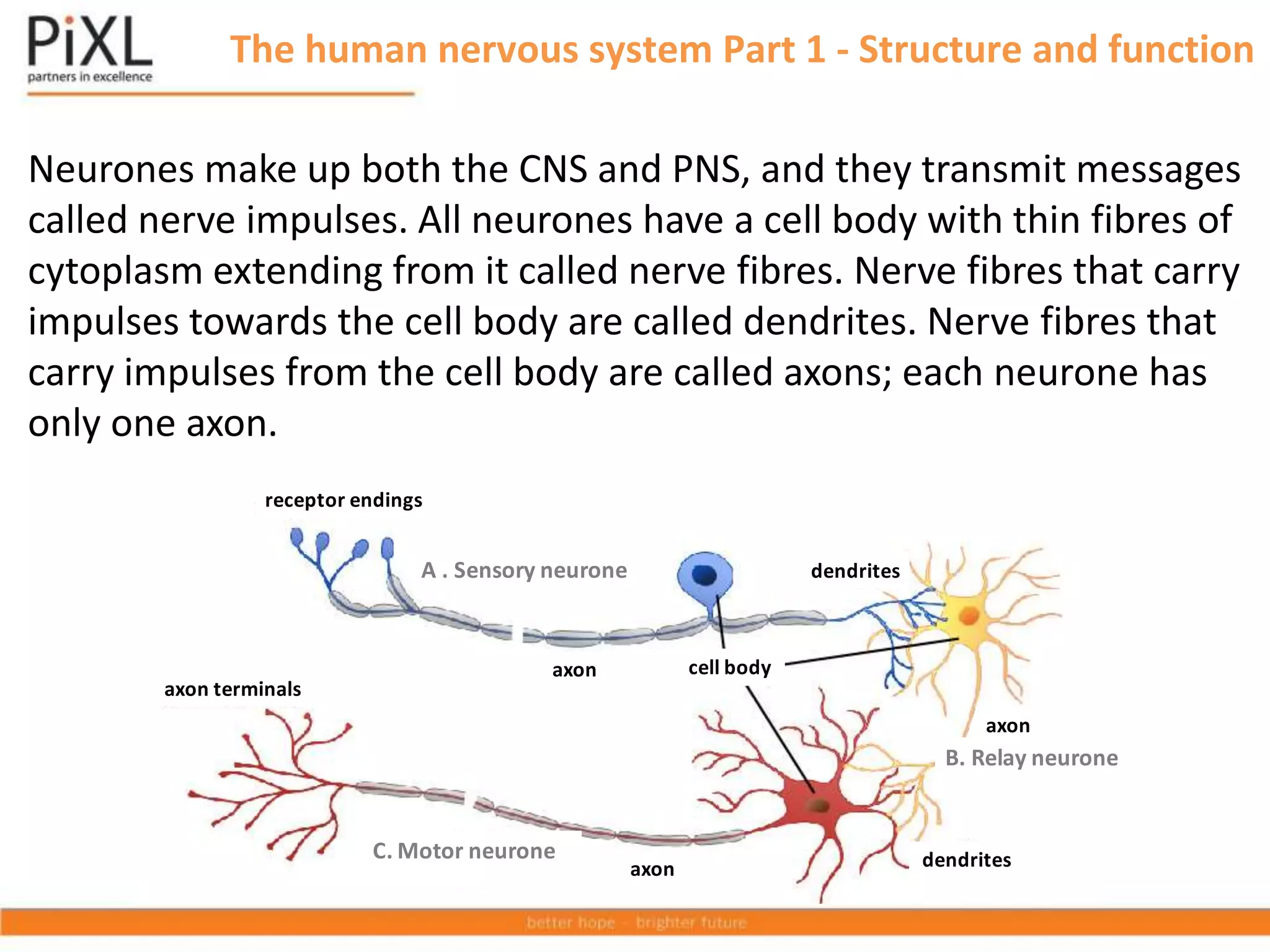
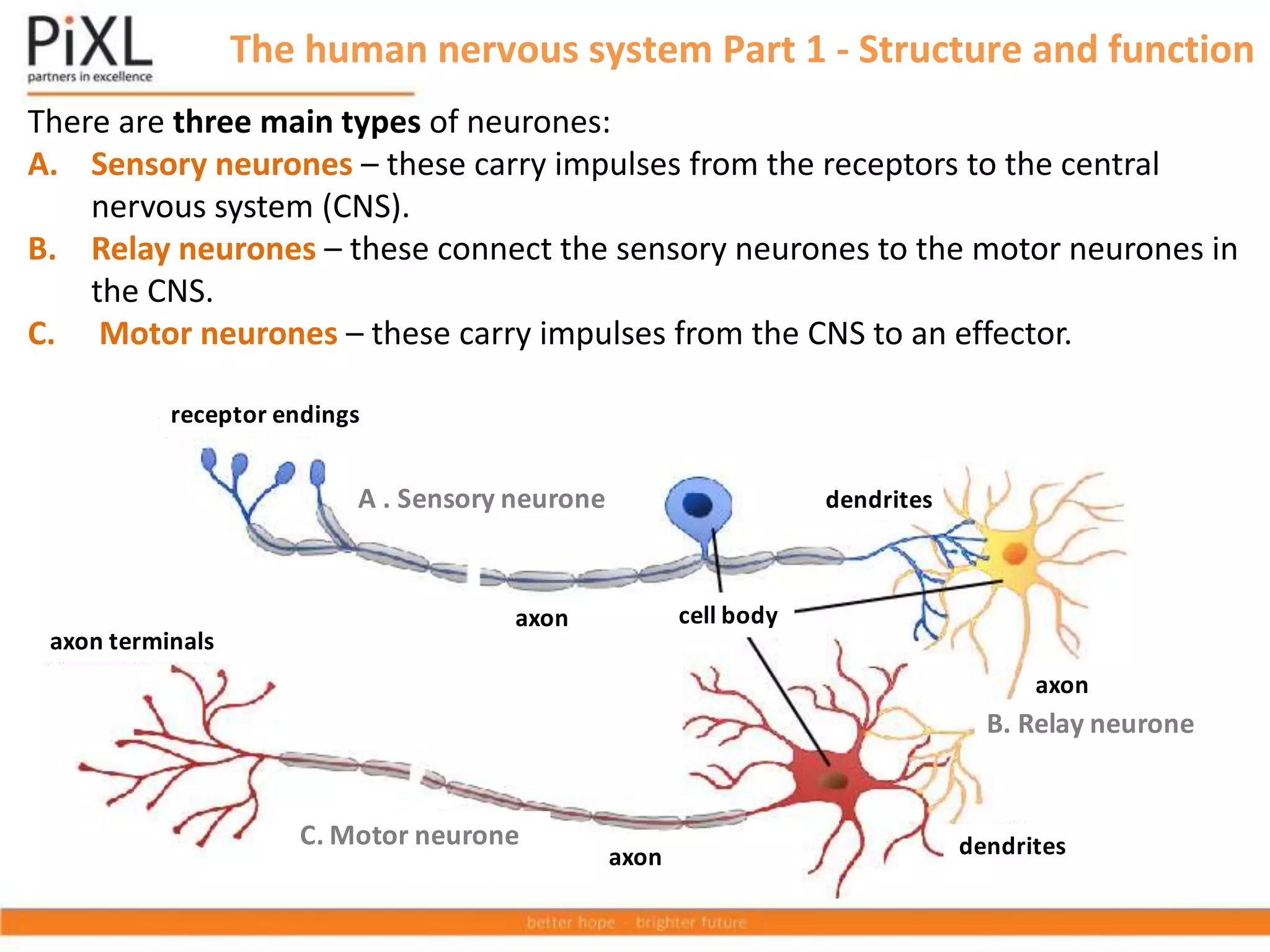
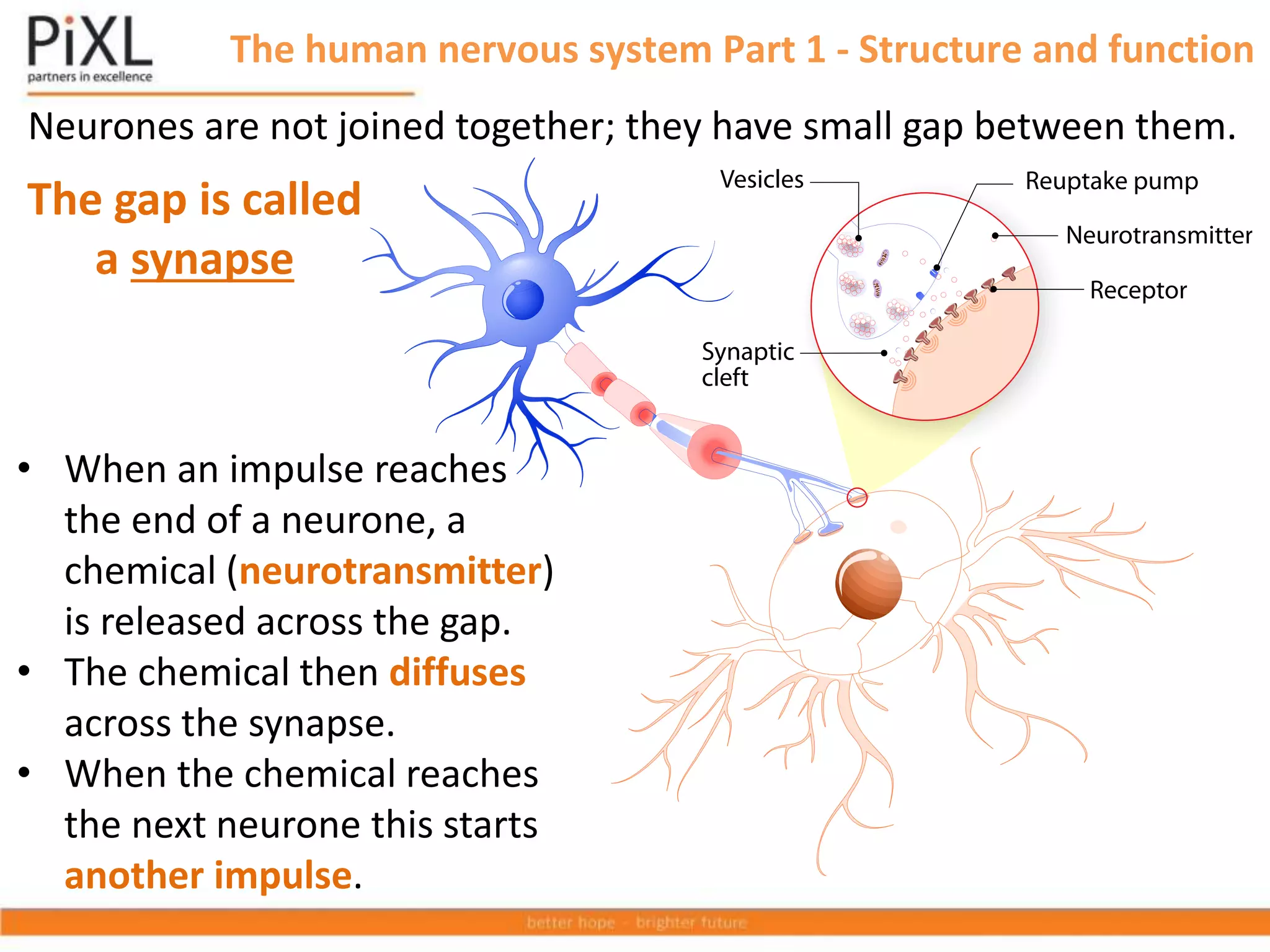
