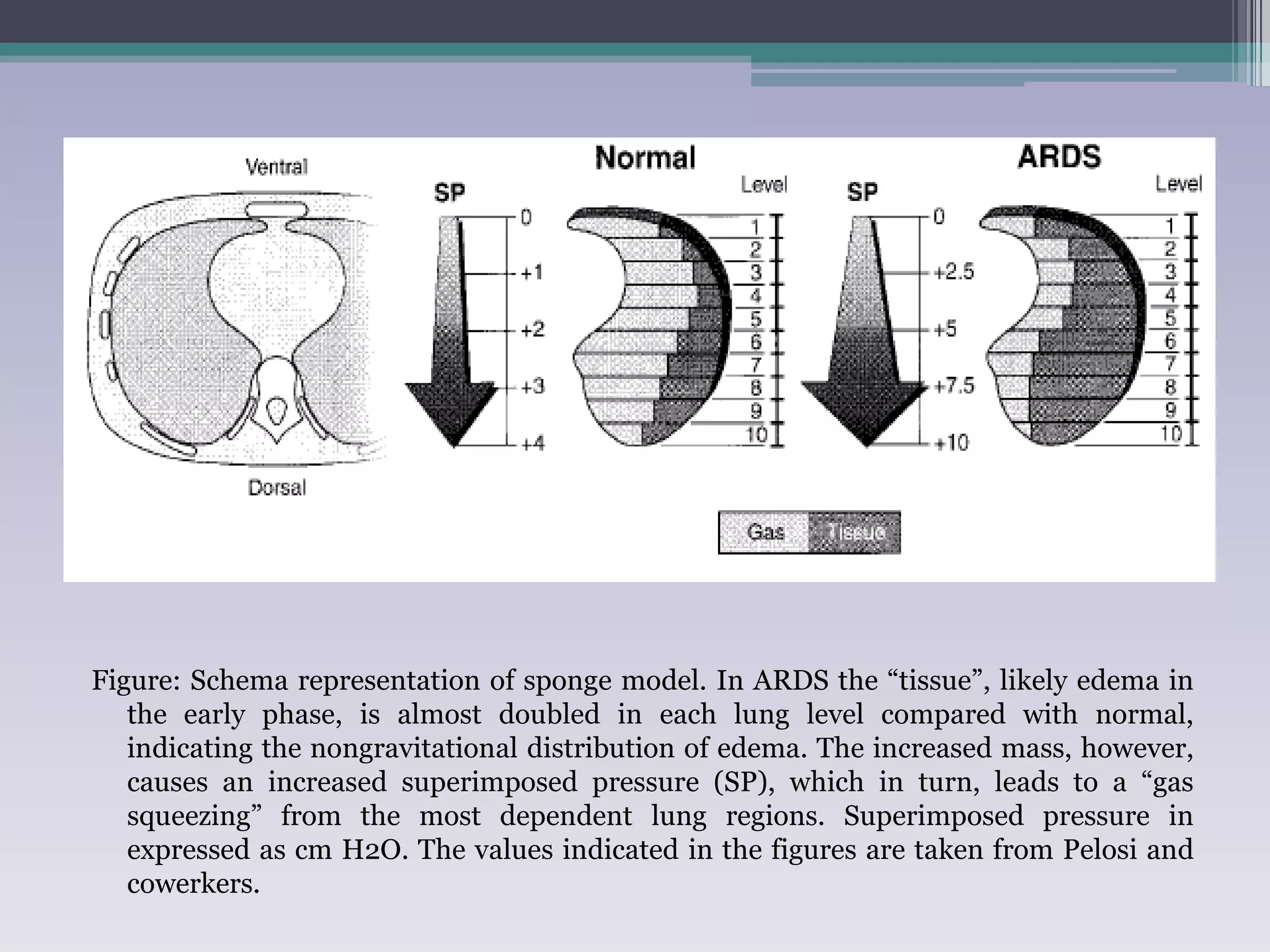
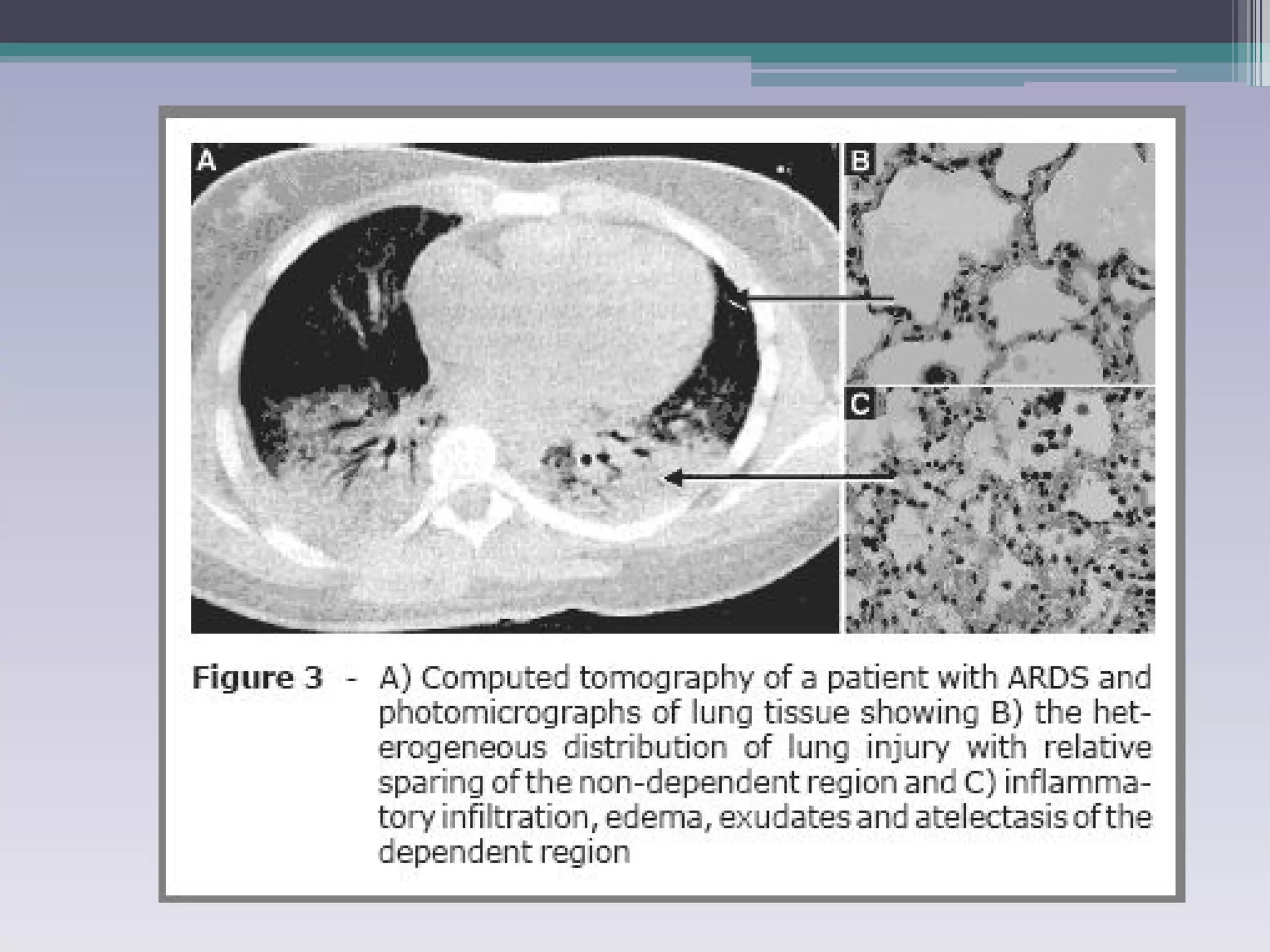
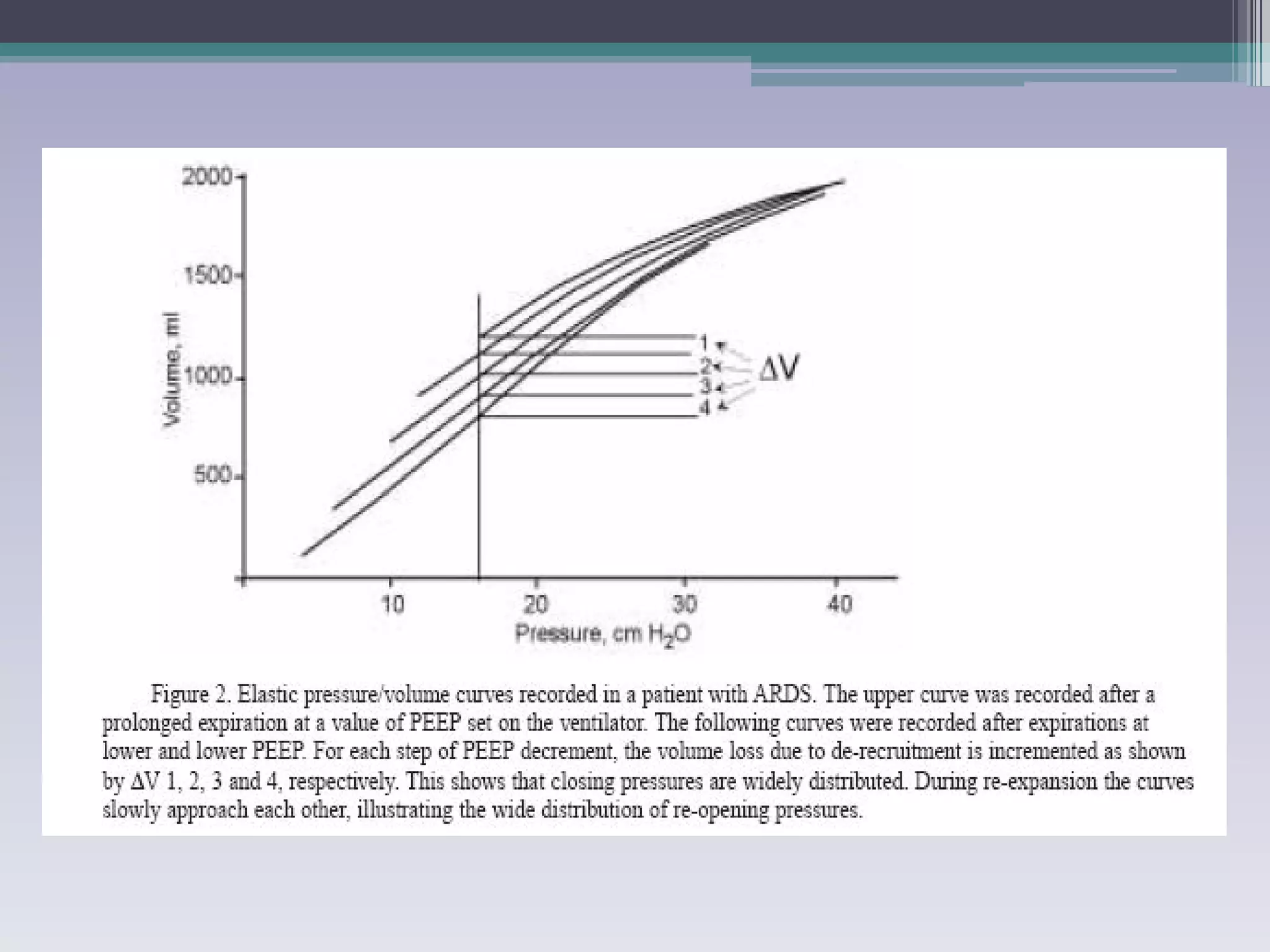
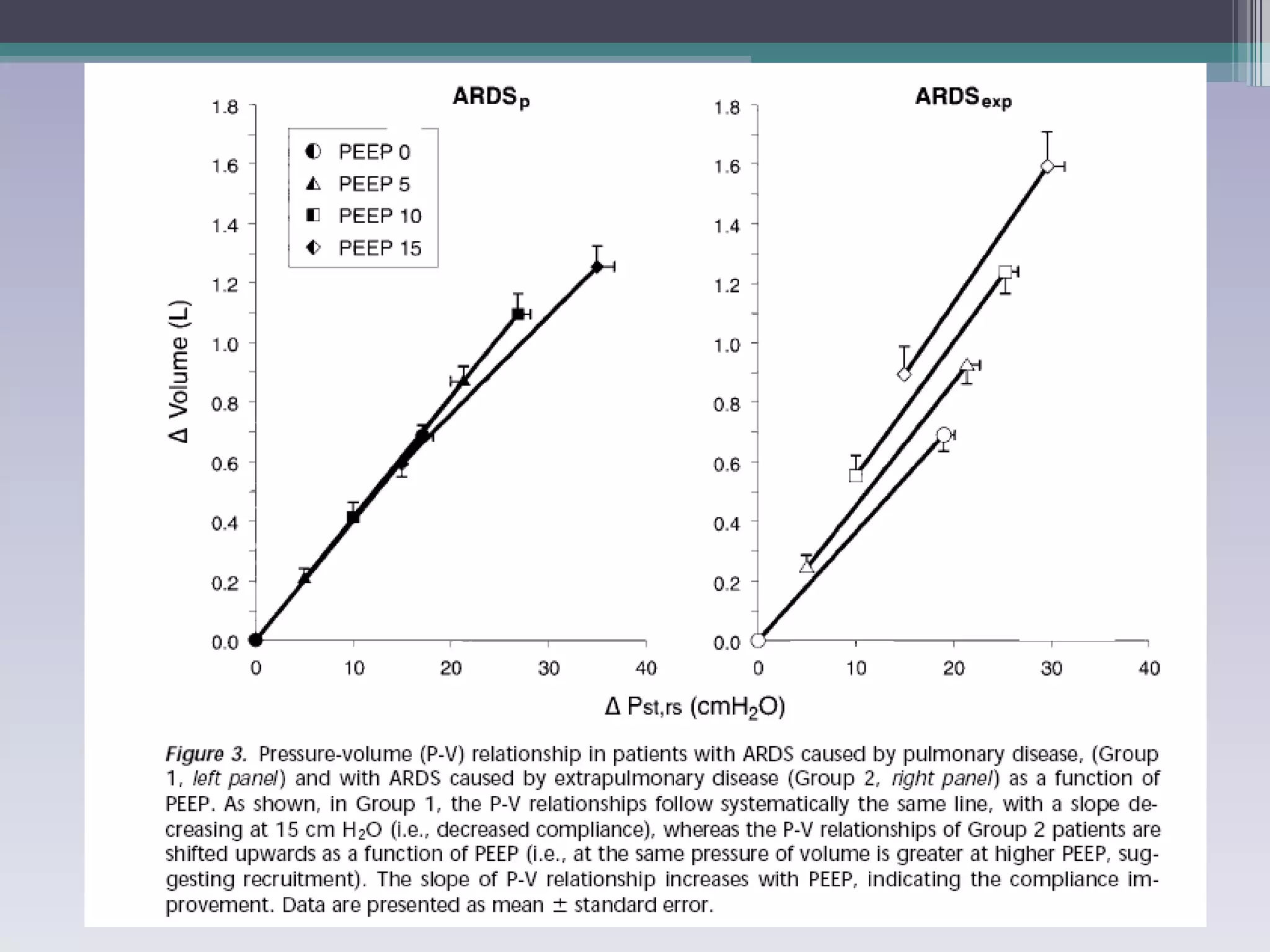
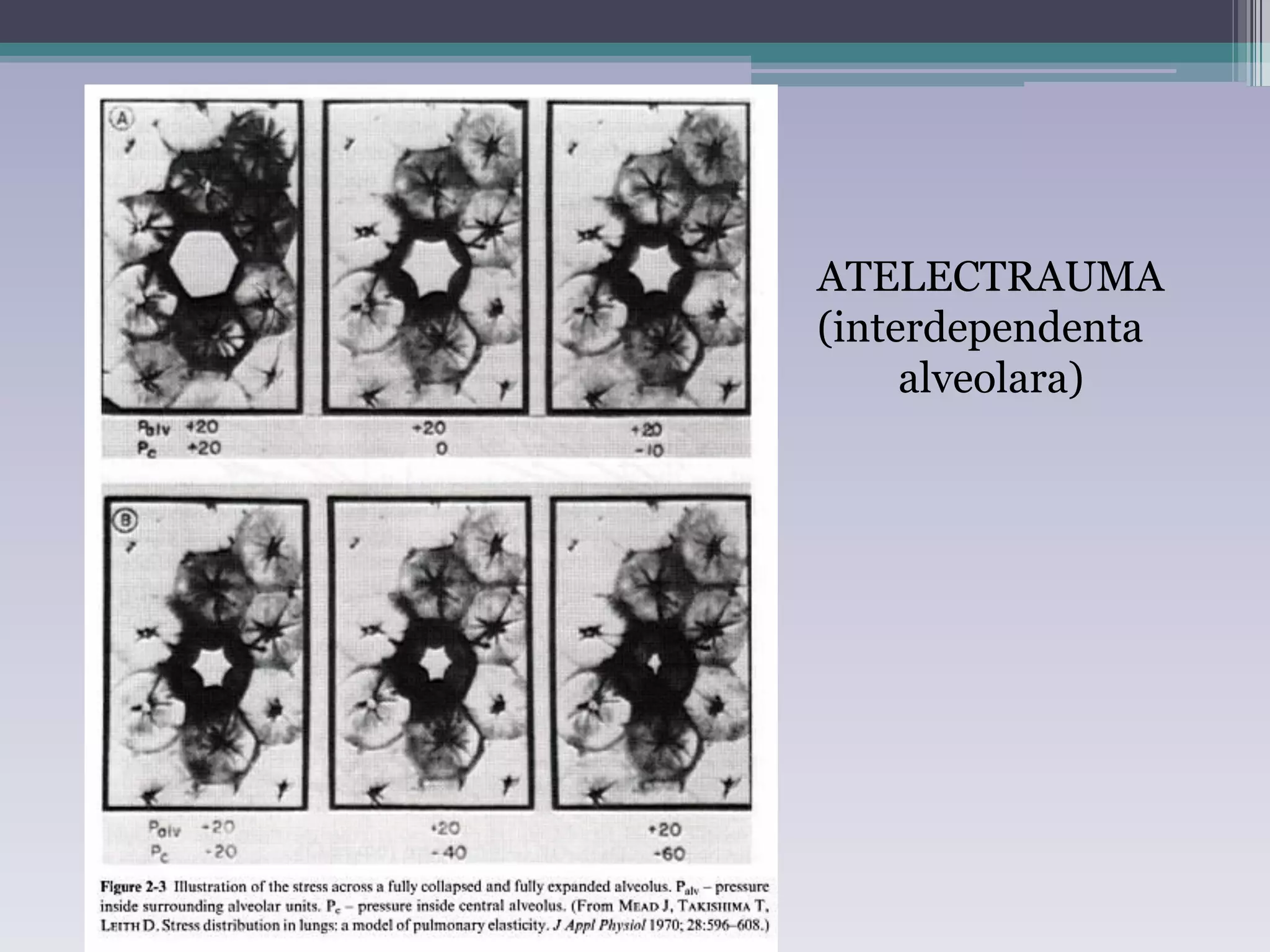
