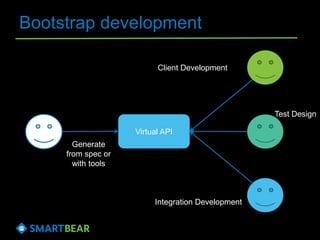
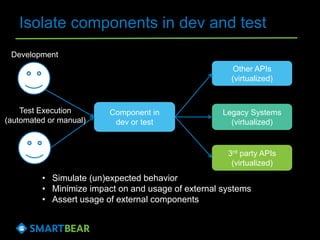
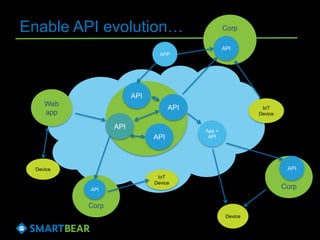
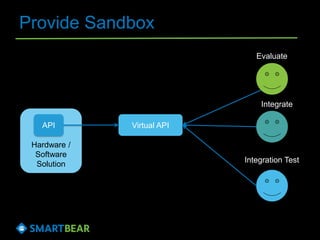
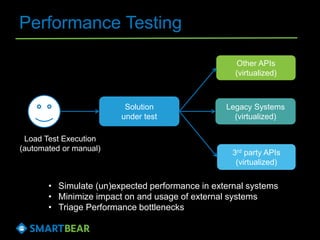
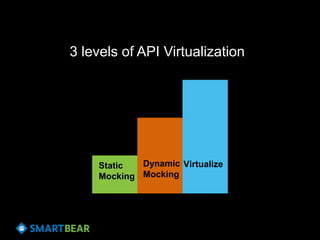
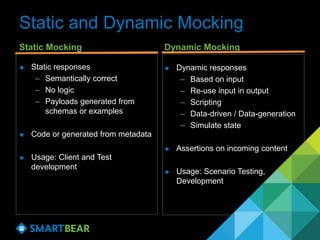
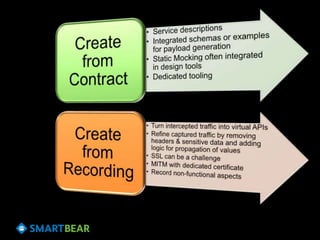
The document discusses the concept of API virtualization, highlighting its role in development and testing by simulating expected and unexpected behavior of APIs. It explains different levels of API virtualization, such as static and dynamic mocking, and provides insights on various tools and methodologies to implement API virtualization effectively. Furthermore, it outlines considerations for managing virtual APIs and when to utilize virtualization based on project complexity and dependencies.