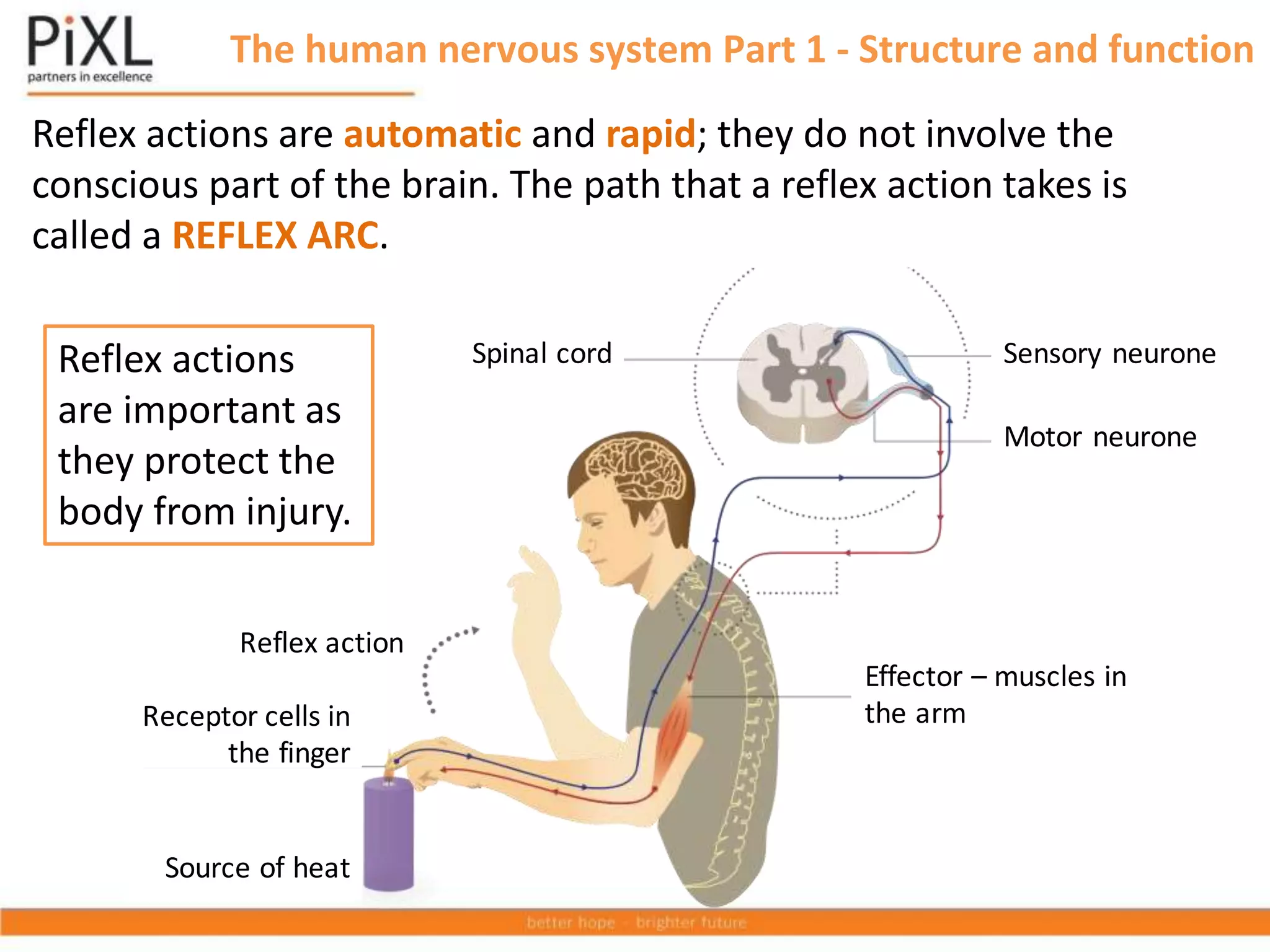
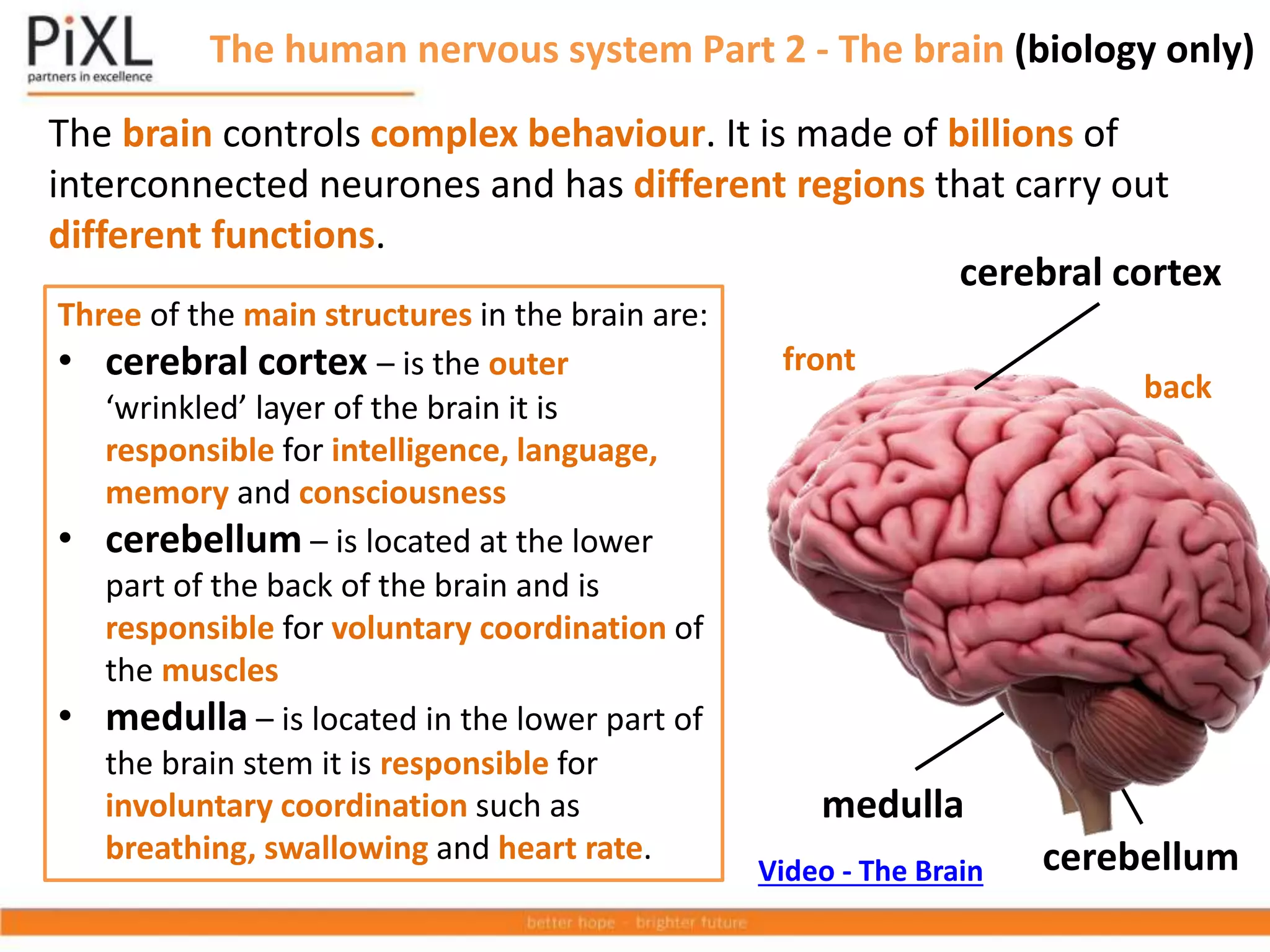
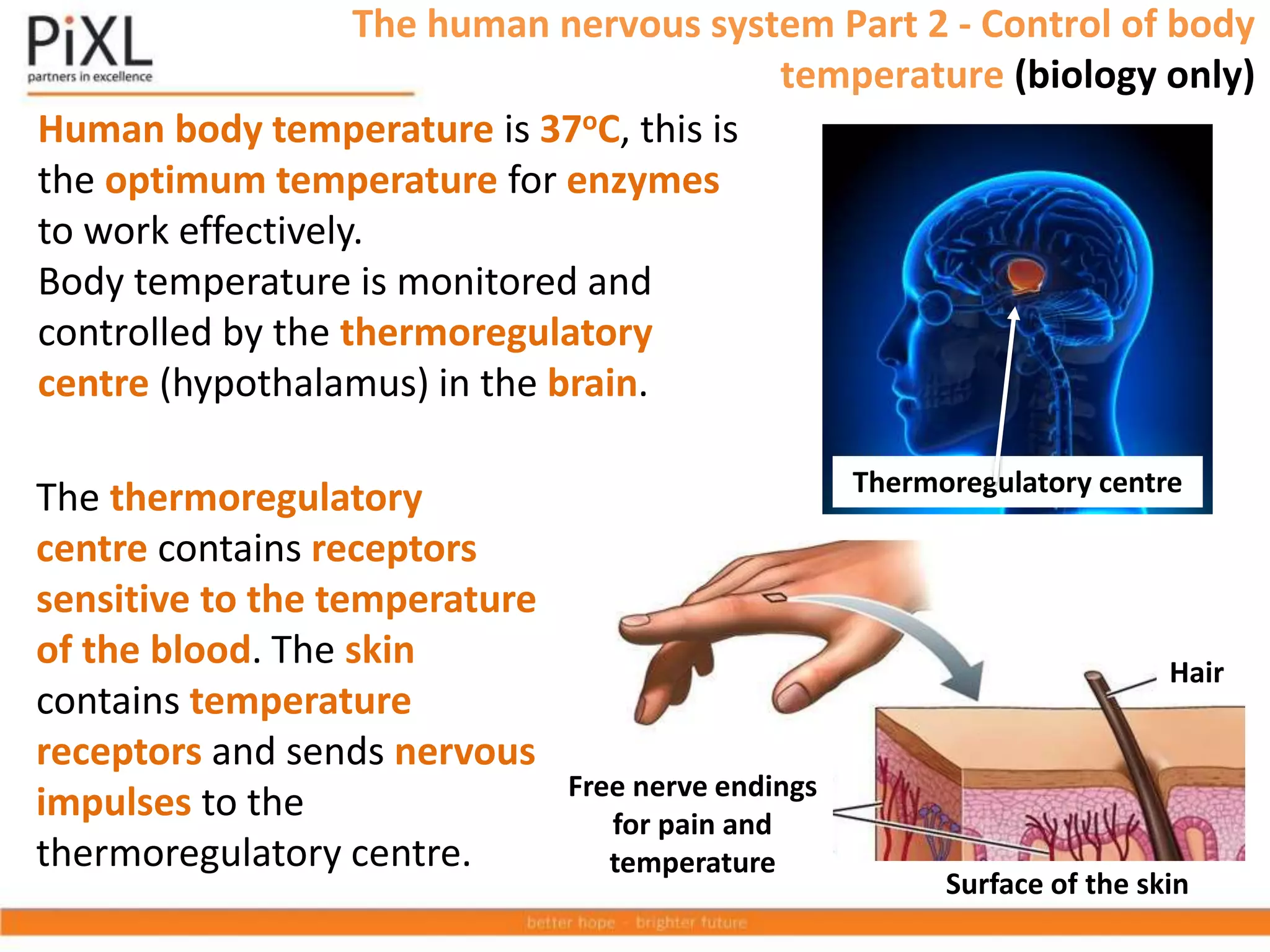
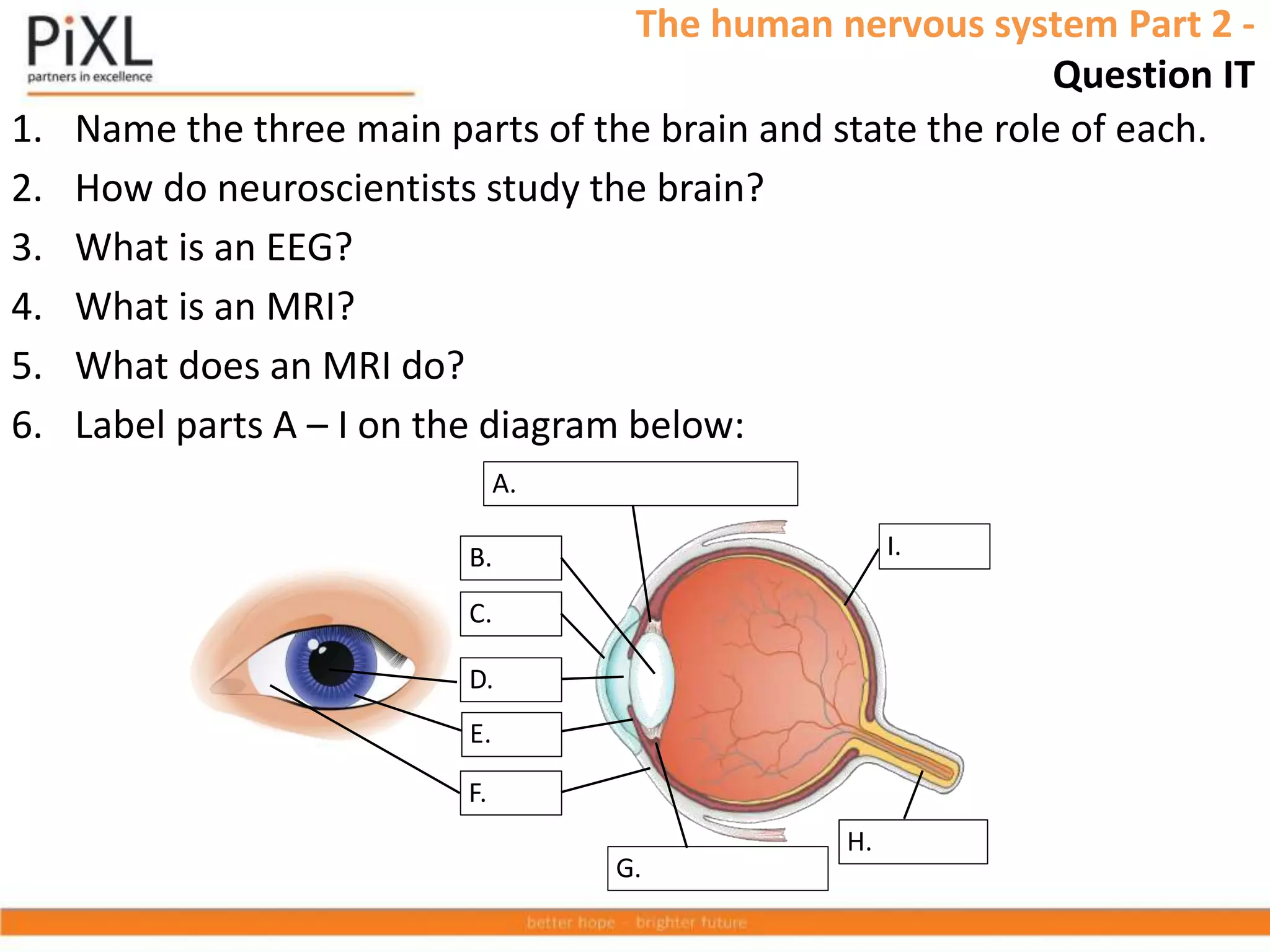
The document describes the structure and function of the human nervous system. It explains that the nervous system detects stimuli through receptors and transmits signals through neurons to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). The CNS coordinates responses by muscles or glands. There are three main types of neurons - sensory neurons carry signals from receptors to the CNS, relay neurons connect sensory and motor neurons in the CNS, and motor neurons carry signals from the CNS to effectors. Neurons transmit signals across synapses using neurotransmitters. Reflex actions provide rapid automatic responses through a reflex arc pathway without involving consciousness.