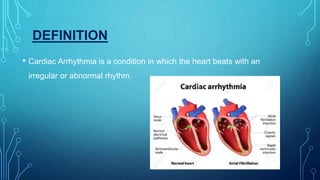
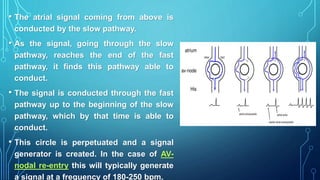
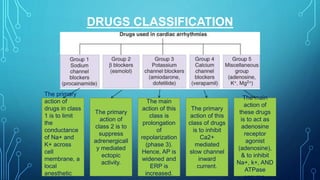
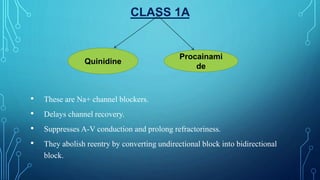
This document discusses anti-arrhythmia drugs and mechanisms. It defines arrhythmia as an irregular or abnormal heart rhythm. The main mechanisms are altered automaticity, triggered activity including early and delayed afterdepolarizations, and reentry which can occur through anatomical circuits or functionally. Drugs classes include sodium channel blockers (Class 1), beta blockers (Class 2), potassium channel blockers (Class 3), calcium channel blockers (Class 4), and others like adenosine, digoxin, and atropine. The classes have different effects on action potential duration and refractory period to suppress arrhythmias.