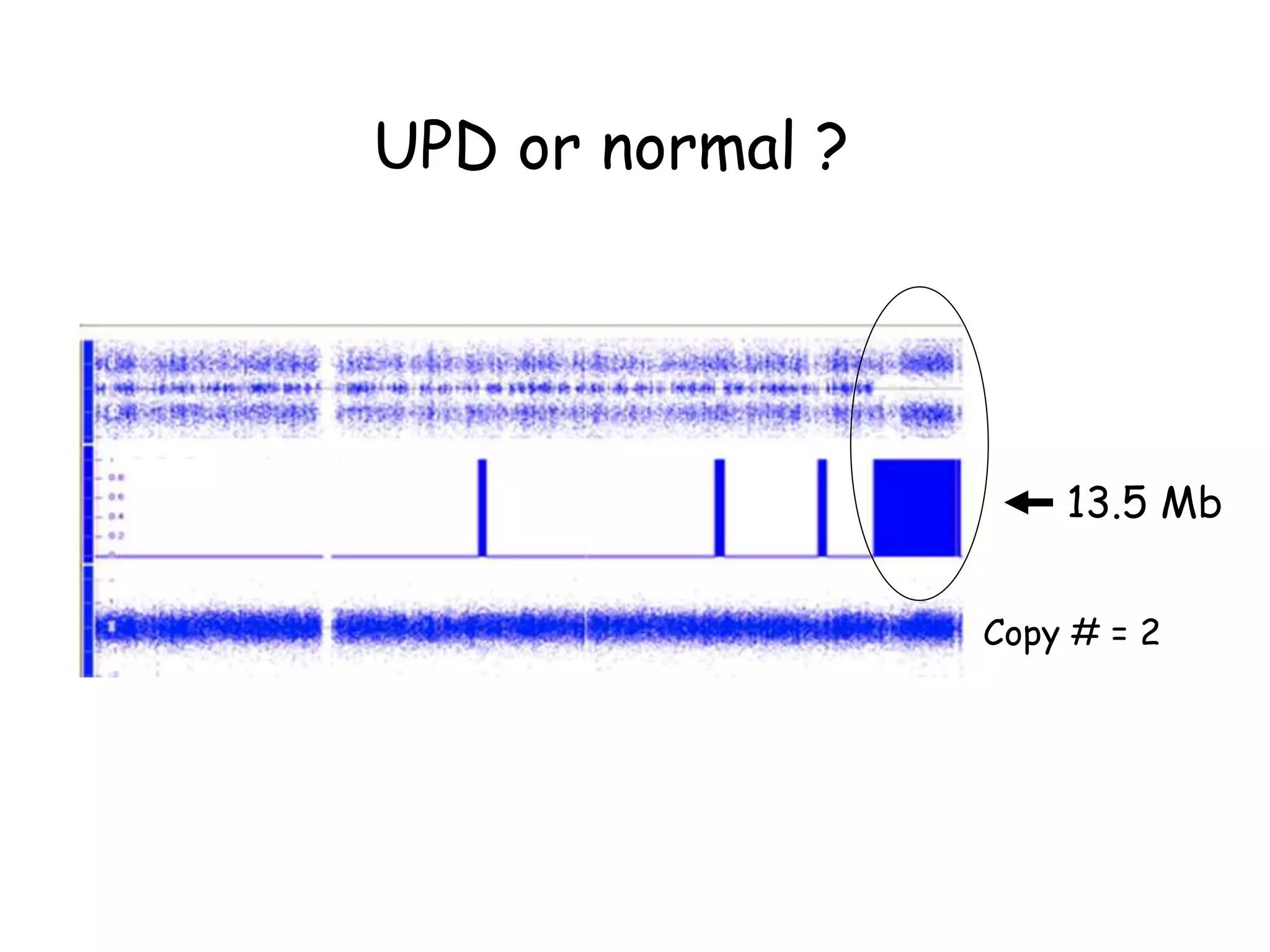
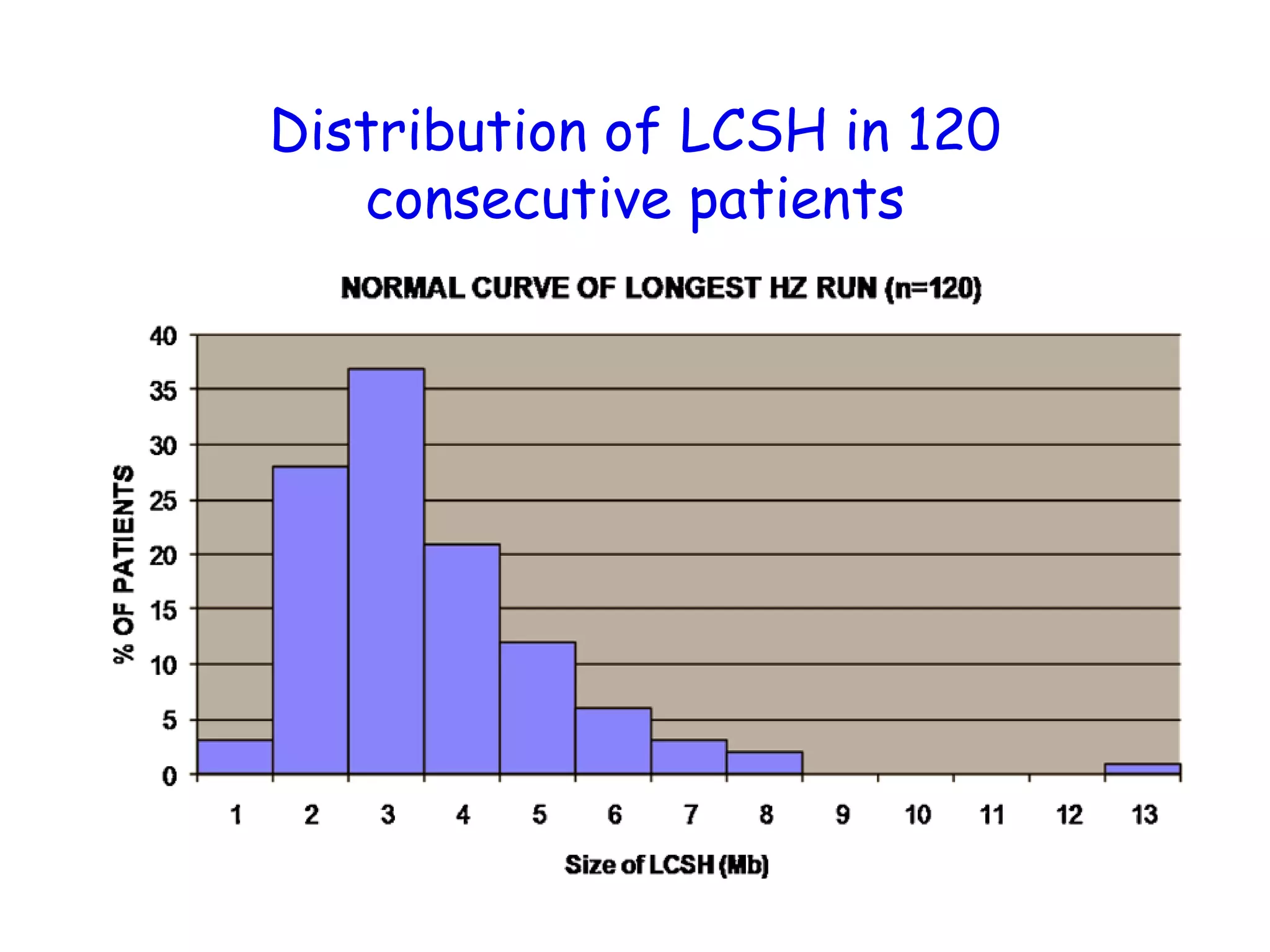
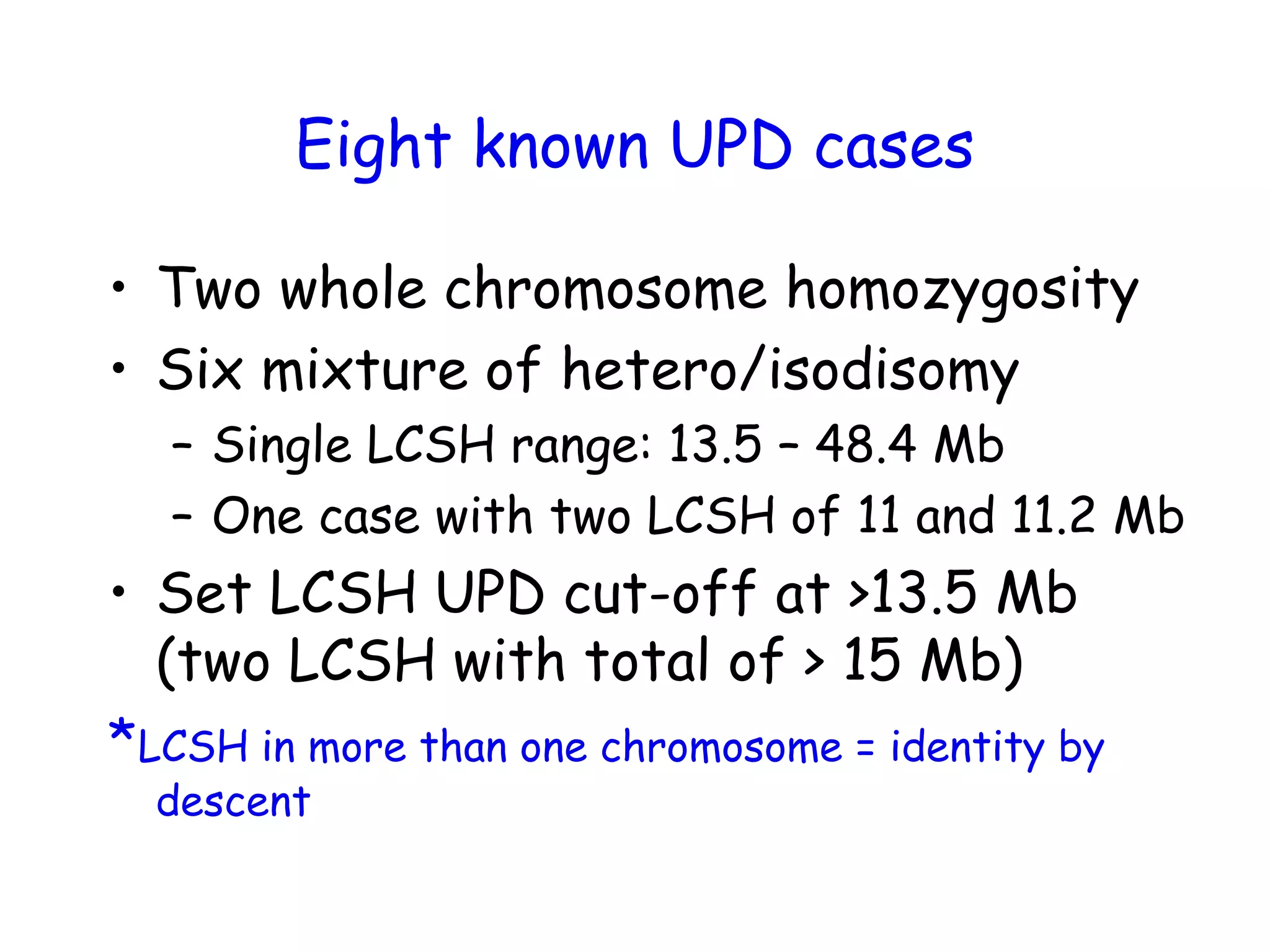
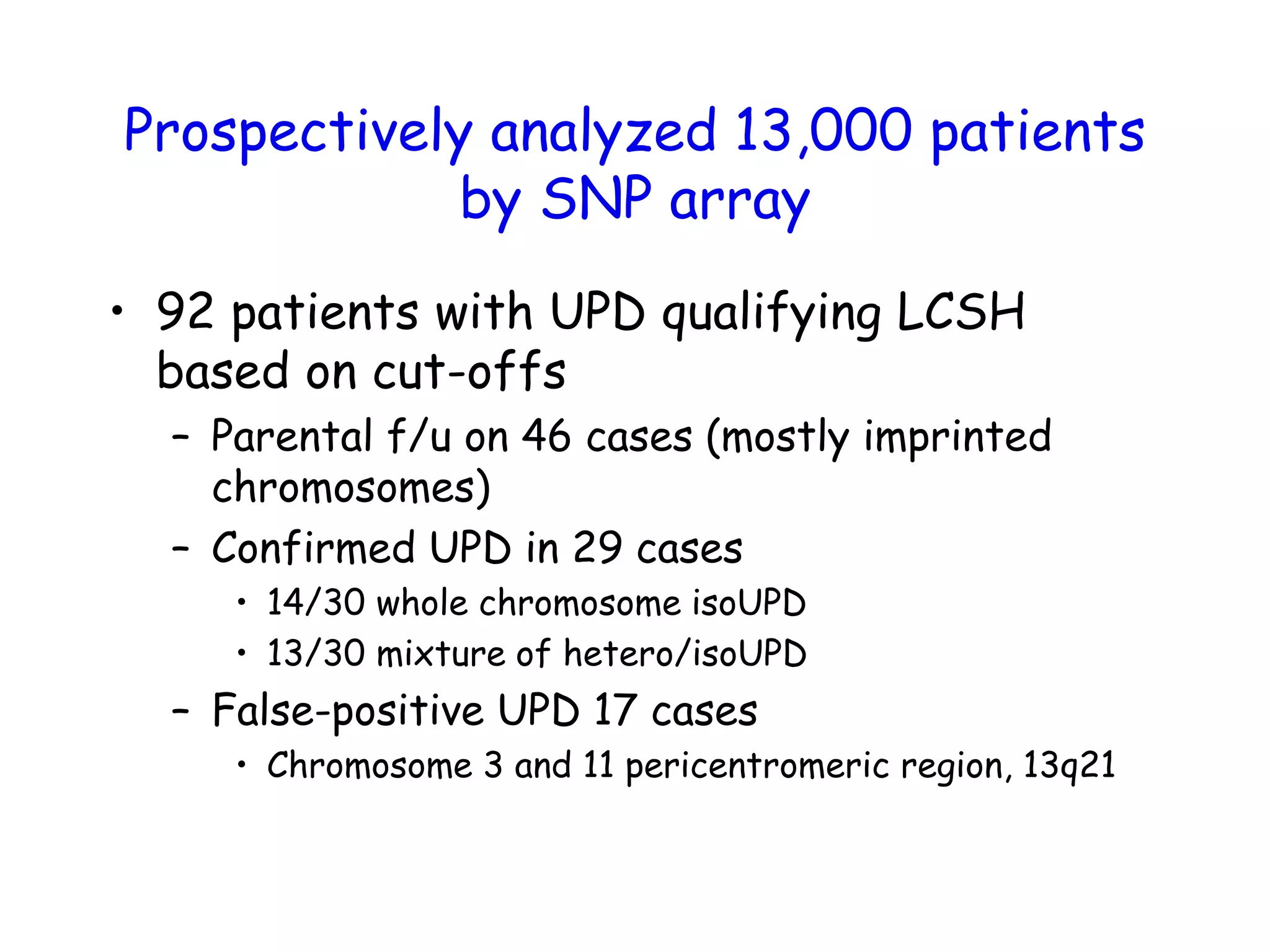