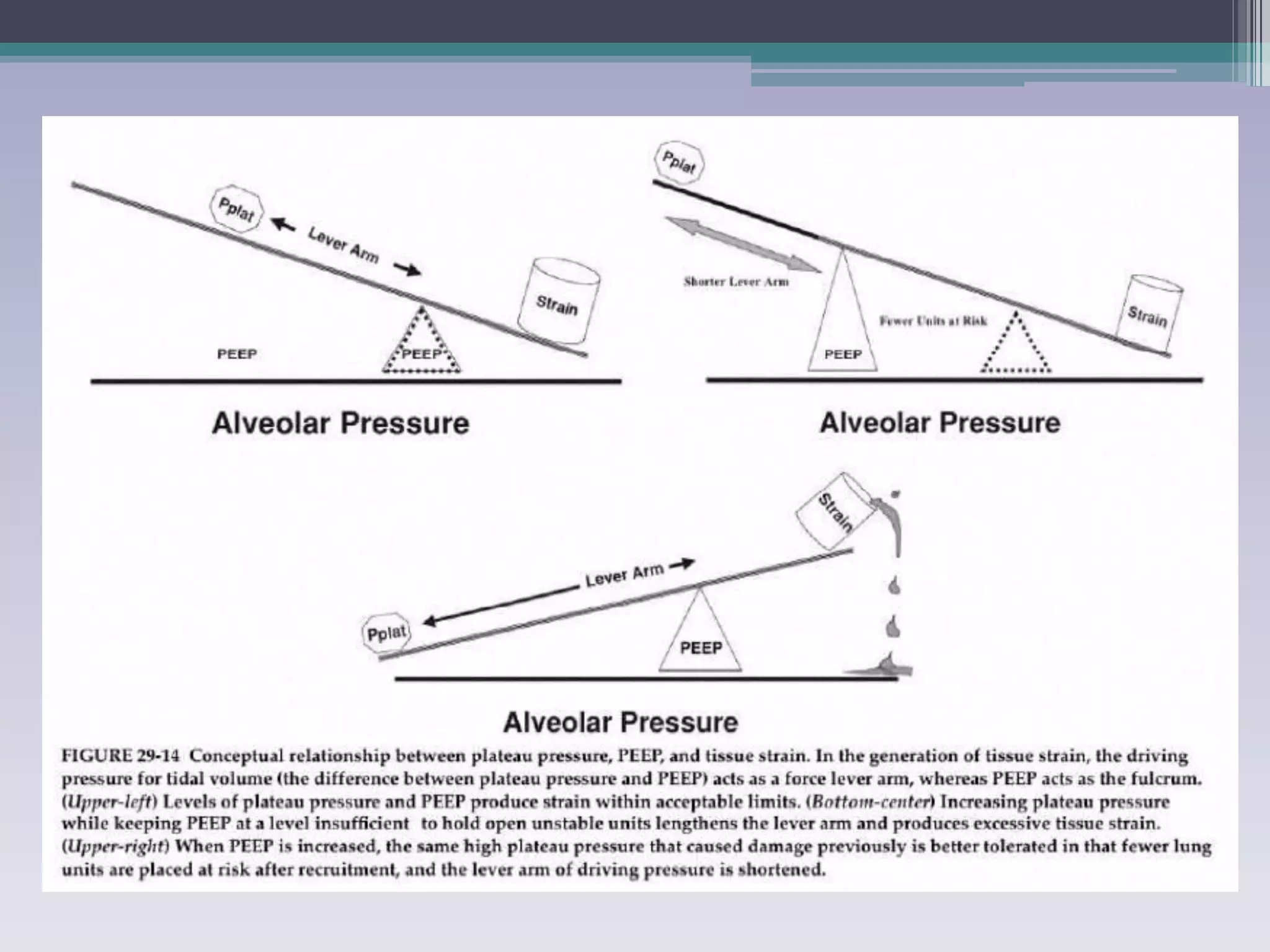
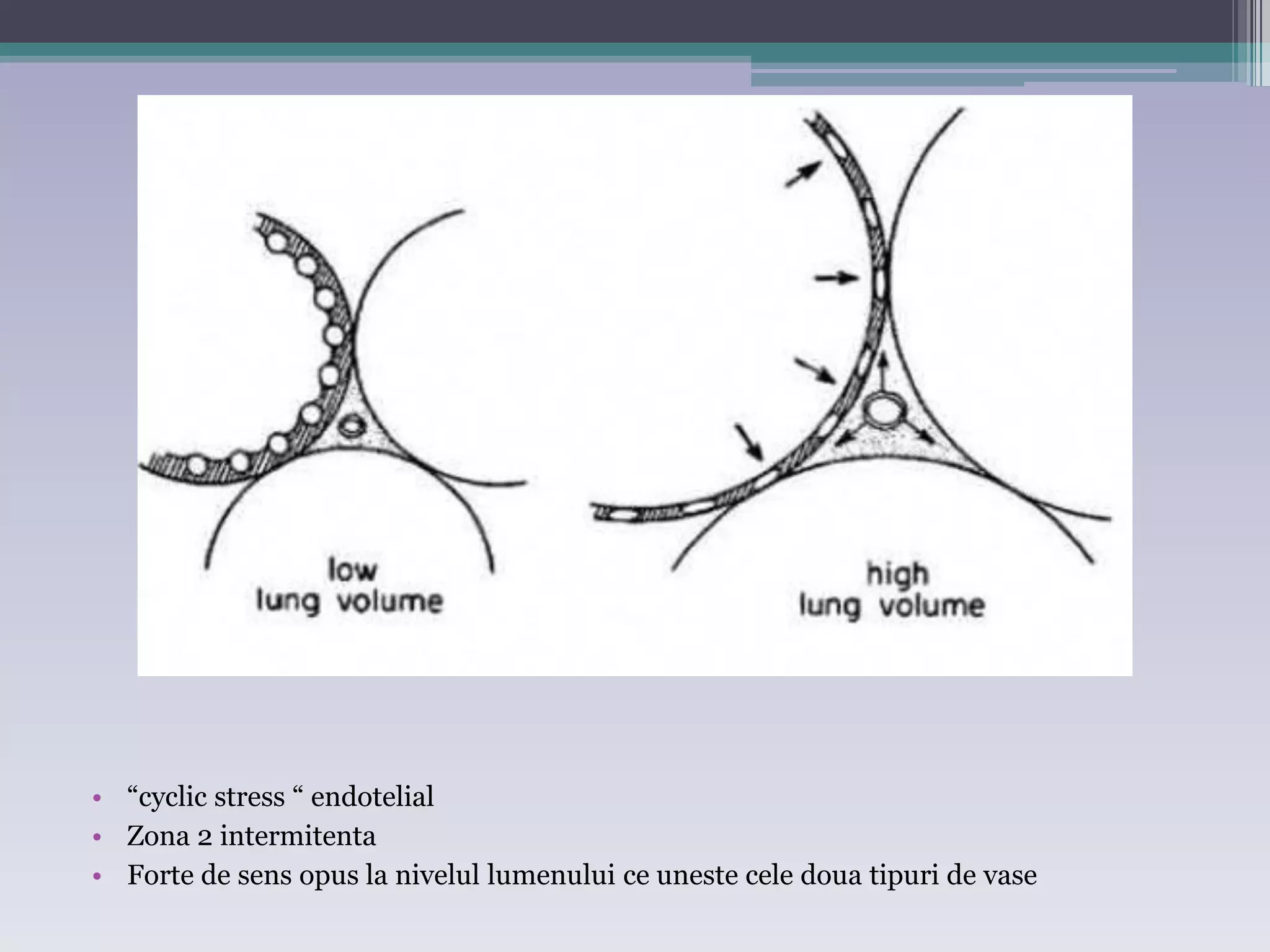
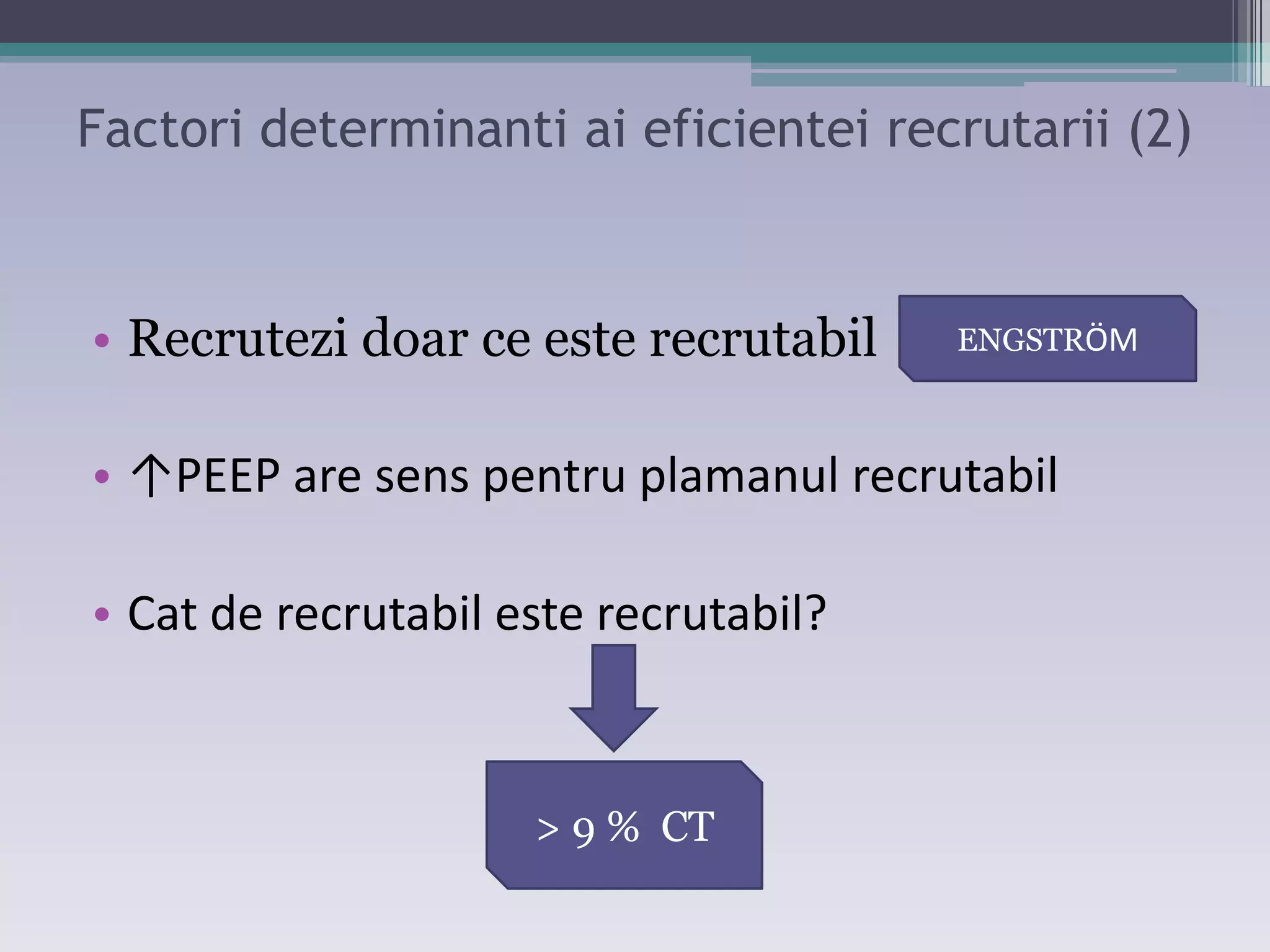
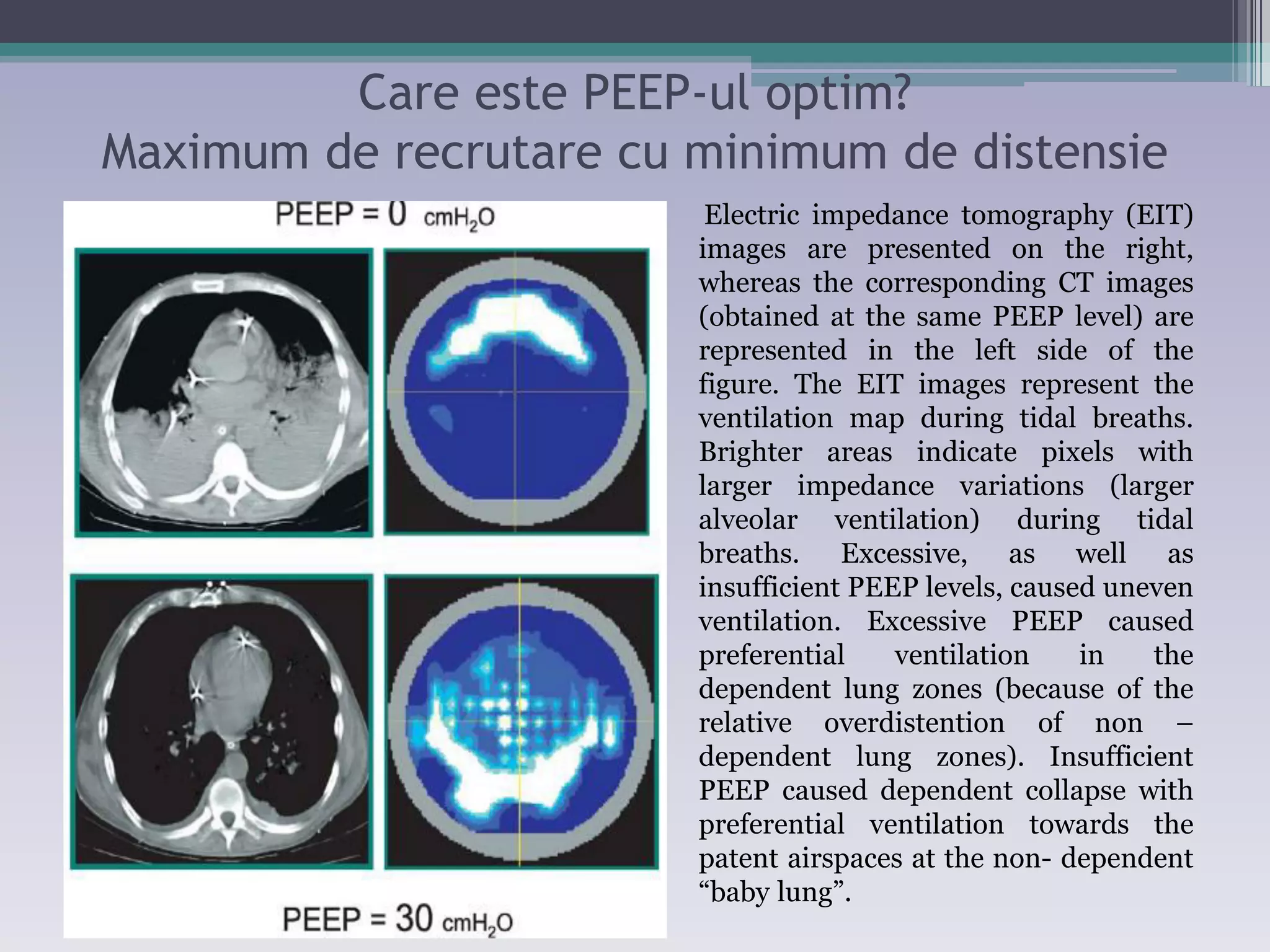
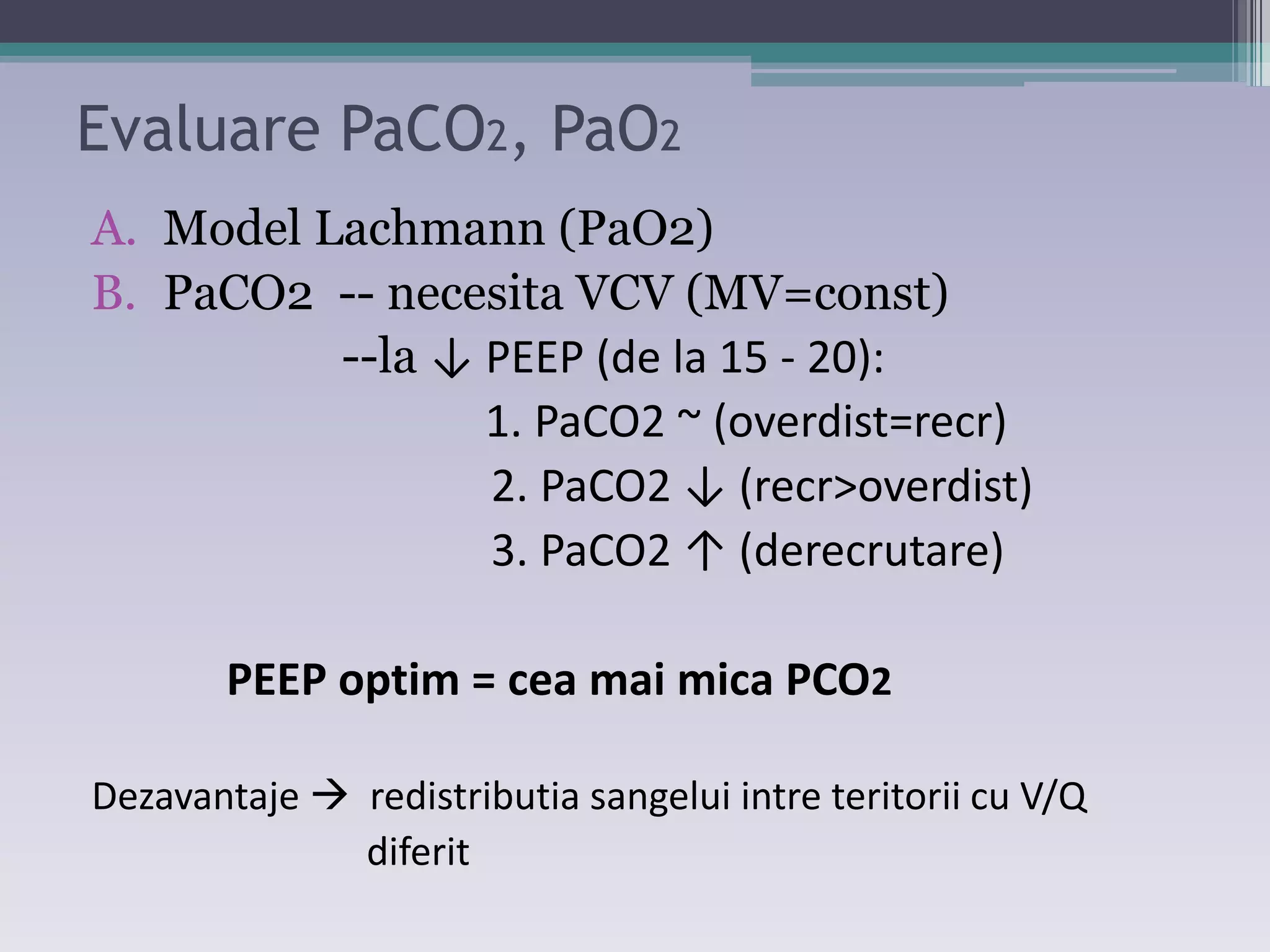
