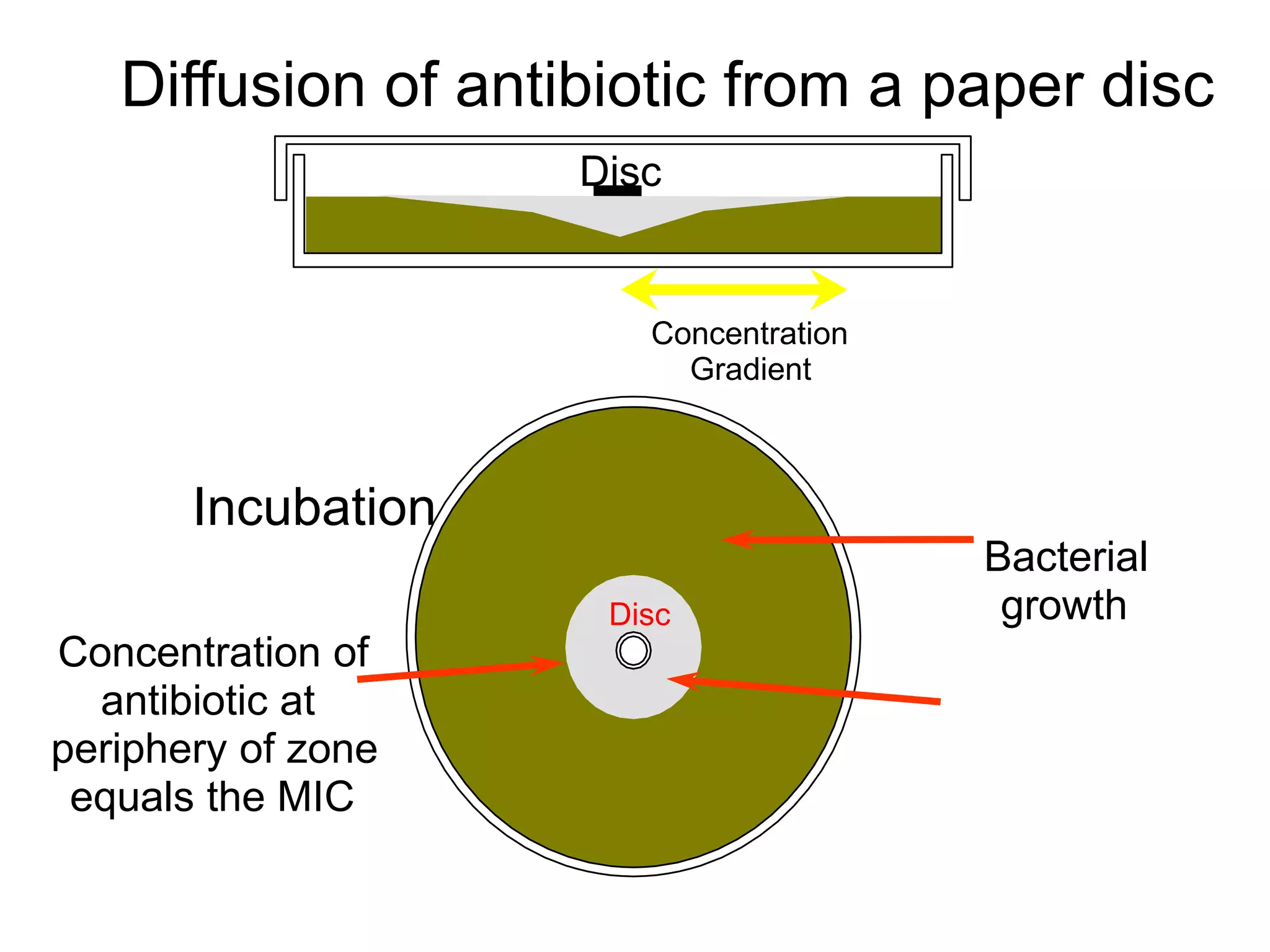
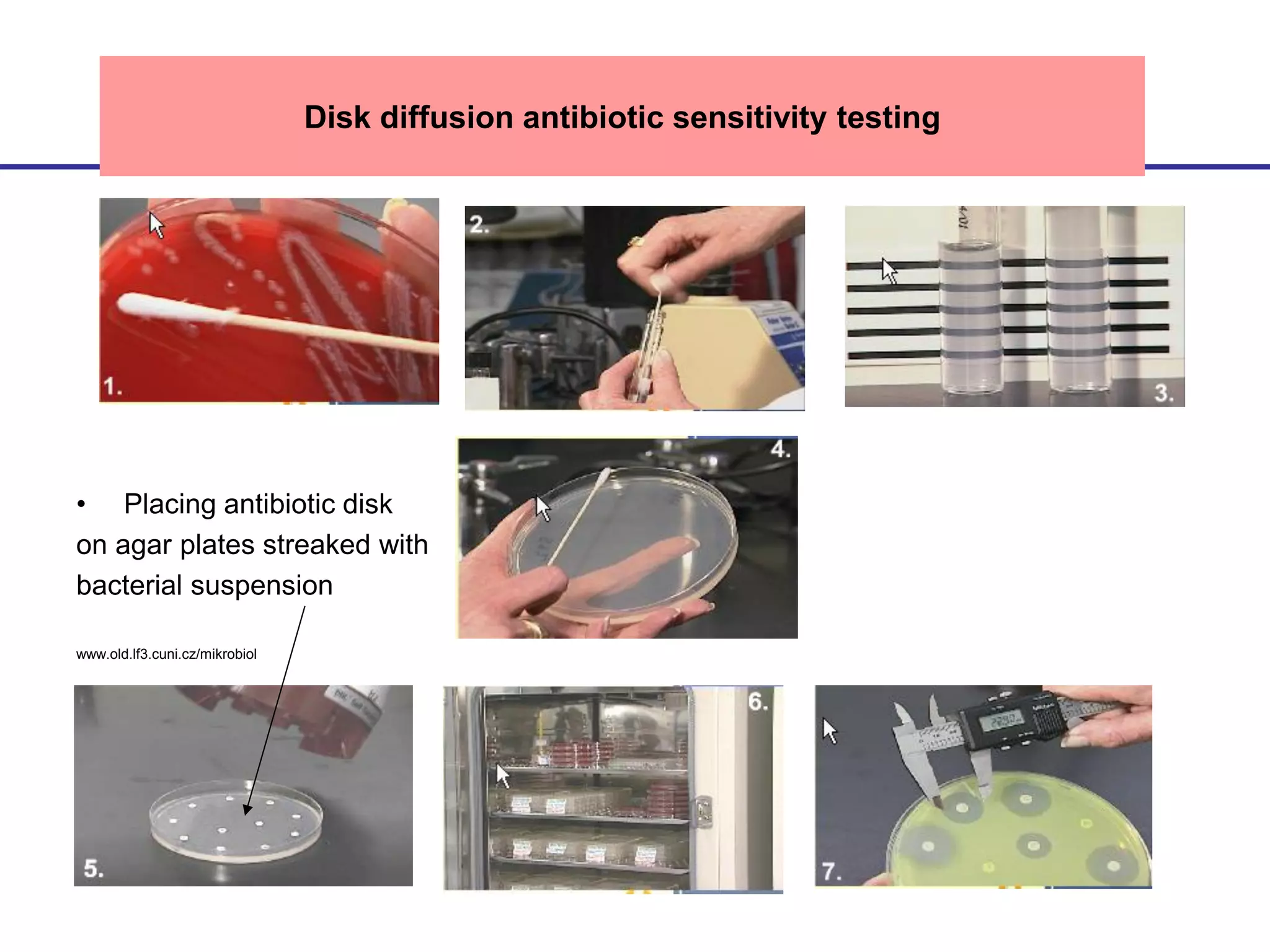
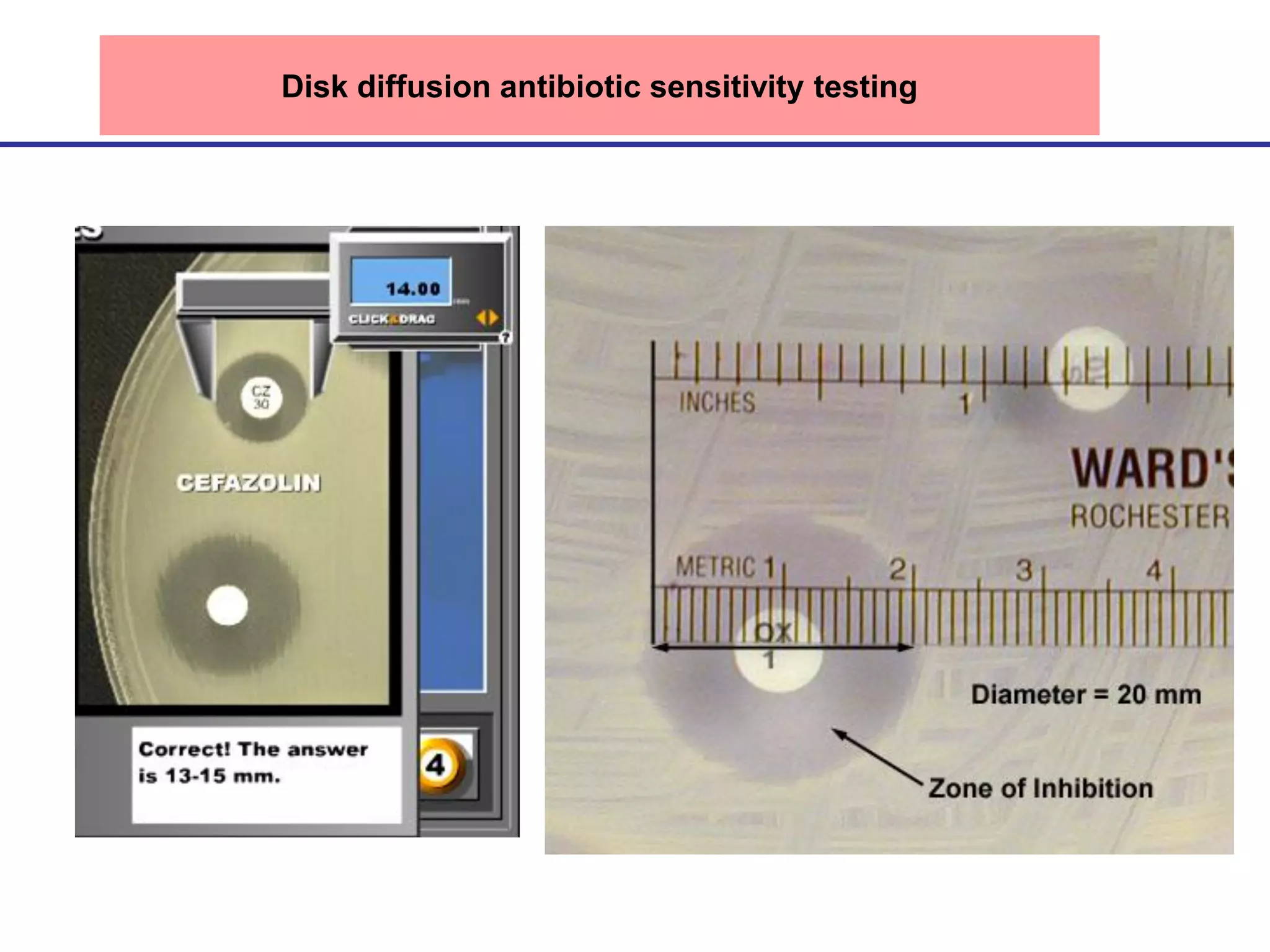
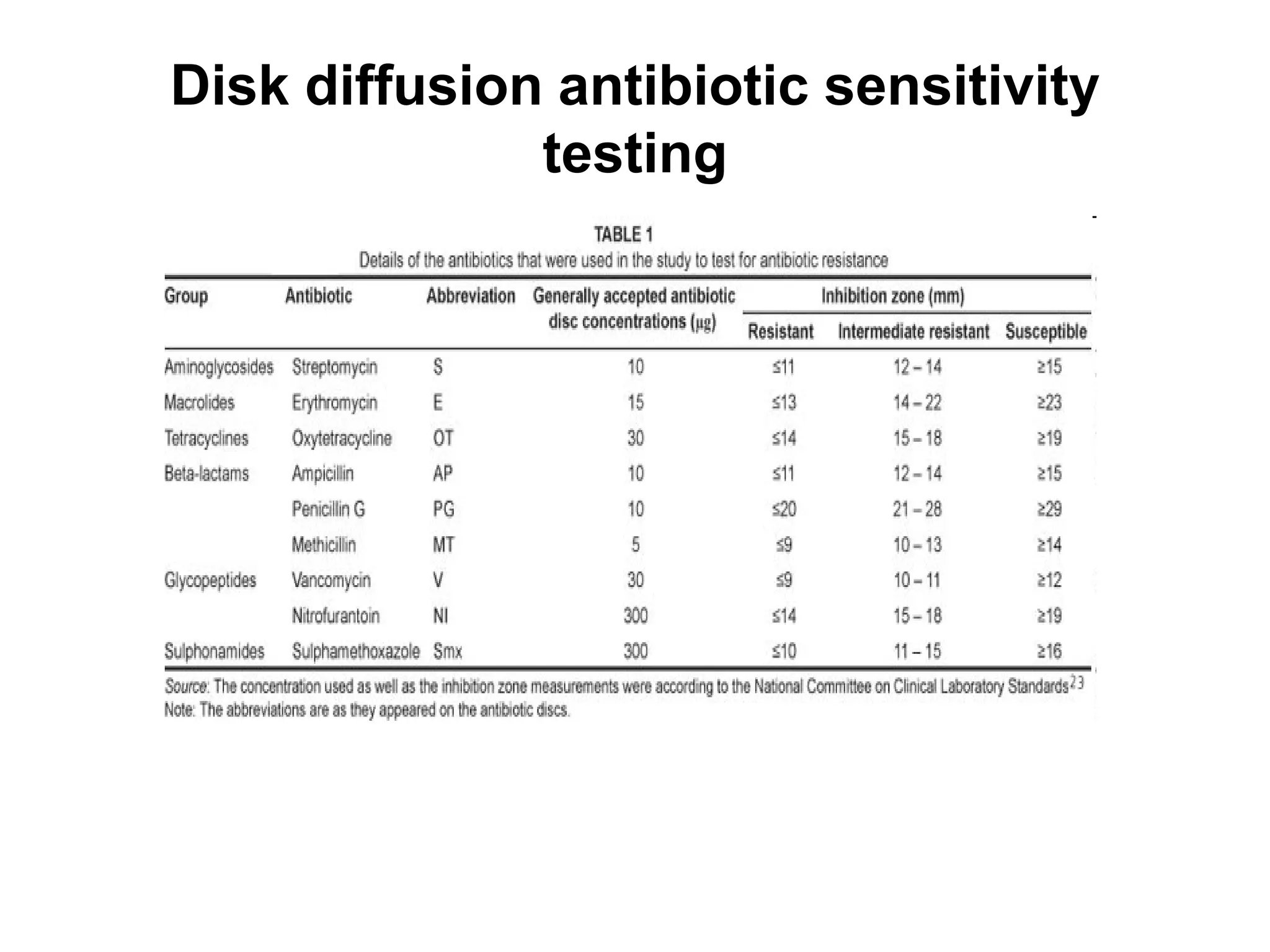