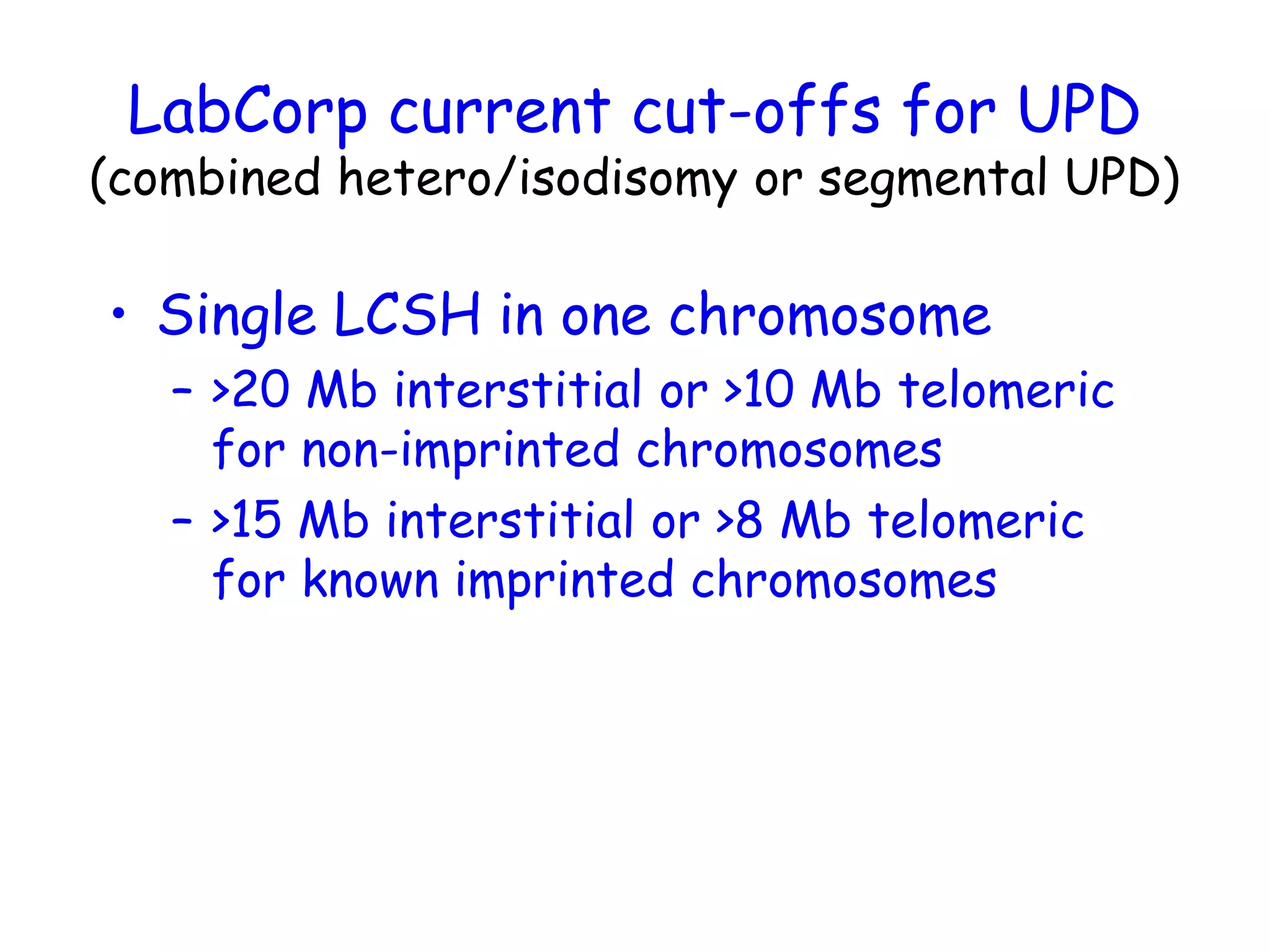
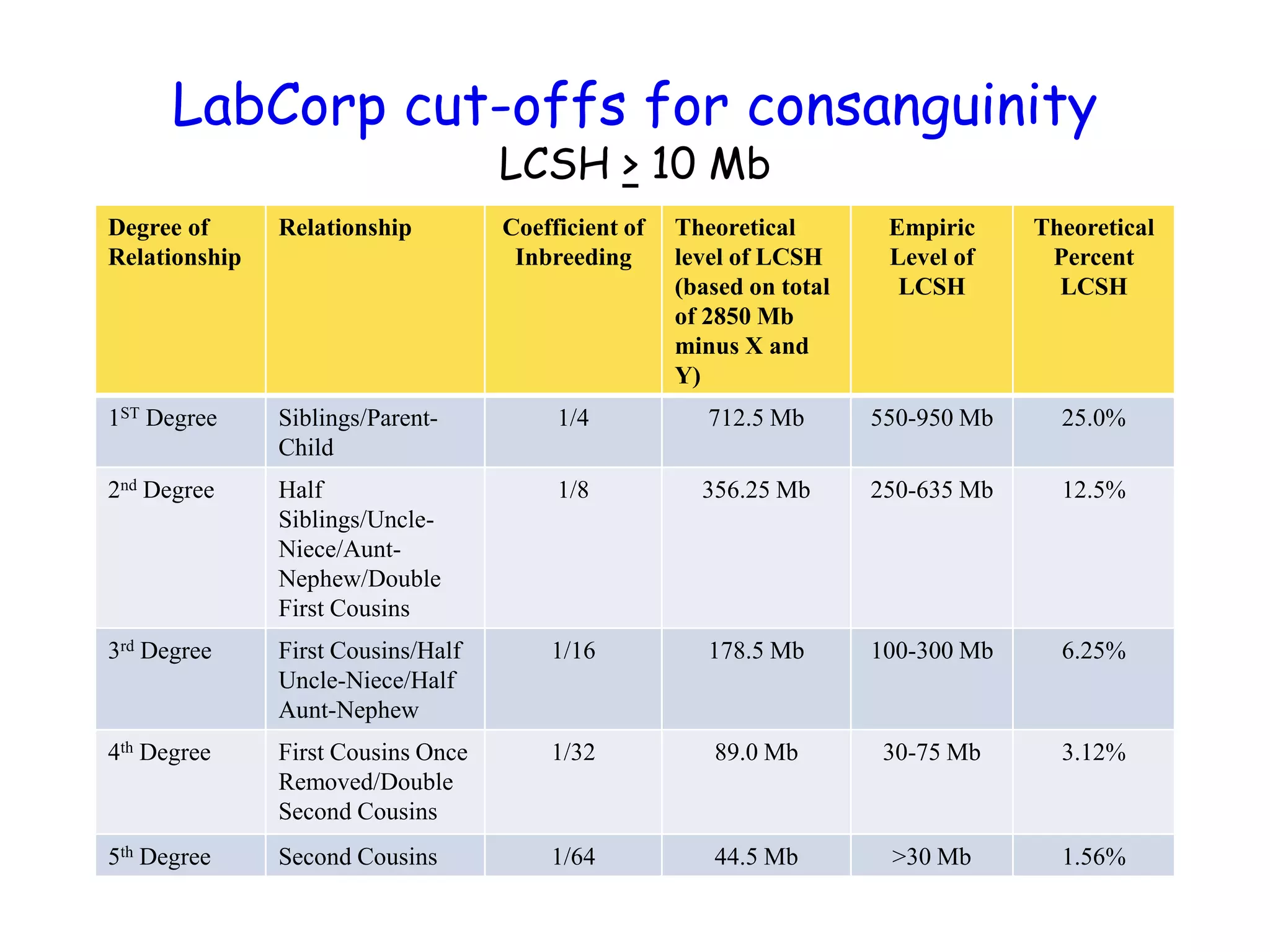
The document summarizes key differences between the Affymetrix CytoScan HD array and previous arrays for detecting copy number variations and single nucleotide polymorphisms. The CytoScan HD array has higher resolution with 1.9 million copy number probes and 750,000 SNP probes compared to older arrays. It requires only patient DNA, has less noise, and provides improved coverage of genes and the genome. The combination of copy number and SNP data enables detection of mosaicism, uniparental disomy, and consanguinity. Studies show the CytoScan HD array can reliably detect copy number changes and parental relatedness at specific size cut-offs.