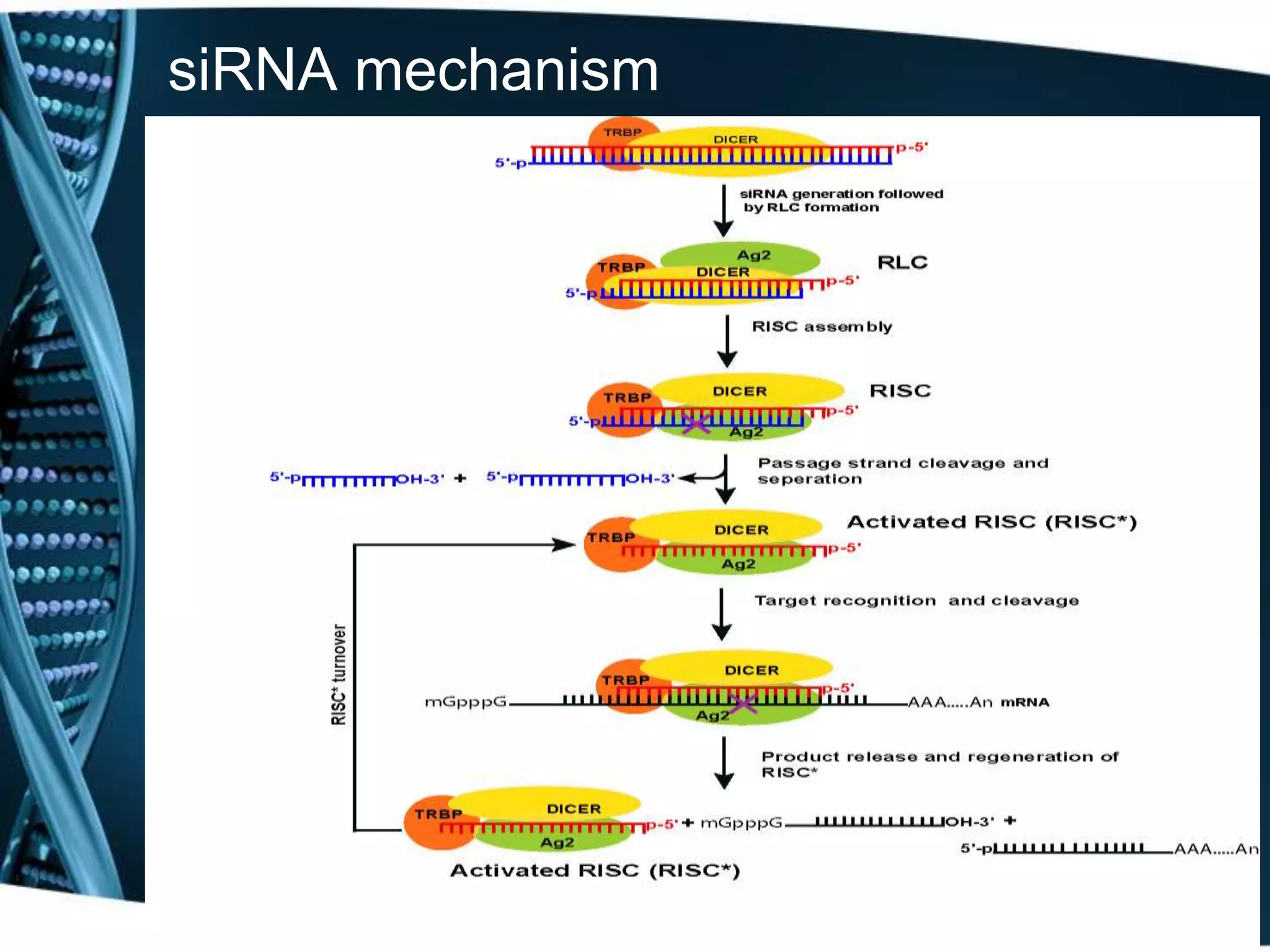
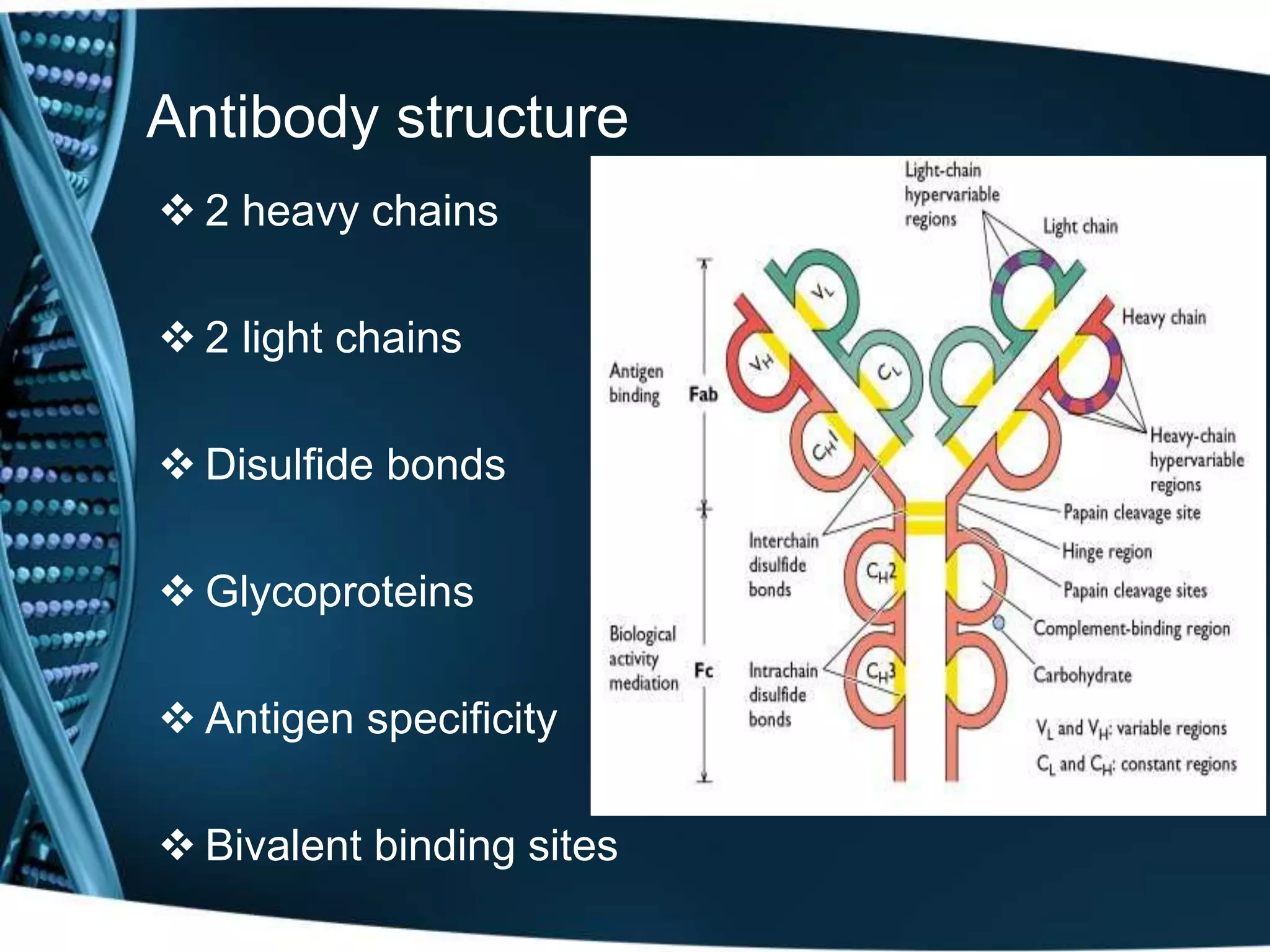
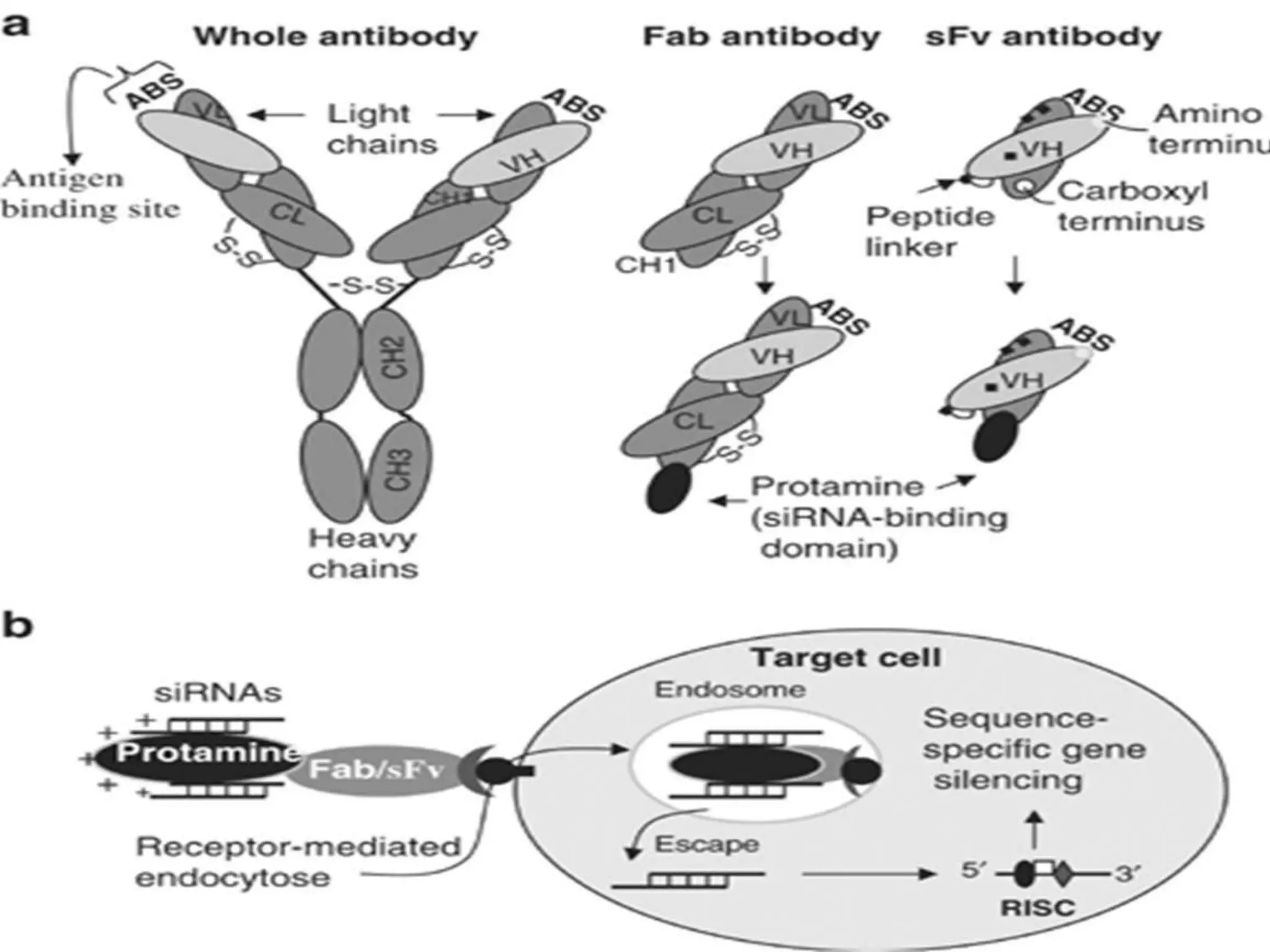
