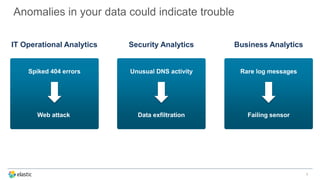
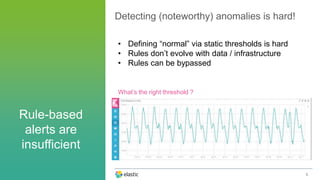
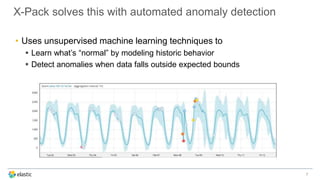
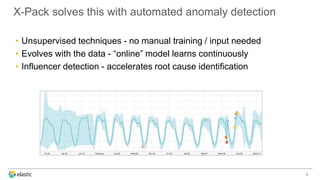
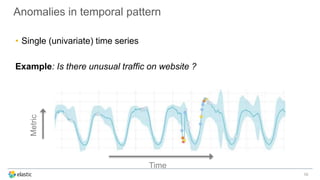
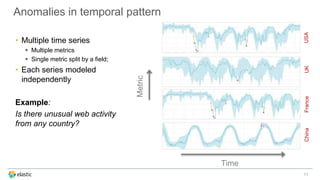
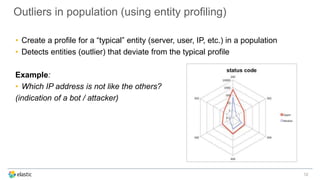
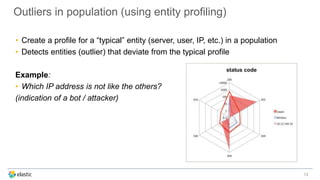
The document discusses the challenges of detecting anomalies in data, particularly in the context of security, operational analytics, and telemetry. It emphasizes the limitations of traditional rule-based approaches and introduces X-Pack’s automated anomaly detection that employs unsupervised machine learning techniques to identify deviations from normal behavior. The solution adapts continuously to evolving data, enabling the detection of various types of anomalies, including unusual traffic patterns and outliers in user behavior.