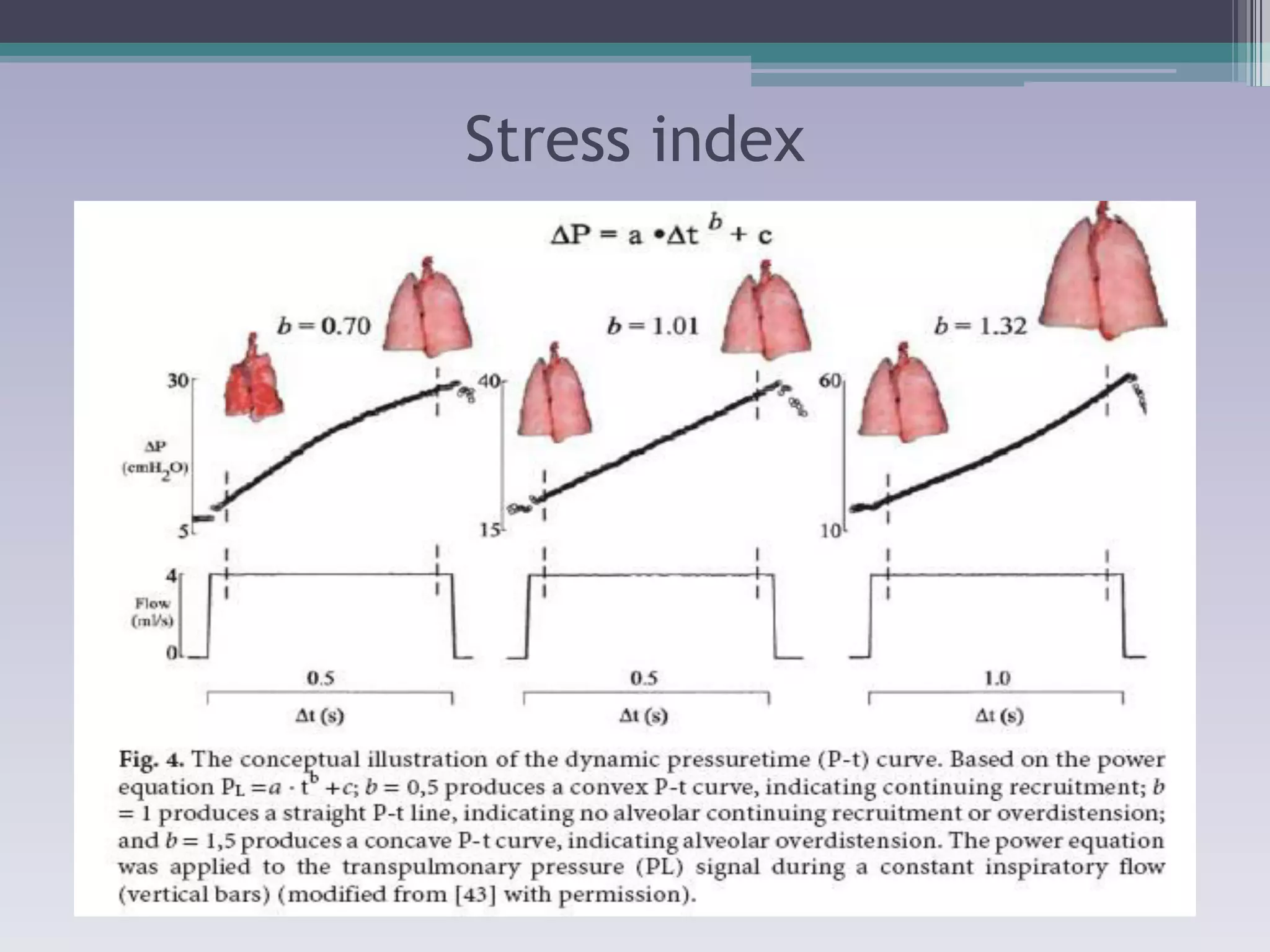
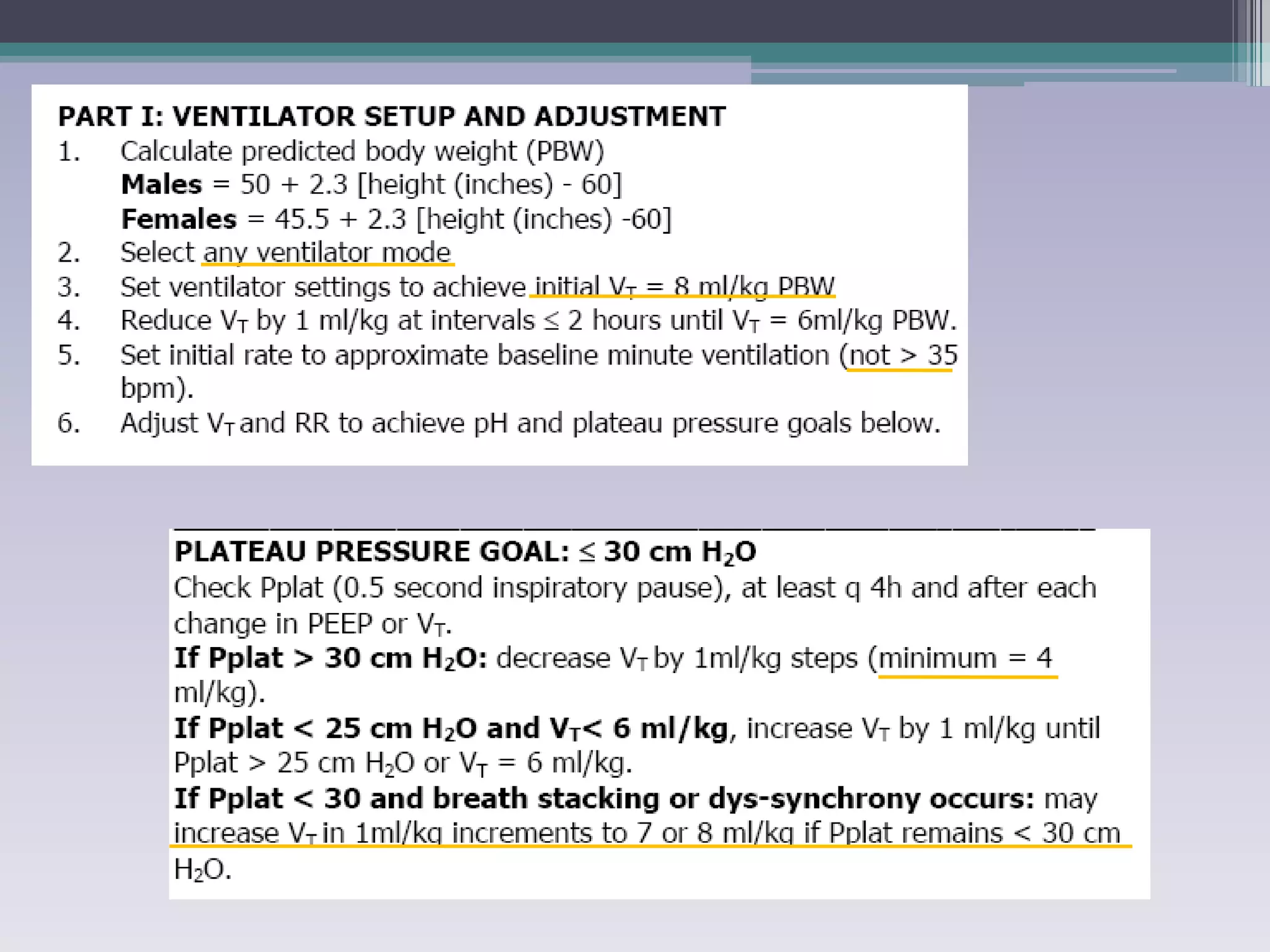
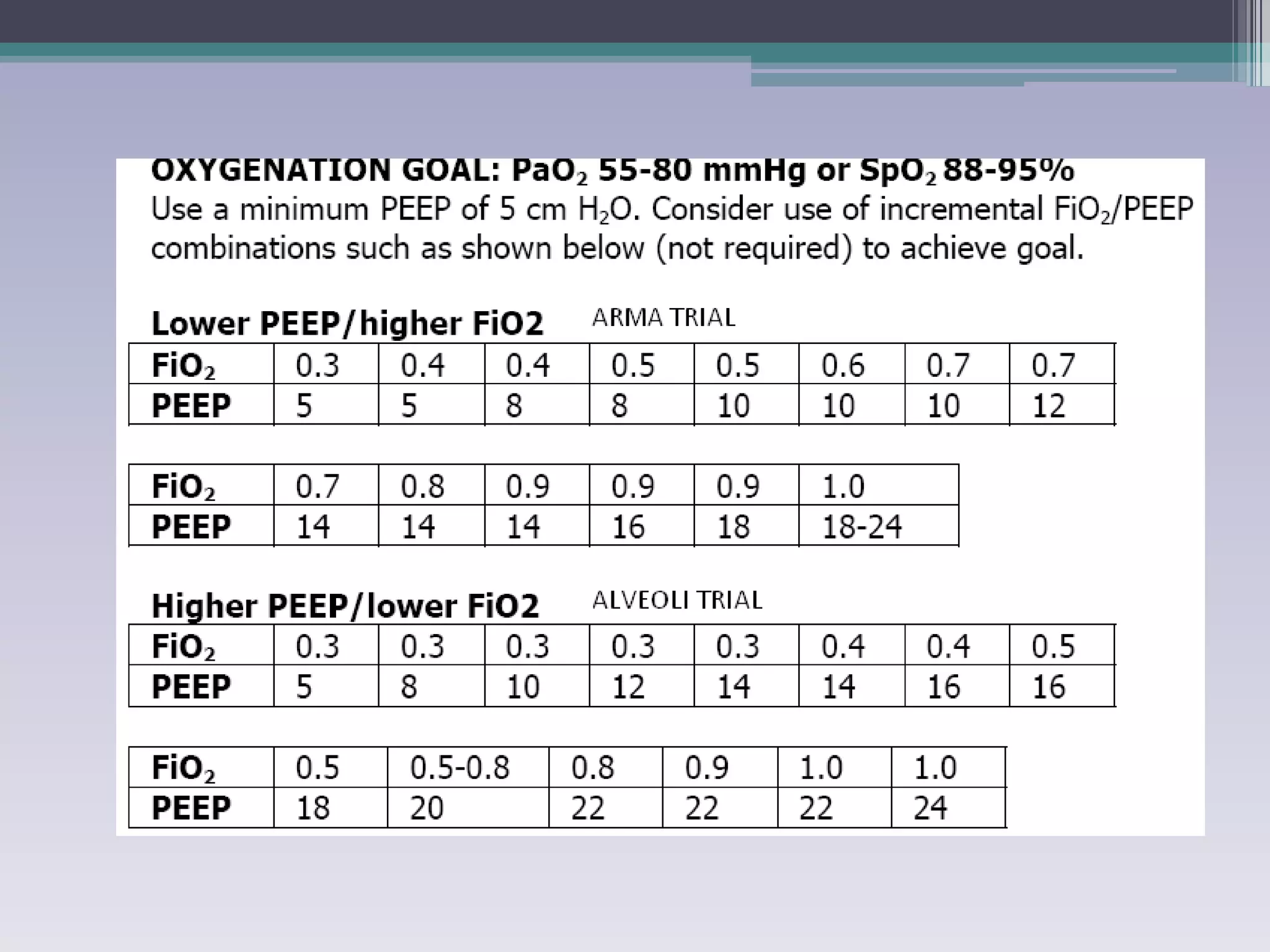
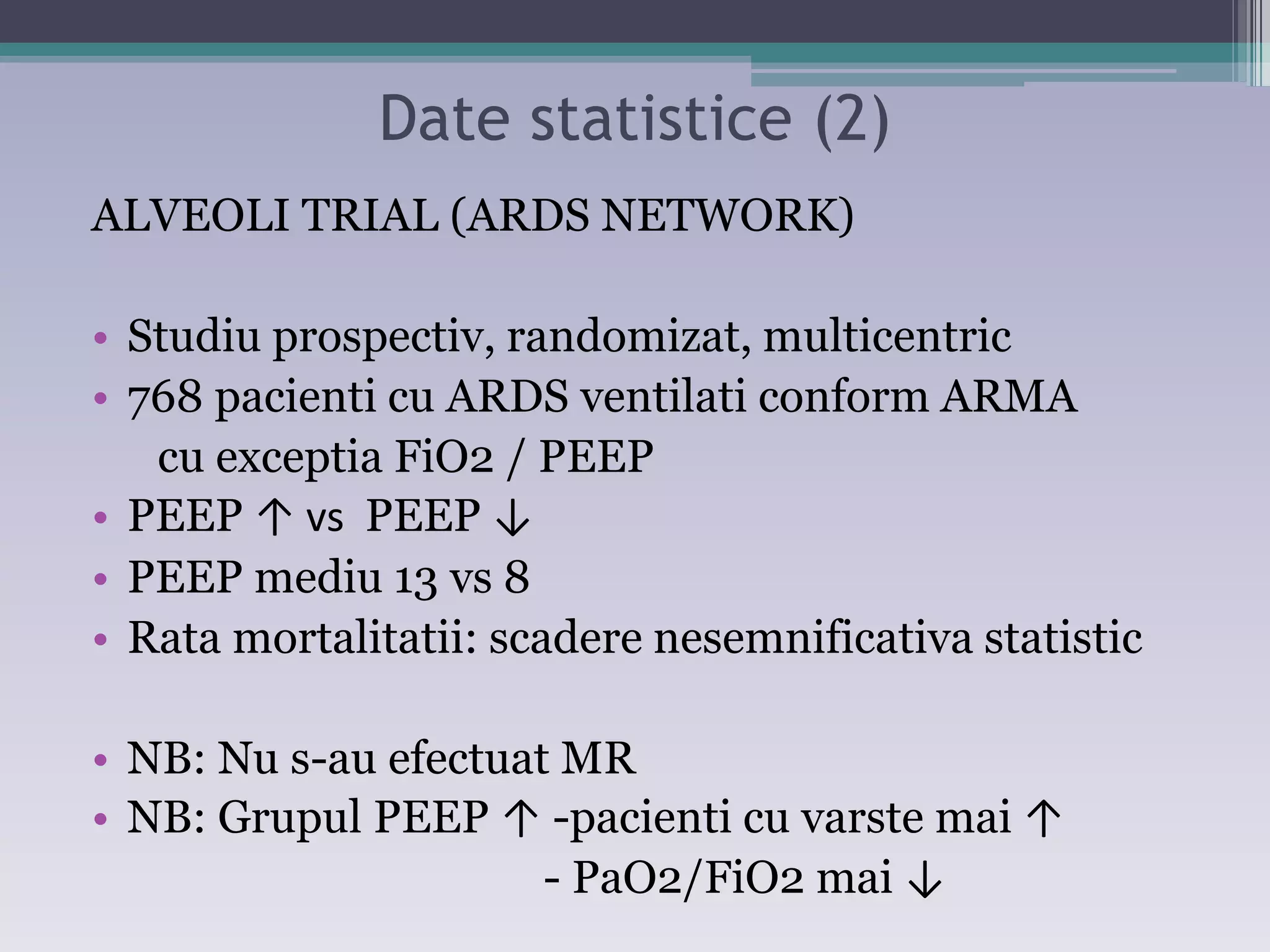
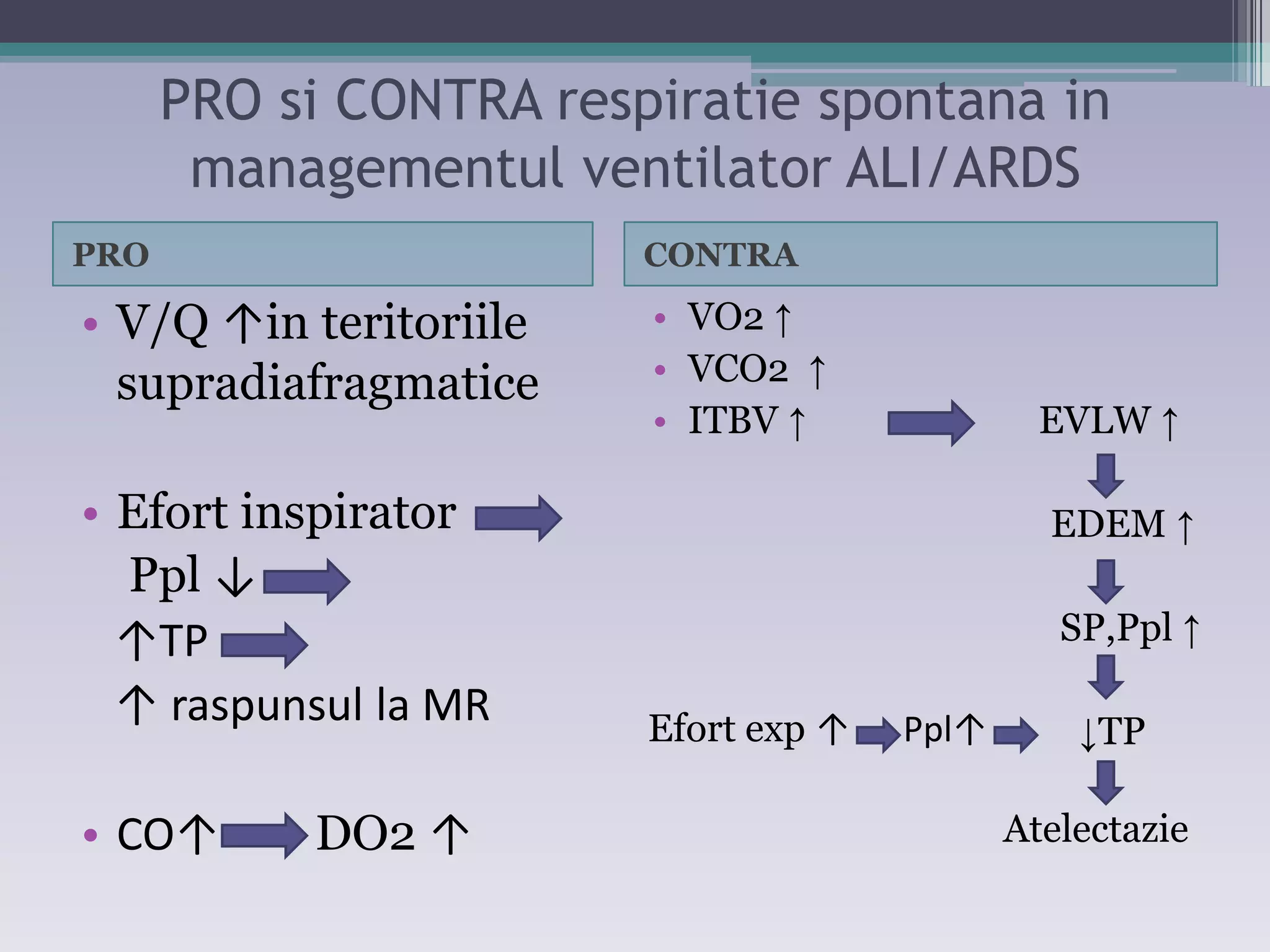