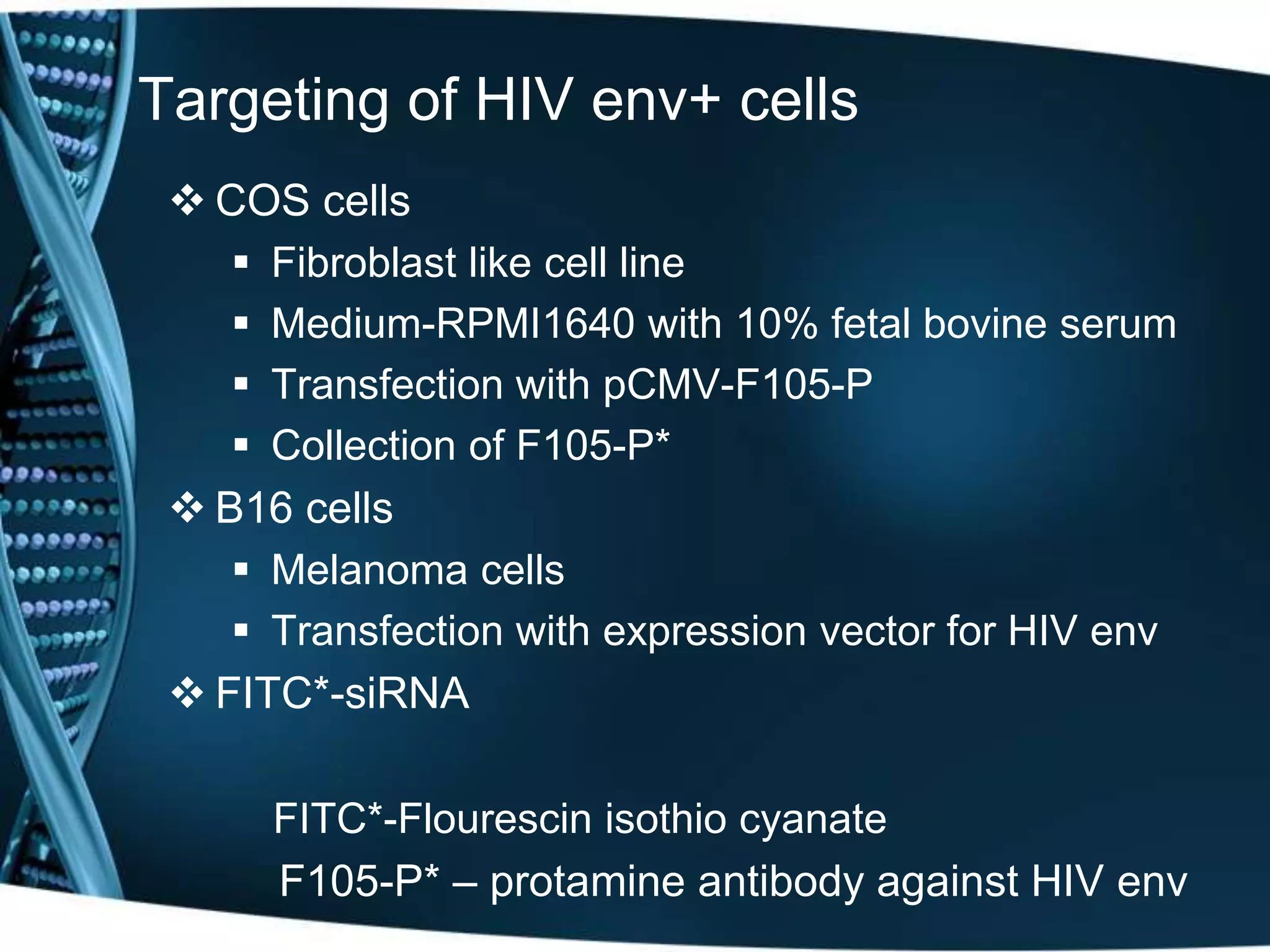
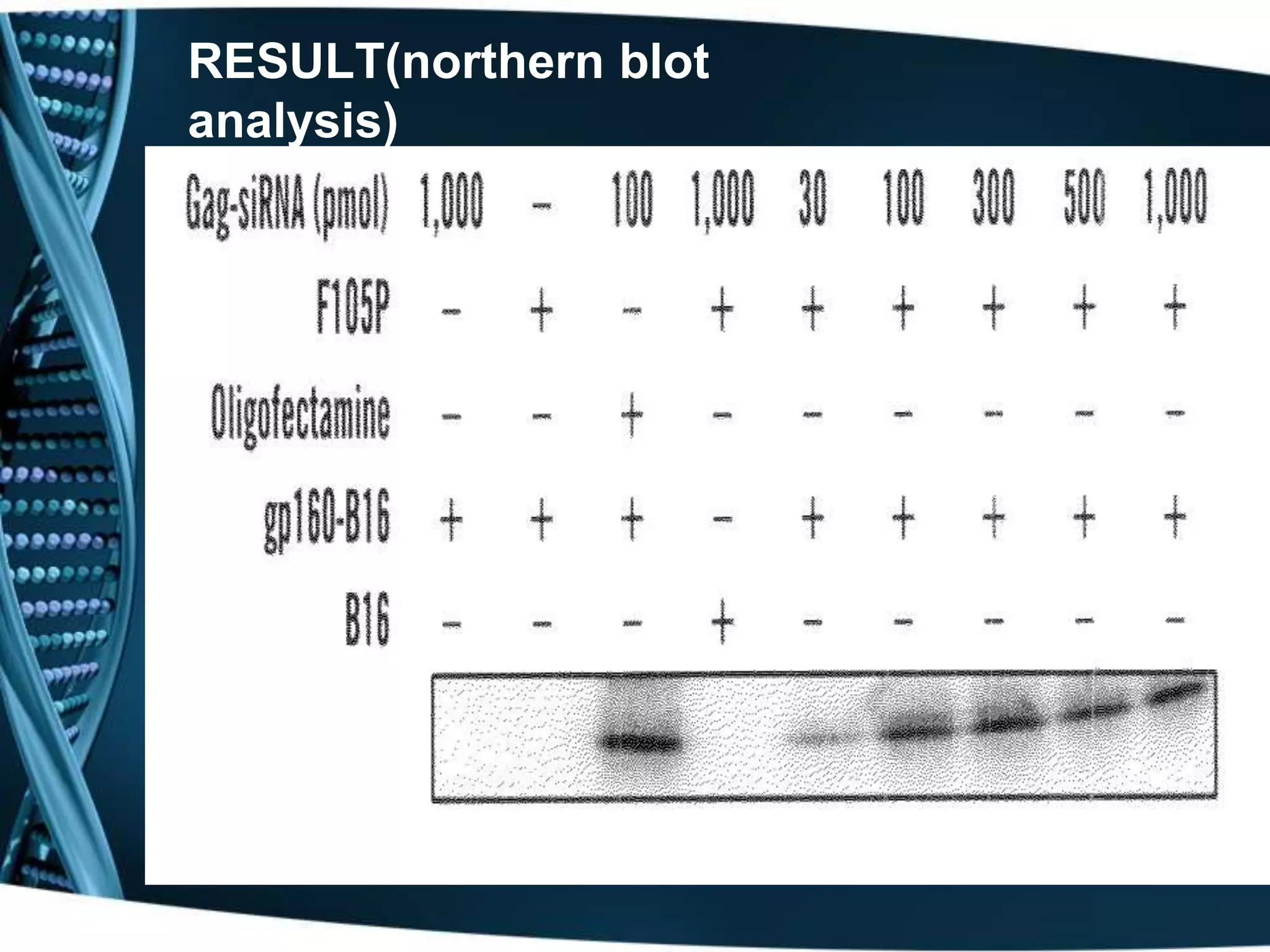
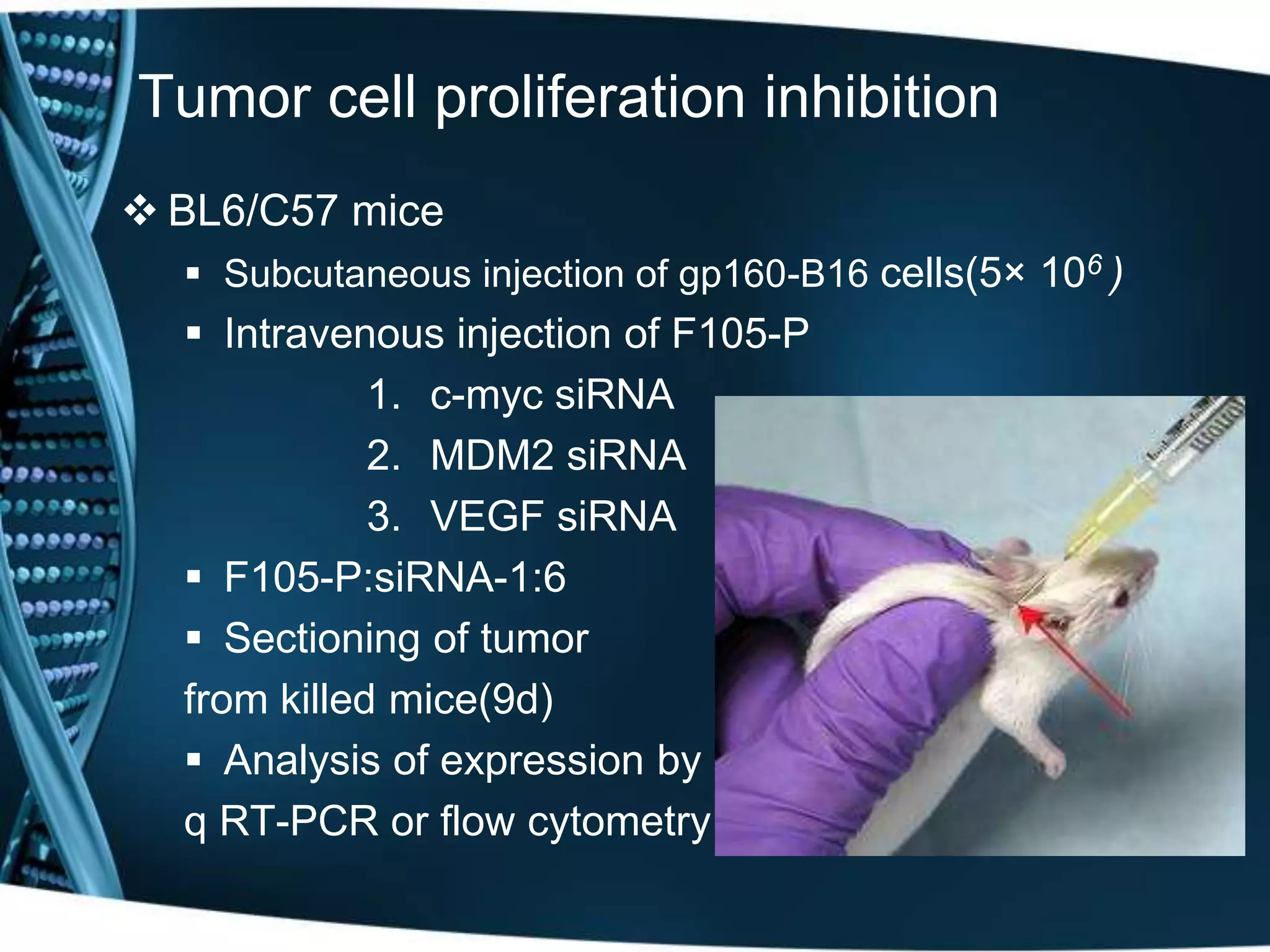
