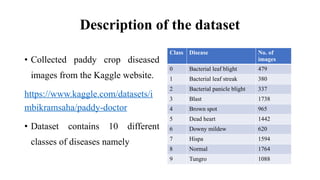
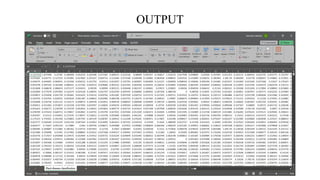
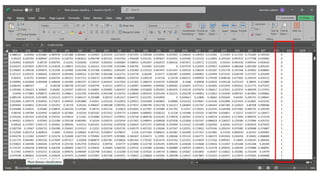
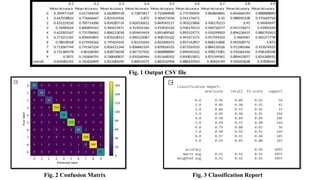
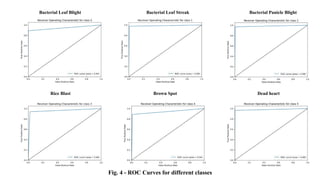
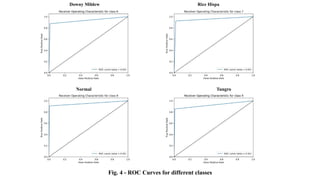
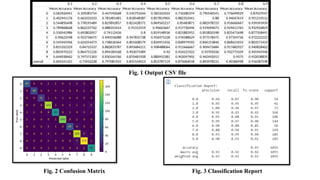
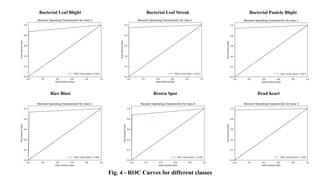
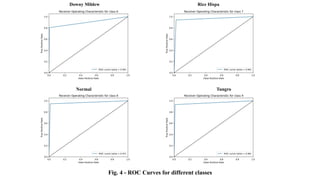
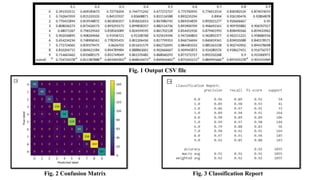
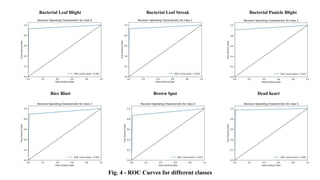
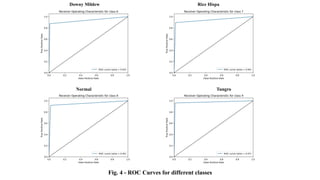
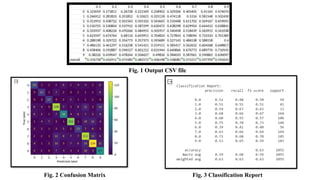
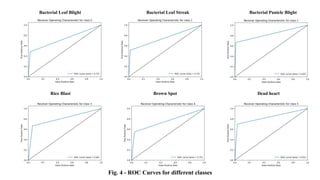
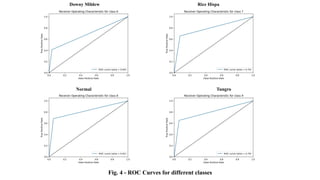
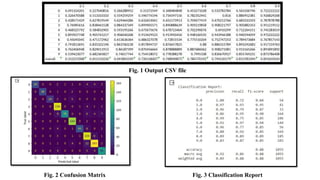
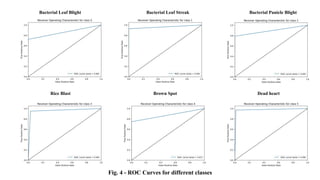
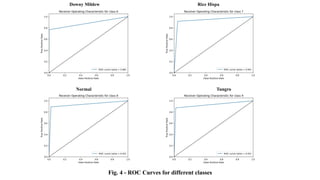
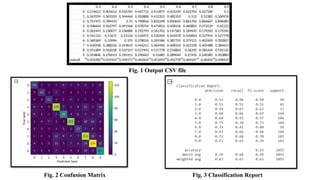
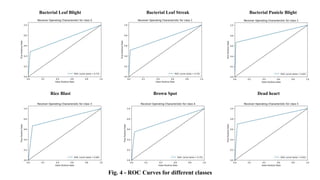
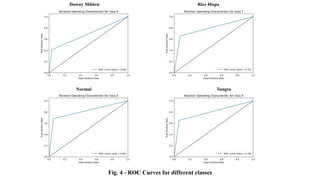
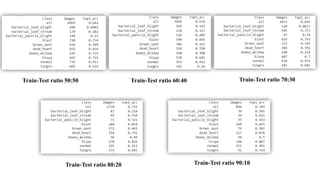
The document discusses advanced machine learning methods for crop image classification, focusing on various algorithms combined with the ResNet architecture. It presents performance metrics for different classifiers like k-nearest neighbors, support vector machines, neural networks, decision trees, and random forests, using a dataset of diseased paddy crop images. Results indicate that the hybrid approaches significantly enhance classification accuracy across multiple disease categories.


![Basic terms
• Machine Learning: Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI)
that involves algorithms and data that automatically analyze and make decisions
by itself without human intervention.
• Image classification: Image classification is the task of assigning a label to an
image from a predefined set of categories.
• Performance metrics
• Accuracy: TP/ [TP+FP+FN+FP]
• Precision: TP/ [TP+FP]
• Recall: TP/ [TP+FN]
• F1 score: 2 x [precision x recall] / [precision + recall]
• ROC AUC: Measures the ability of the model to distinguish between classes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bam22-075-241107134013-a7aac0c3/85/Application-of-Advanced-Machine-Learning-Methods-for-Crop-Image-Classification-pptx-3-320.jpg)