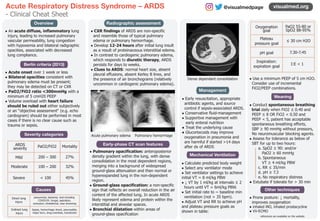
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is an acute inflammatory lung injury causing hypoxemia. It is diagnosed using Berlin criteria including onset within 1 week, bilateral opacities on imaging, and low PaO2/FiO2 ratio. Radiographically, ARDS presents as diffuse opacities resembling pulmonary edema that emerge 12-24 hours after injury. Management involves mechanical ventilation with low tidal volumes, conservative fluid management, treating the underlying cause, and considering strategies like prone positioning to improve oxygenation. ARDS has various causes including direct lung injury from pneumonia, inhalation, or indirect injury from sepsis, shock, or pancreatitis.