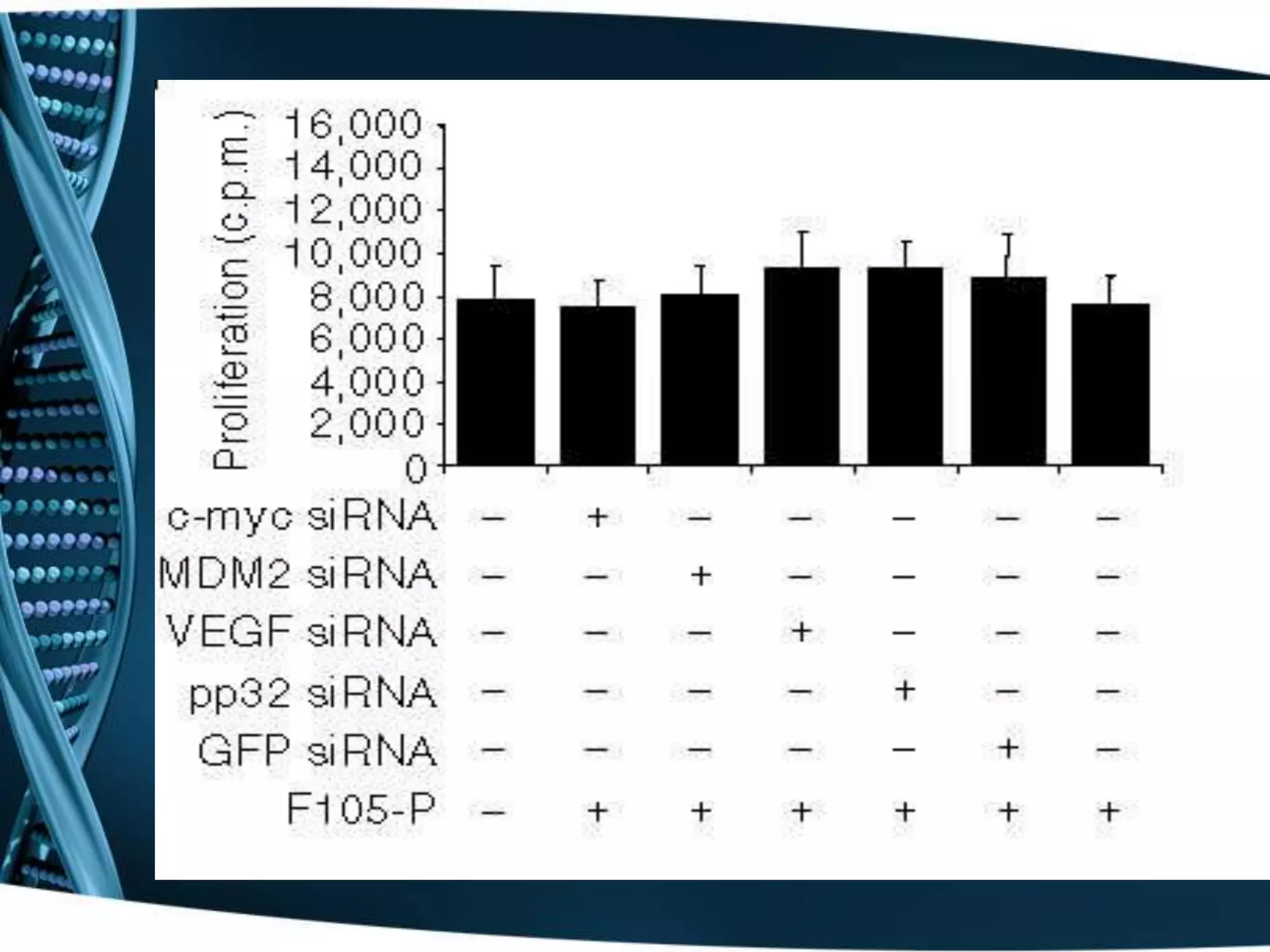
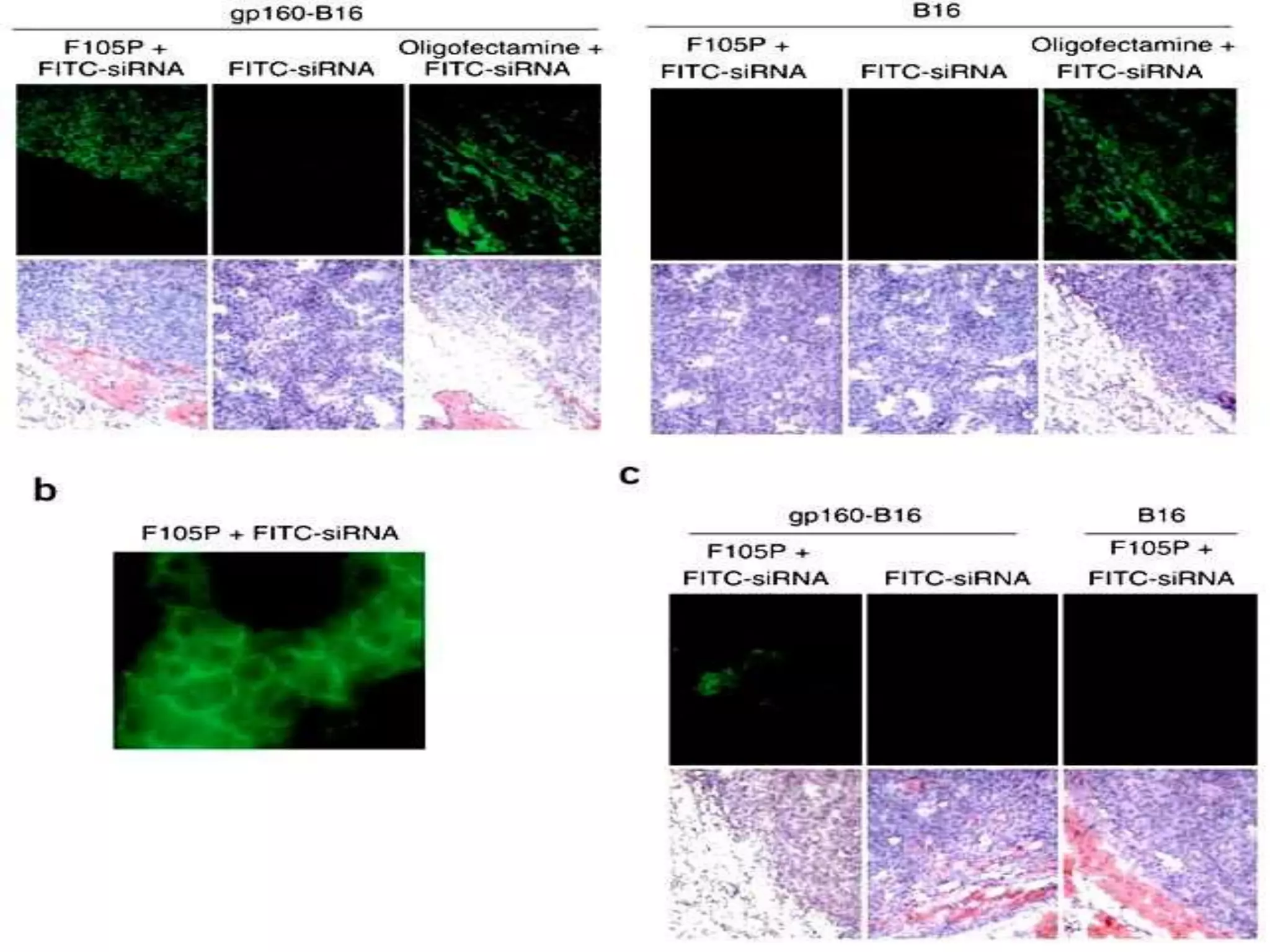