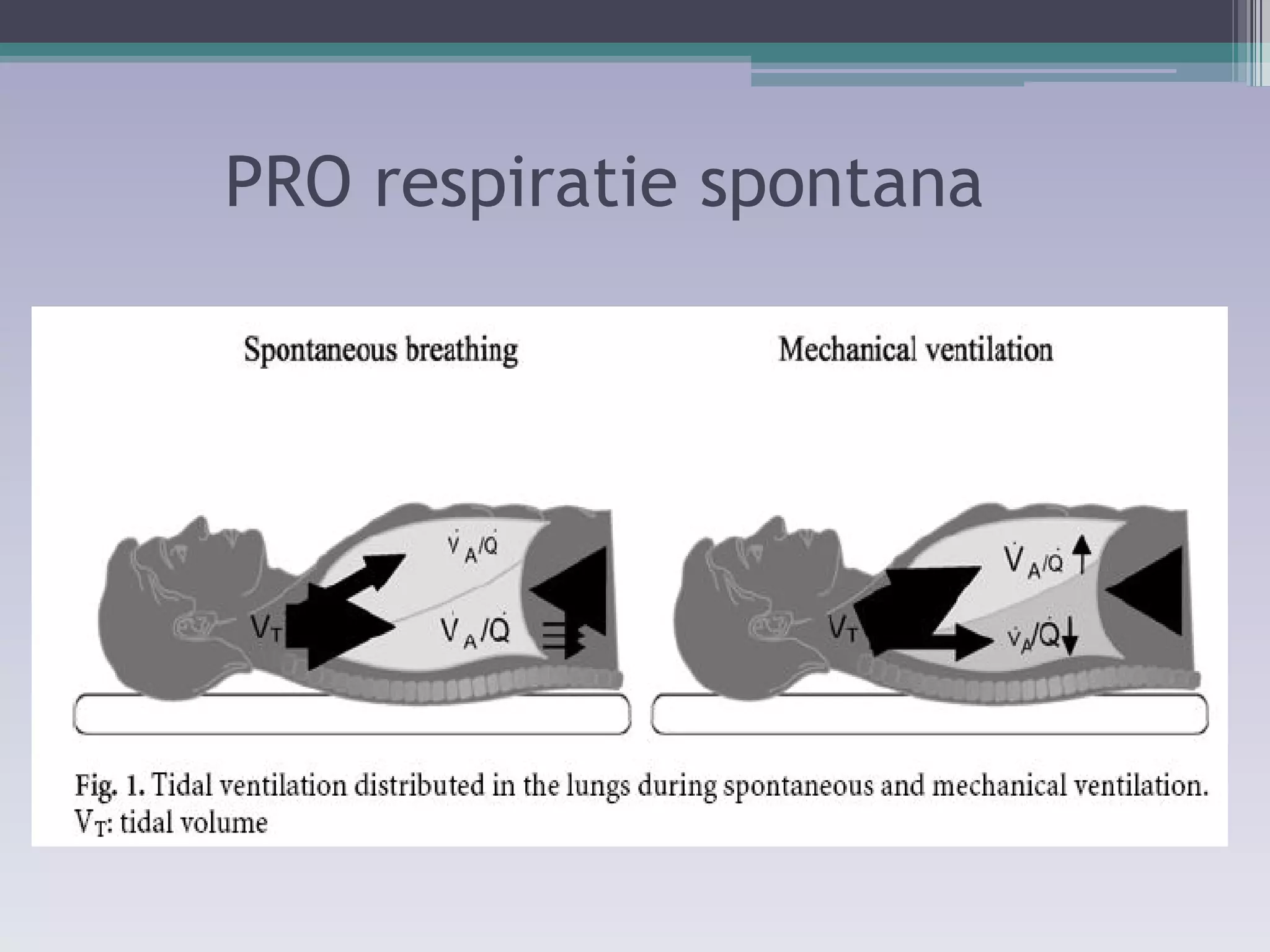
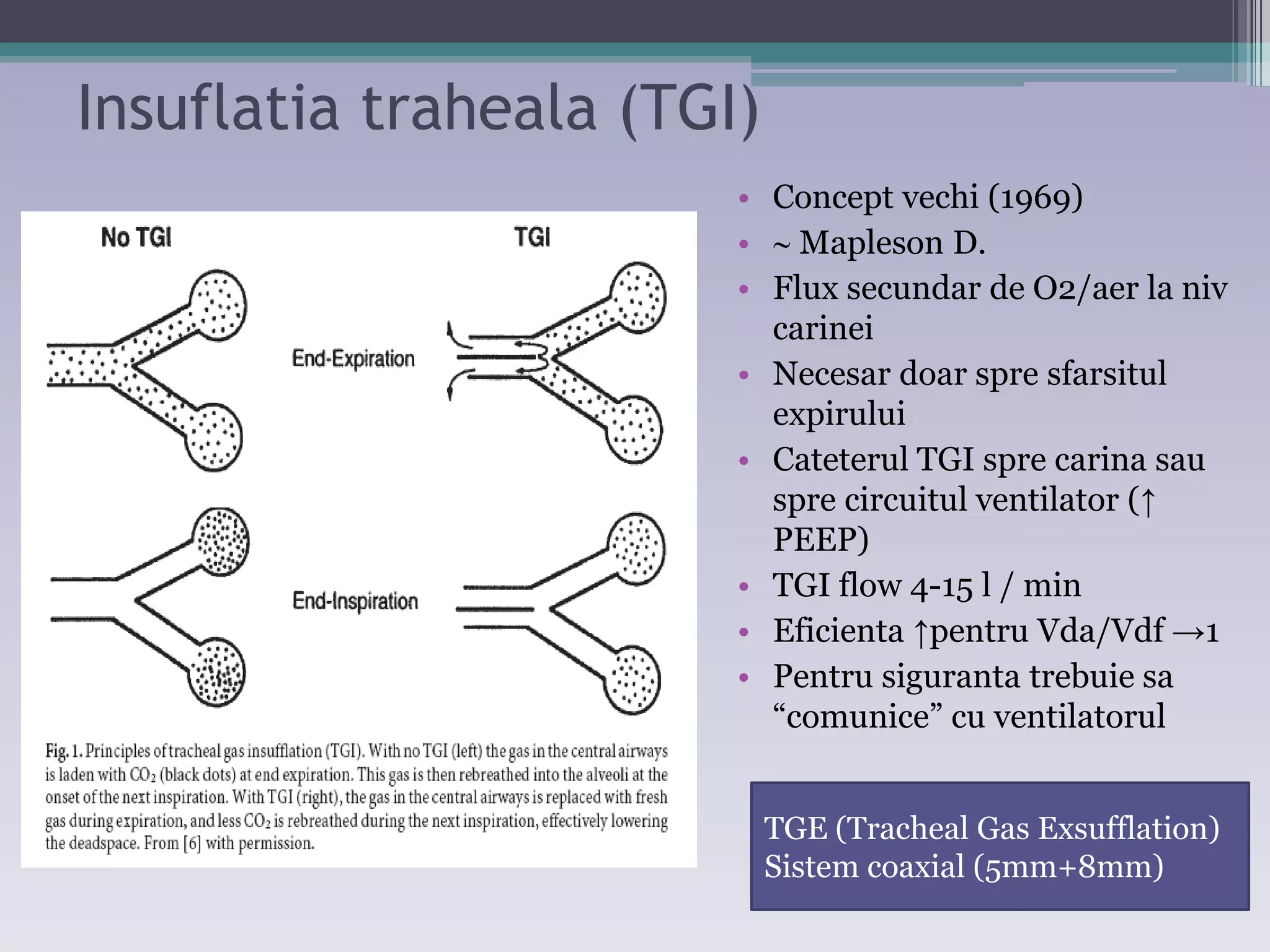
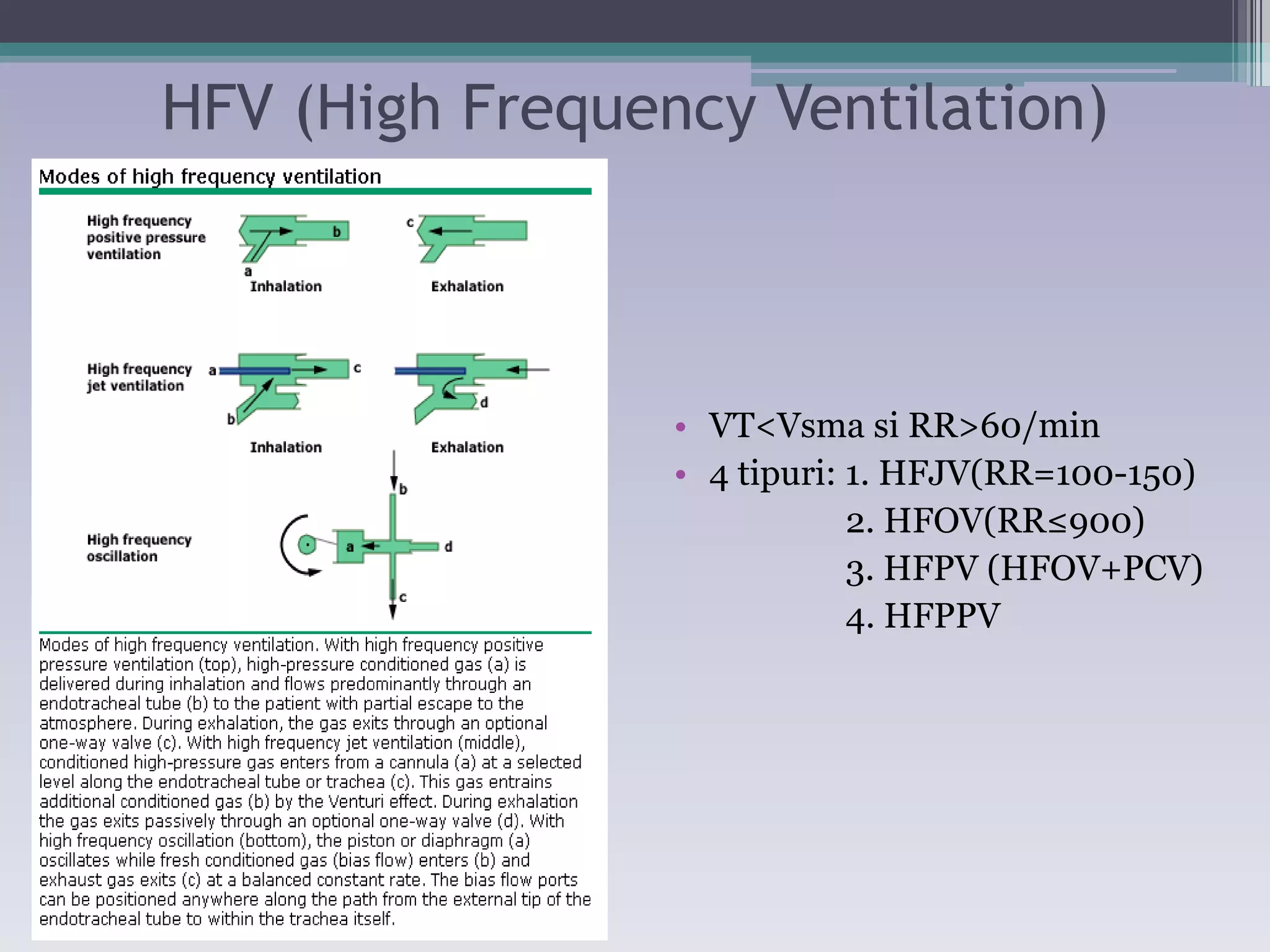
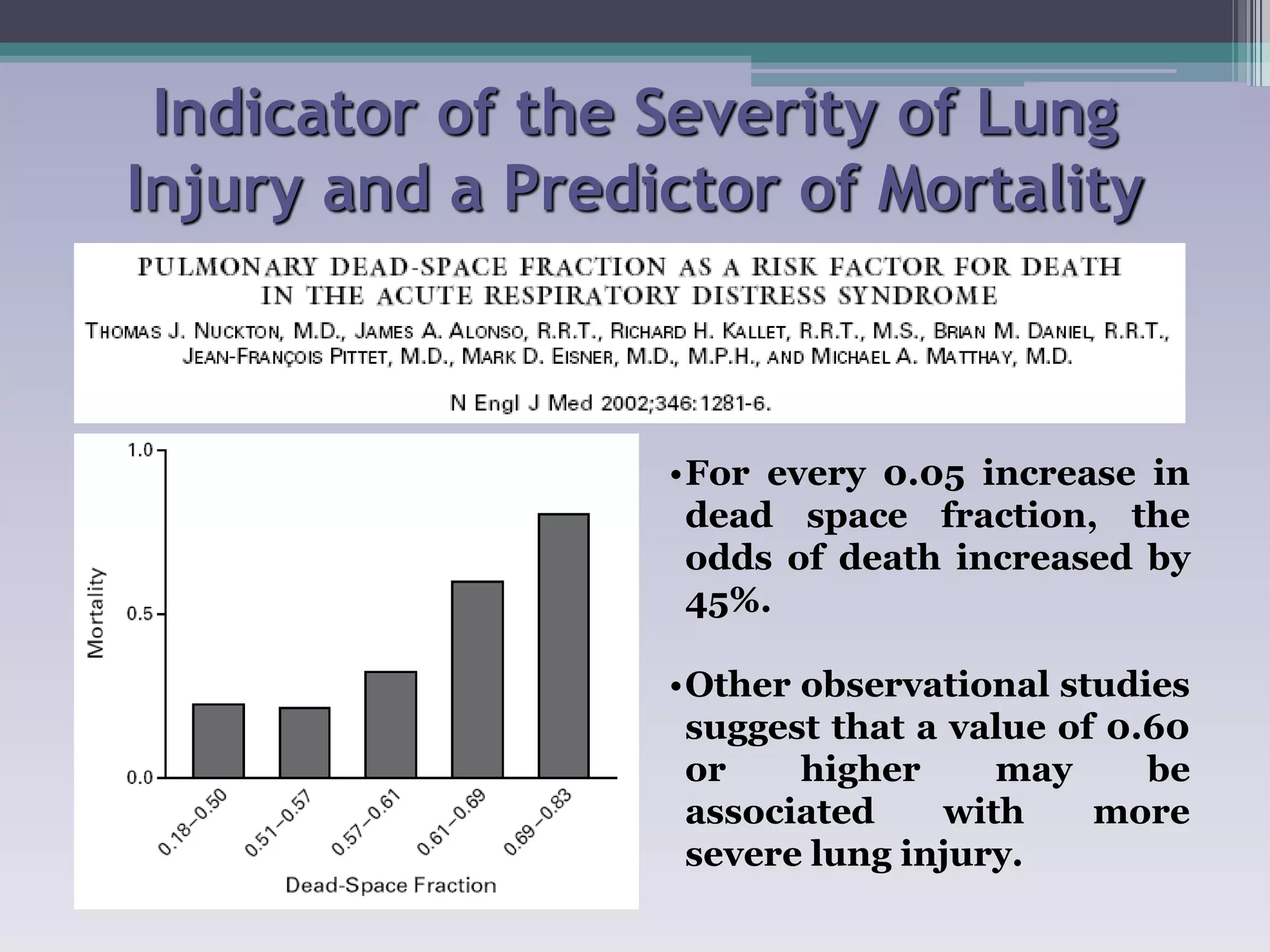
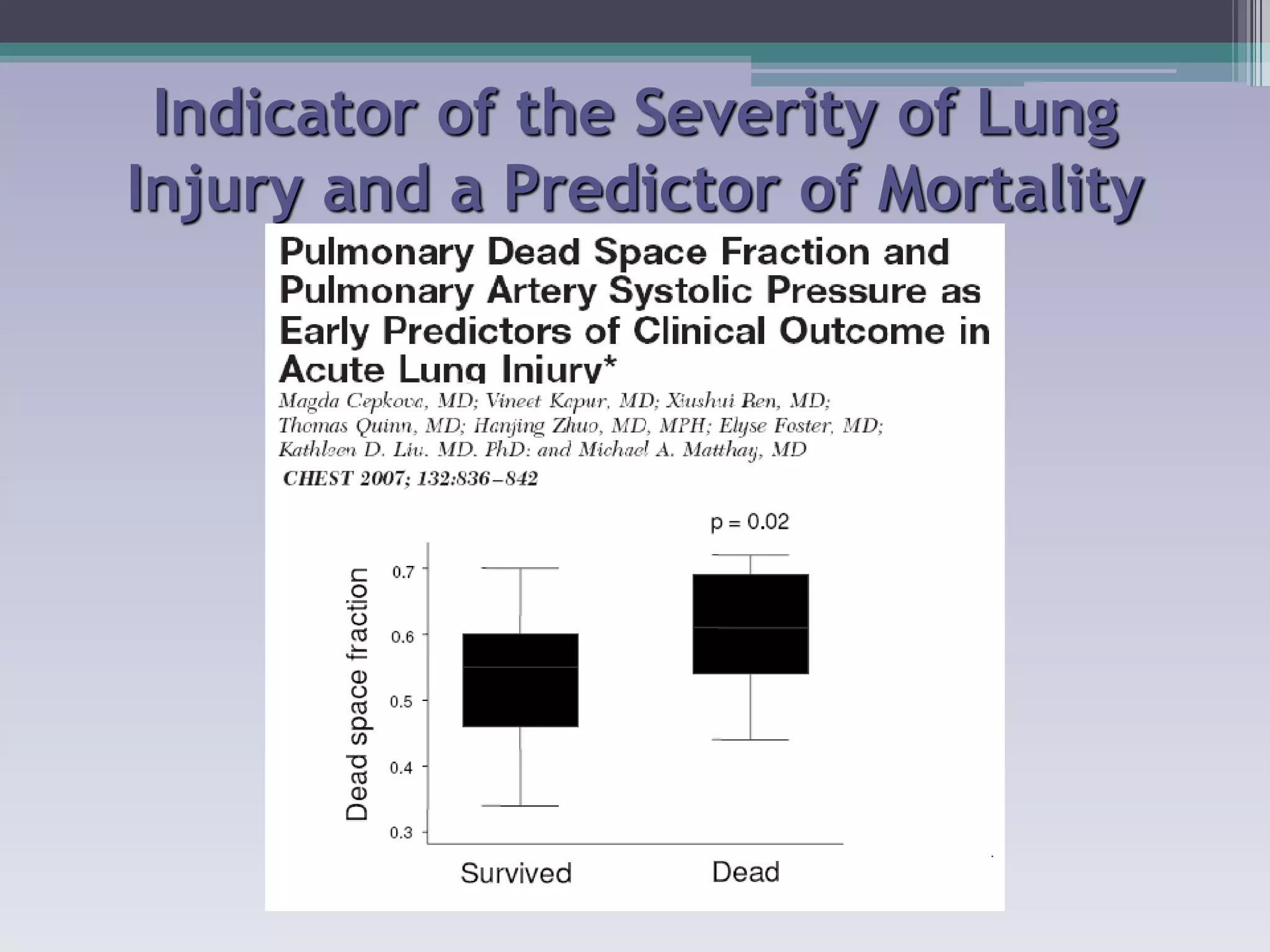
