Data mining refers to extracting hidden patterns from large databases and is a step in the Knowledge Discovery in Databases (KDD) process. KDD is the broader process of finding knowledge within data and involves data preparation, pattern analysis, and knowledge evaluation. It is needed due to the impracticality of manually analyzing large, complex databases. The KDD process includes understanding goals, data selection, preprocessing, mining, pattern recognition, interpretation, and discovery. Examples of applying KDD include grouping students, predicting enrollments, and assessing student performance.

![What is Data Mining?
Data mining [1] refers to the extraction of
hidden information from large databases.
Data Mining and KDD i.e Knowledge
discovery in databases are often used
interchangabily but Data mining is just a
step in KDD process.
What is KDD?
KDD [1] refers to the broad process of finding
knowledge in data and it the "high-level"
application of particular data mining methods.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofkdditsfuturescope-140910100307-phpapp01/85/Application-of-KDD-its-future-scope-2-320.jpg)


![Steps in KDD Process[2]
STEPS-
Understanding Goals
Data Selection
Data Preprocessing
Data Mining
Patterns Recognition
Interpretation / Evaluation
Knowledge discovery
Figure 1-KDD Process](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofkdditsfuturescope-140910100307-phpapp01/85/Application-of-KDD-its-future-scope-5-320.jpg)
![KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY IN THE REAL
WORLD[3]
There are a wide range of applications of KDD in real world like in
business, artificial intelligence, health care, science, marketing, finance,
fraud detection, manufacturing, telecommunications, and Internet agents
and many more.
APPLICATIONS IN EDUCATIONAL INSTITUTES/SCHOOLS
GROUPING OF STUDENTS
Clustering is used to group similar
students into a cluster.
Figure 2-Cluster of students](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofkdditsfuturescope-140910100307-phpapp01/85/Application-of-KDD-its-future-scope-6-320.jpg)

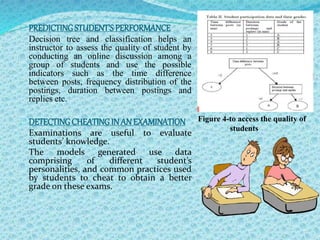
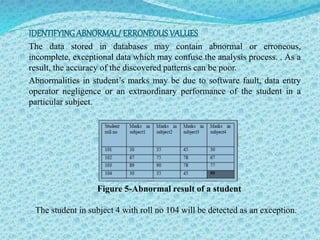
![FUTURE SCOPE OK KDD[4]
Although no human being can foretell the future, we believe that there are
plenty of interesting new challenges ahead of us, and quite a few of them
cannot be foreseen at the current point of time. Here we describe one of the
future scope of KDD that is, in chess(computer) game.
EDUCATIONAL CHESS PROGRAMS
There could be a program that could analyzes a
certain position or an entire game on an abstract
strategic level, tries to understand your opponent’s
and your own plans, and provides suggestions on
different ways to proceed.
Figure 6-Educational
chess programs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofkdditsfuturescope-140910100307-phpapp01/85/Application-of-KDD-its-future-scope-10-320.jpg)
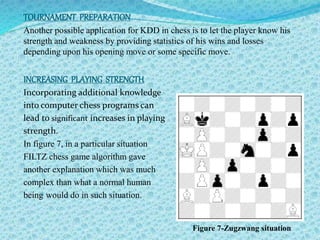
![REFERENCES
[1] Paulraj Ponniah, "Data Warehousing Fundamentals for IT
Professionals",Wiley, pp. 400–402,2010
[2] Oded Maimon, Lior Rokach," introduction to knowledge discovery in
databases",Department of Industrial Engineering,2012
[3] Manoj Bala,"study of applications of data mining techniques in
education",Vol. No. 1, Issue No. IV, Jan-Mar, (IJRST),2012
[4] Johannes F¨urnkranz," Knowledge Discovery in Chess
Databases",Austrian Research Institute for Artificial Intelligence,2001](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/applicationofkdditsfuturescope-140910100307-phpapp01/85/Application-of-KDD-its-future-scope-12-320.jpg)