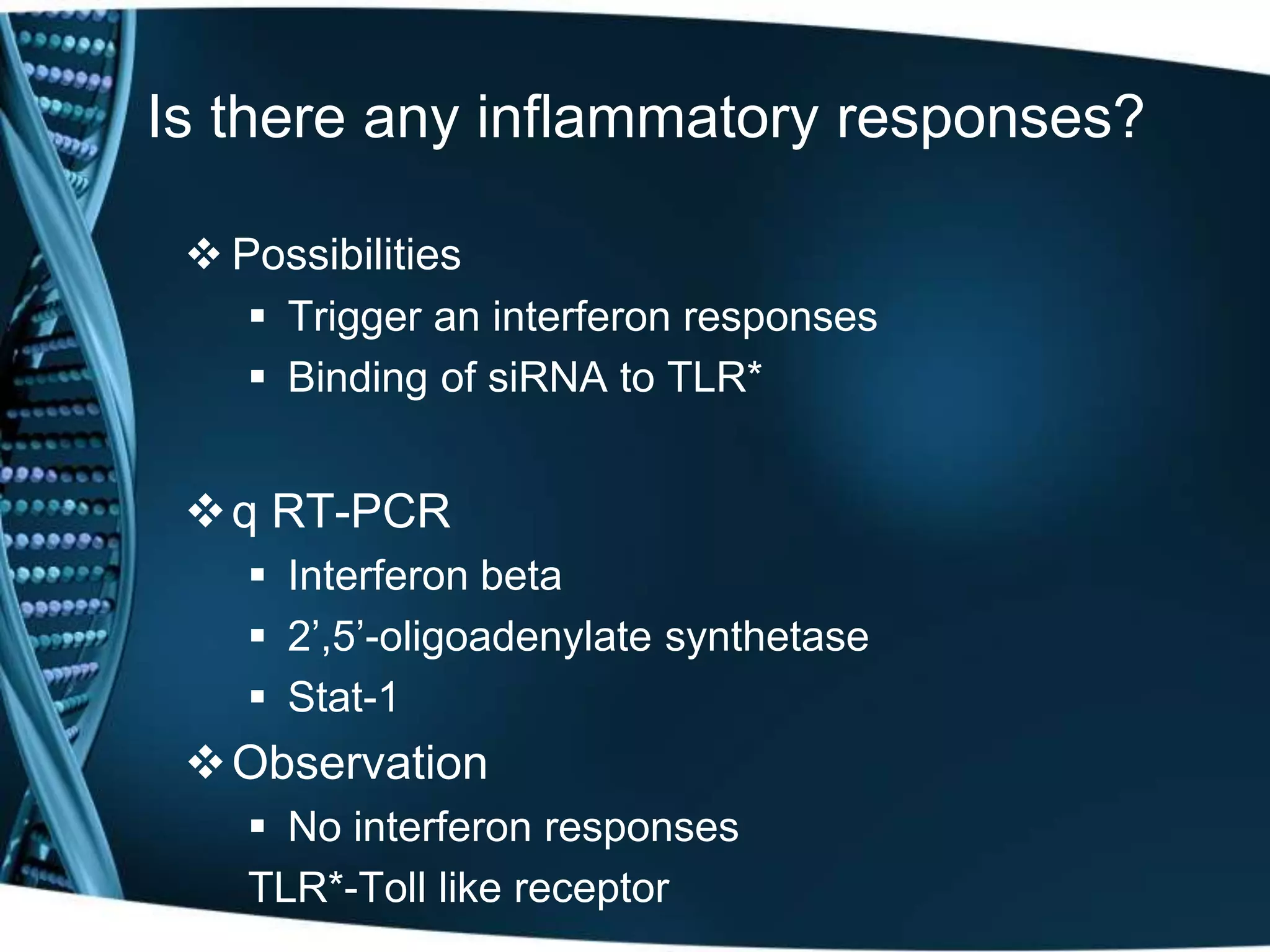
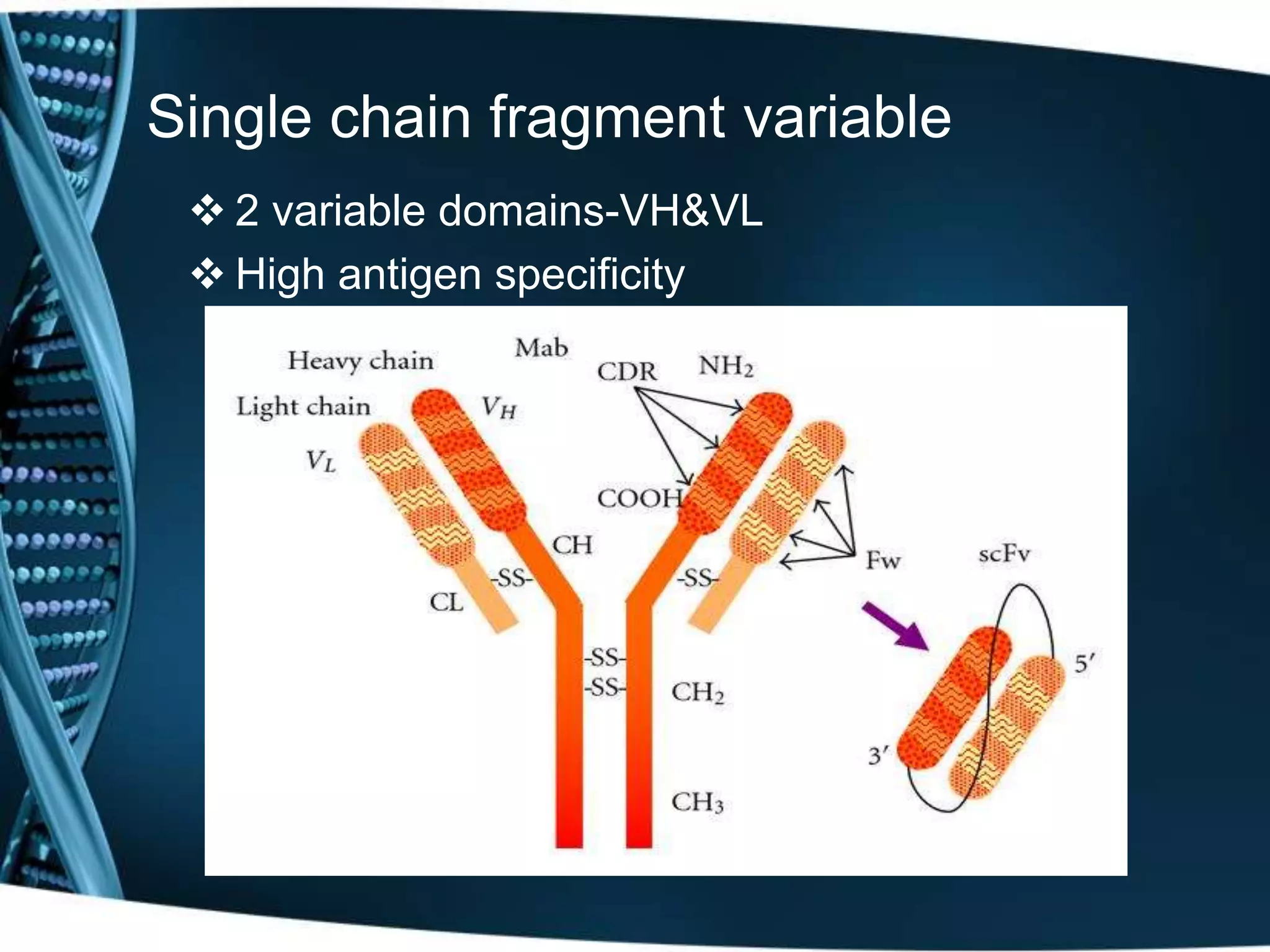
The document discusses the development of a protamine-antibody fusion (F105-P) for the in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) targeted at HIV and cancer cells to achieve gene silencing. It details experimental results indicating the effective binding and delivery of siRNAs, along with the observed reductions in HIV replication and tumor cell proliferation. The study concludes with recommendations for enhancing gene silencing efficiency through modifications and combinations of siRNAs.