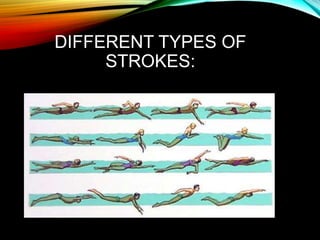
This document provides information and tips about water safety and swimming rescues. It discusses how to recognize someone in distress in the water and the four categories of difficulties swimmers may face. It also outlines non-swimming and swimming rescue techniques, including approaches, defenses, carries, releases and escapes. Finally, it details different swimming strokes, towing methods, and considerations for rescue swimming. The overall focus is on learning to recognize distress signals, performing safe rescues, and preventing injury to both victims and rescuers.