This document provides an overview of arrays in C programming. It defines an array as a collection of similar data types stored under a single name. The key points covered include:
- Types of arrays include one-dimensional (1D), two-dimensional (2D), and multi-dimensional (MD) arrays.
- The declaration, initialization, and accessing of elements for 1D and 2D arrays is demonstrated through examples.
- Common array operations like addition, subtraction, and multiplication of matrices are shown.
- Advantages of arrays include efficient representation of multiple values of the same type. Disadvantages include static/fixed size and difficulty with insertions/deletions.
- Ar






![• The lower bond of an array is zero 0.
• The upper bond of an array is n-1.
for ex.-int a[9] is an array that stores 9 integers
• Array index start with zero(0).
• Array end with n-1.
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
100 102 104 106 108 110 112 114 116
index
elements
Memory address](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-7-320.jpg)




![A list of items can be given one variable name using
only one subscript and such a variable is called a one-
dimensional Array.
•Syntax
data_type ArrayName[size];
data_type : is a valid data type like int, float,char
Arrayname : is a valid identifier
size : maximum number of elements that can
be stored in array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-12-320.jpg)
![1. Declaration of on Array
To declare an array to syntax is-
Data_ type variablename [size];
o The type of data which you
want to store like – int , float
, char.
o Means the name
of an Array.
o The number of Array
type variable.
Ex.- int a [3];
• Type of array variable is “integer”.
• Its variable name is a.
• 3 is the size of the array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-13-320.jpg)
![2. Initialization
• An elements of an array must be initialized, otherwise they
may contain “garbage” value.
• An array can be initialized at either of the following stages
o At compile time
o At run time
• At the time of declaration and
initialization at the same time.
• For ex.- int a[5]={1,2,3,4,5}
An array can be explicitly in
initialization at run time.
• To initialize multiple array variable for loop is used.
for ex.-
for (i=0;i<5;i++)
{
scanf (“%d”,&a[i]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-14-320.jpg)
![3.Assessing
• To print the element of an array is known as
assessing.
• To assessing the element of an array for loop is
used frequently.
for ex.-
for (i=0; i<5 ;i++)
{
printf (“%d”,a[i]);
} OUTPUT:
0
1
2
3
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-15-320.jpg)
![Examples:-
1) Enter a one-d array
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a[10],i;
printf(“enter the array=“);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i]);
}
printf(“the entered array is=“);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
{
printf(“%d”,a[i]);
}
return(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-16-320.jpg)

![• C allows us to define such tables of items by using
two-dimensional arrays.
•The two dimensional array are declared as follows-
type array_name[row_size][column_size];
For ex.- int a [3][2];
Data type
Array name Row=3
Column=2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-18-320.jpg)
![1. Declaration 2D ARRAY
• To declare an array to syntax is.
• The syntax of 2D array is
datatype arrayname[row] [column];
2.Initializing 2D ARRAY
• Like 1D array ,2D array initialized.
• Tow for loop is used .
ex.-
for (i=0 ;i<3; i++)
{
for (j=0;j<3;j++)
{
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-19-320.jpg)
![3.Assessing 2D ARRAY
• For loop is used.
Ex.-
for (i=0; i<3; i++)
{
for(j=0; j<3;j++)
{
printf(“t%d”,a[i][j]);
}
print(“n”);
}
• To print the element of an array
is known as assessing.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-20-320.jpg)
![/* addition of two matrix/*
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j;
int a[3][3],b[3][3],c[3][3];
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“enter the matrix a=”);
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“enter the matrix b=”);
scanf(“%d”,&b[i][j]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-21-320.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
c[i][j]=a[i][j]+b[i][j];
}
}
Printf(“/n addition of two matrix=“);
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(J=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“%d”,c[i][j]);
}
printf(“/n”);
}
}
return(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-22-320.jpg)

![/*subtraction of two matrix/*
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j;
int a[3][3],b[3][3],c[3][3];
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“enter the matrix a=”);
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“enter the matrix b=”);
scanf(“%d”,&b[i][j]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-24-320.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
c[i][j]=a[i][j]-b[i][j];
}
}
Printf(“/n substract of two matrix=”);
{
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(J=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“%d”,c[i][j]);
}
printf(“/n”);
}
}
return(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-25-320.jpg)

![/*multiplication of two matrix/*
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
int a[3][3],b[3][3],c[3][3];
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“enter the matrix a=”);
scanf(“%d”,&a[i][j]);
}
}
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“enter the matrix b=”);
scanf(“%d”,&b[i][j]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-27-320.jpg)
![for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
c[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<3;k++)
{
c[i][j]=c[i][j]+a[i][k]*b[k][j];
}
}
}
printf(“n enter the matix a is =”);
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“t%d”,c[i][j]);
}
printf(“n”);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-28-320.jpg)
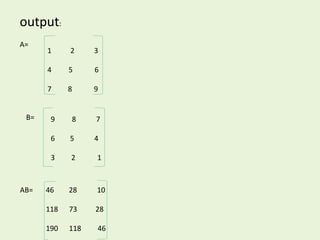
![printf(“n enter the matrix b is =”);
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“t%d”,b[i][j]);
}
printf(“n”);
}
printf(“n the multiplication is =”);
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
{
printf(“t%d”,c[i][j]);
}
printf(“n”);
}
return(0);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-29-320.jpg)

![• C allows arrays of three or more dimensions. The exact limit
is determined by the compiler
•Syntax-
Datatype aray_name[s1][s2][s3]………….[Sm];
• For ex-
int MyArray[2][3][4];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/array2hina-141216125201-conversion-gate02/85/Array-2-hina-32-320.jpg)