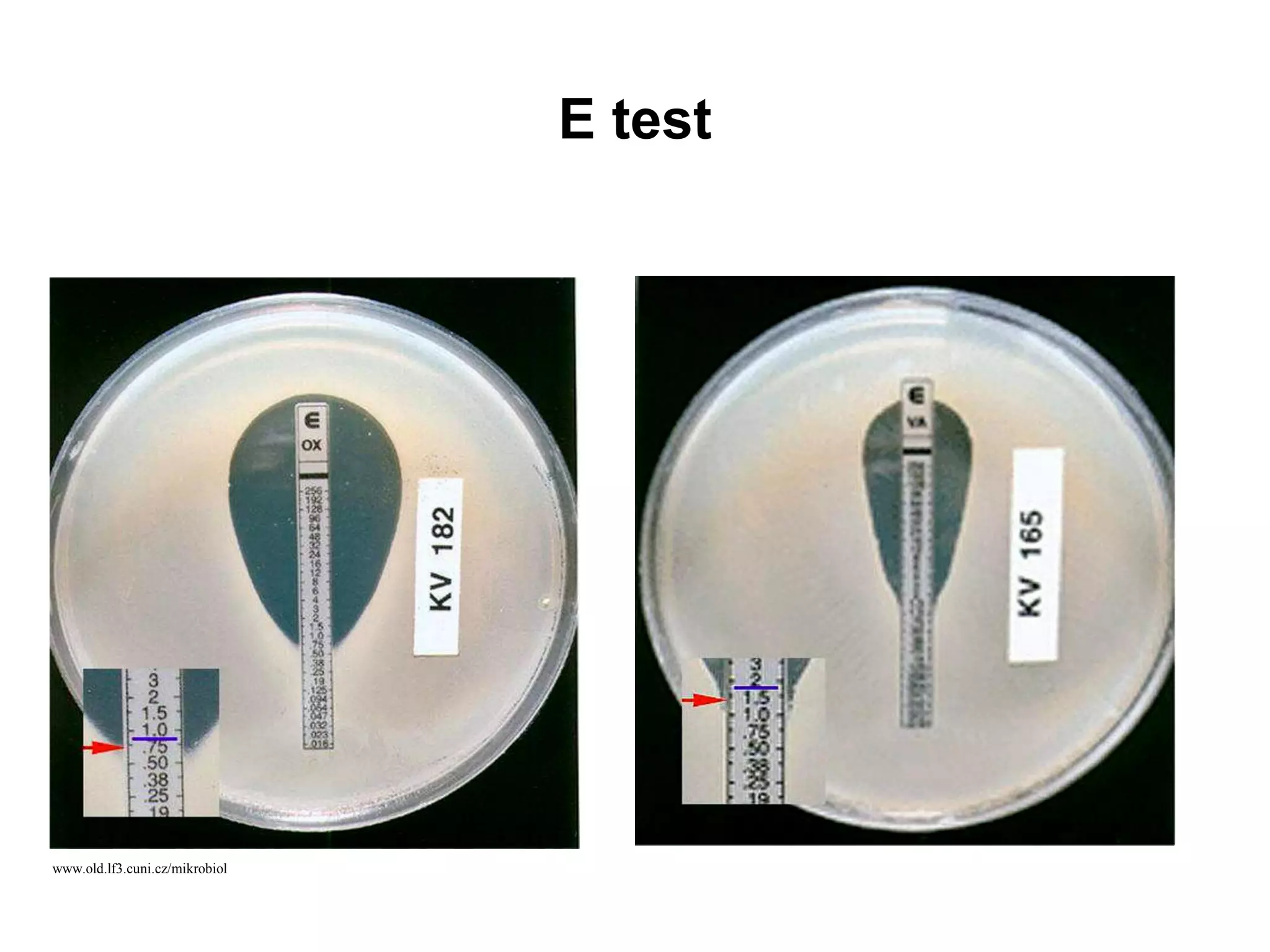
Disk diffusion antibiotic sensitivity testing involves placing antibiotic-impregnated disks on agar plates streaked with bacteria. If the bacteria are susceptible to a particular antibiotic, a zone of inhibition without bacterial growth forms around the disk. The size of this zone is compared to standardized values to determine susceptibility. Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) testing determines the lowest concentration of antibiotic that prevents visible bacterial growth through serial dilutions of antibiotics in broth with bacteria. Both methods are used to guide effective antibiotic treatment by identifying antibiotics bacteria are sensitive to.