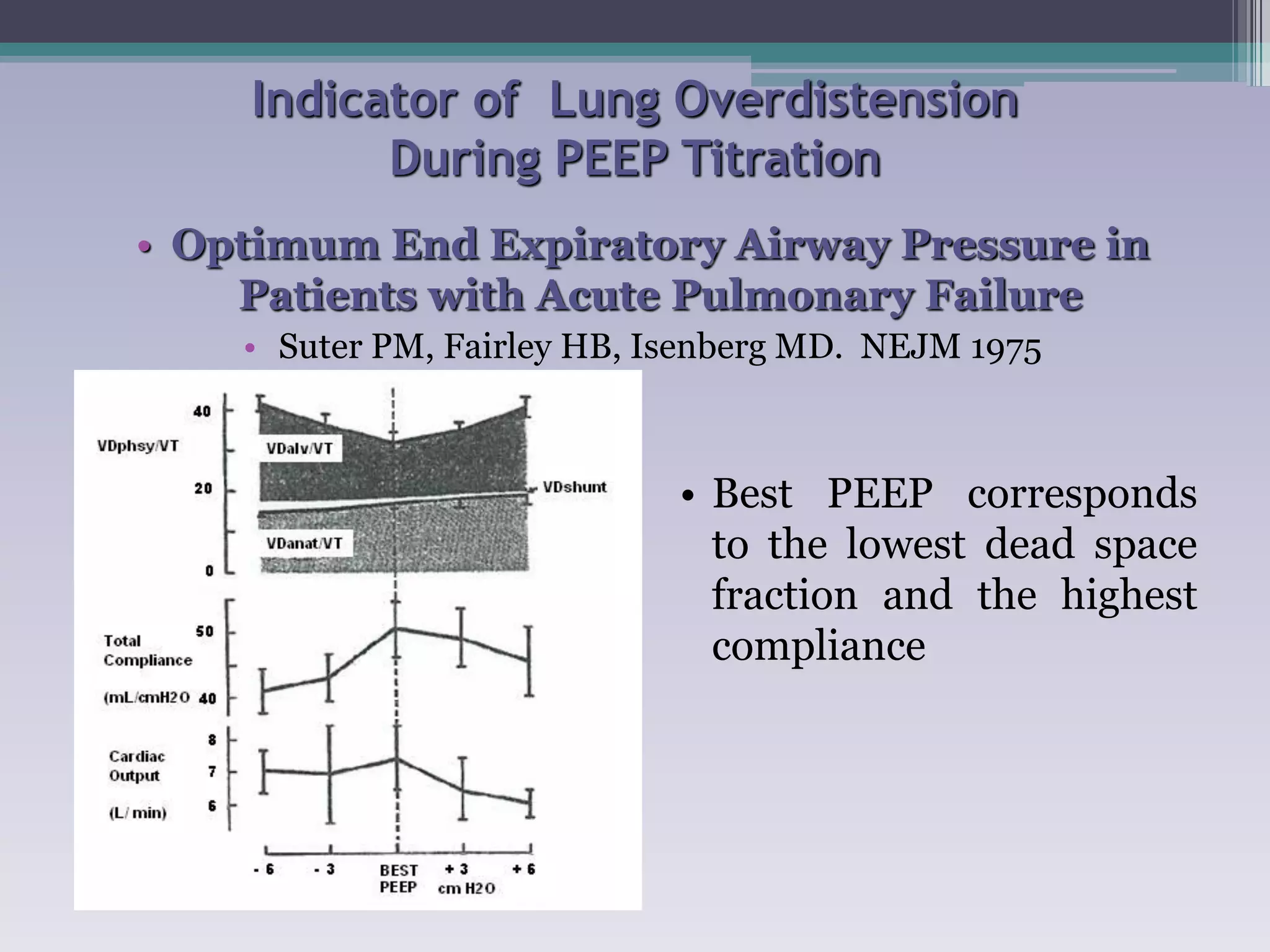
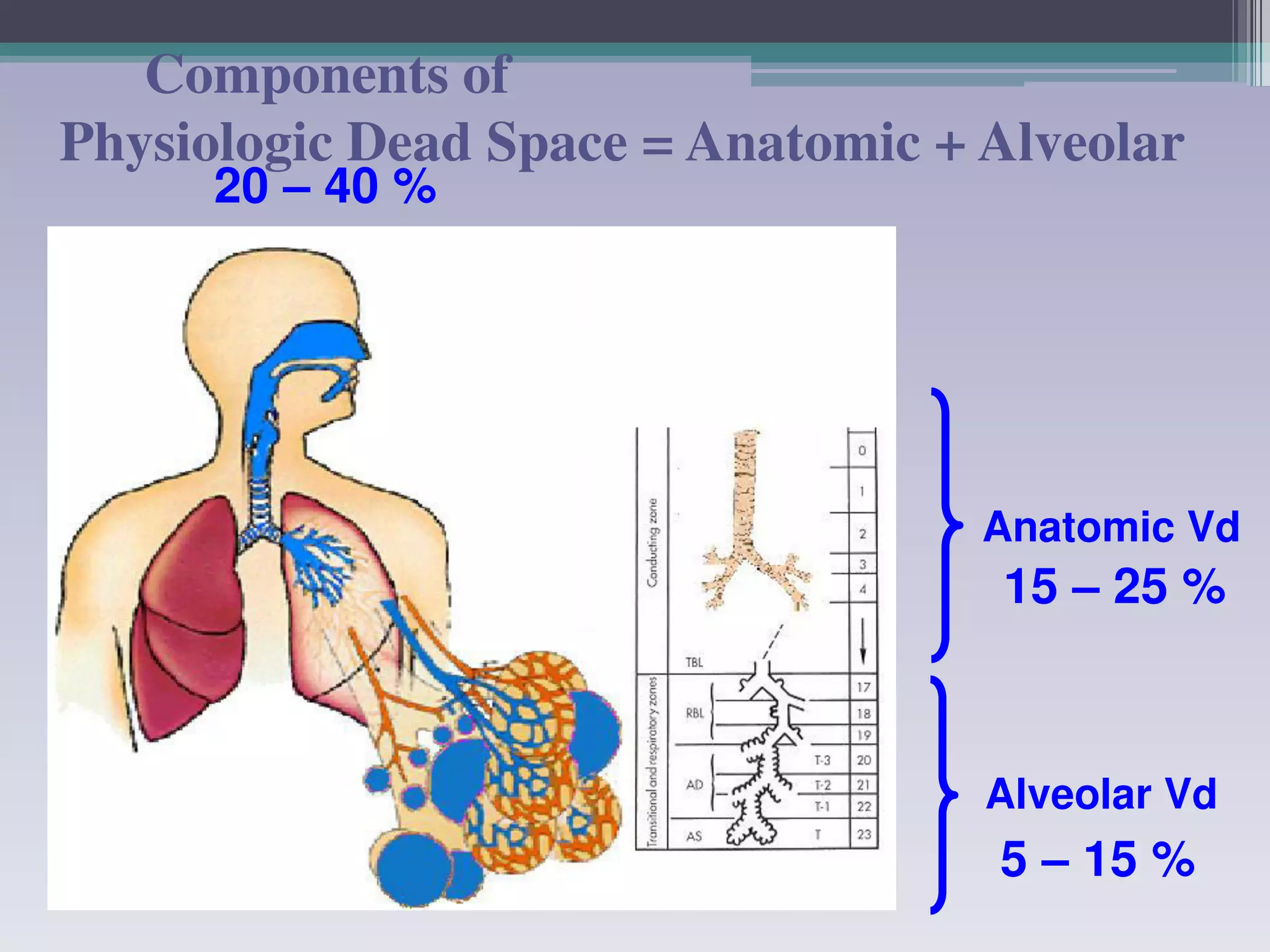
This document discusses principles of ventilation in acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). It defines ALI/ARDS and describes the pathophysiology involving increased vascular and alveolar permeability leading to pulmonary edema. Ventilator-induced lung injury can occur from high pressures, volumes, and alveolar collapse/reopening during mechanical ventilation. The "open lung approach" aims to recruit collapsed alveoli and maintain them open using maneuvers like higher positive end-expiratory pressure and periodic recruitment breaths to high pressure while limiting tidal volumes and airway pressures. Proper positive end-expiratory pressure setting and periodic recruitment are important to optimize ventilation in ALI/ARDS patients.