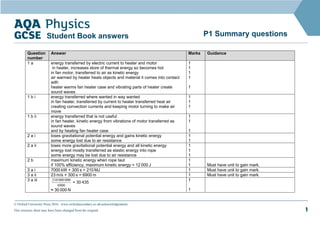
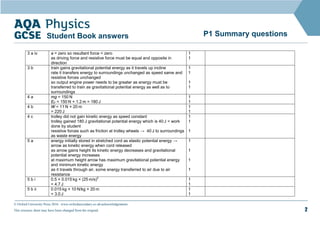
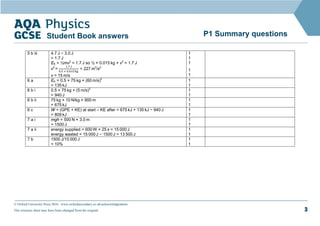
1. This document contains sample questions and answers about energy transfers and transformations. Questions cover topics like energy transfers in a fan heater, kinetic and potential energy changes in falling objects, and calculating work, power and efficiency in simple machines.
2. The answers provide calculations and explanations for how energy is transferred or transformed in each situation. For example, kinetic energy of a moving trolley is explained to be lost to friction rather than increasing its speed.
3. Key energy terms like kinetic energy, gravitational potential energy, work, and efficiency are applied to quantitatively analyze examples involving energy changes in physical systems.