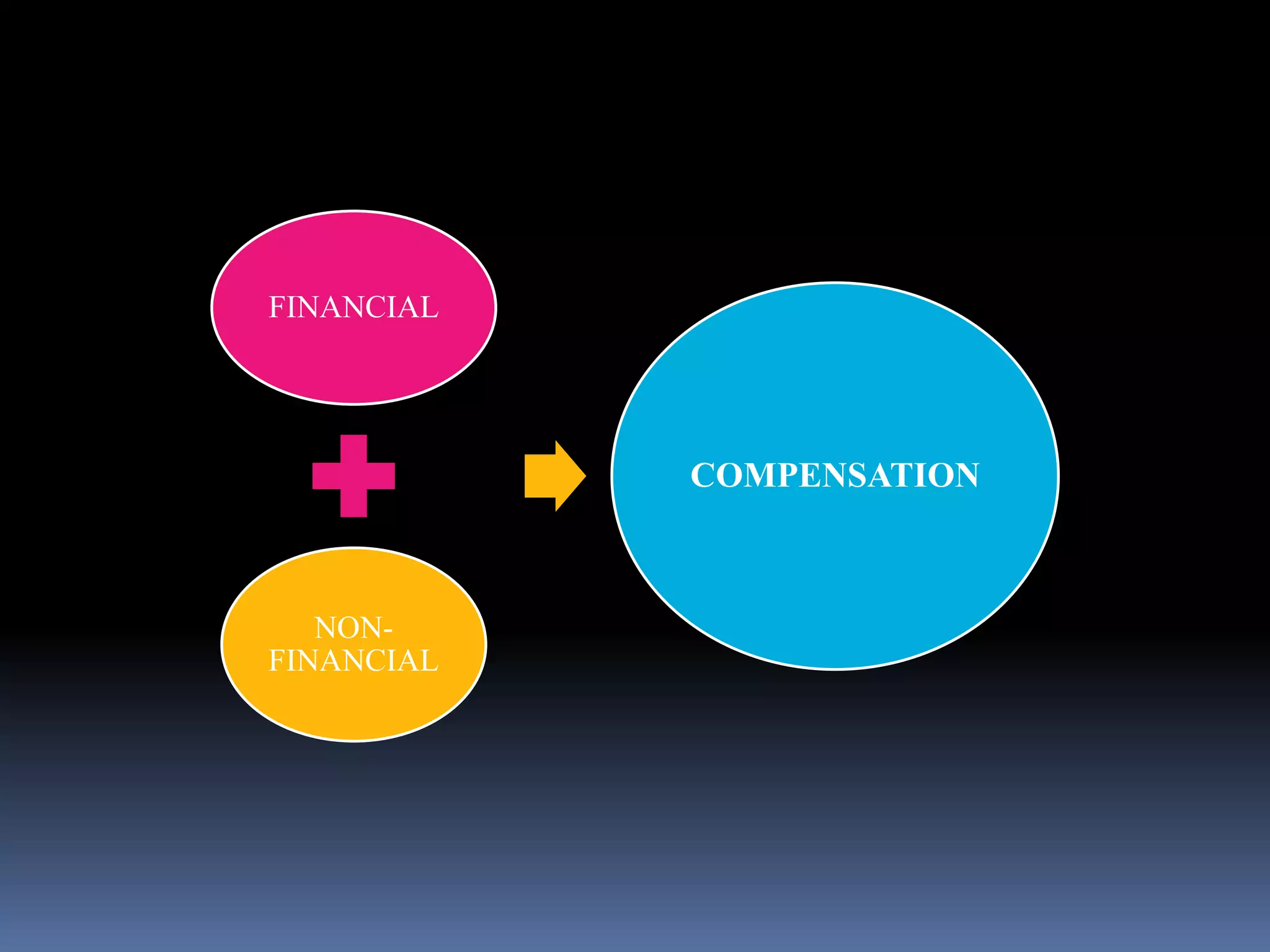
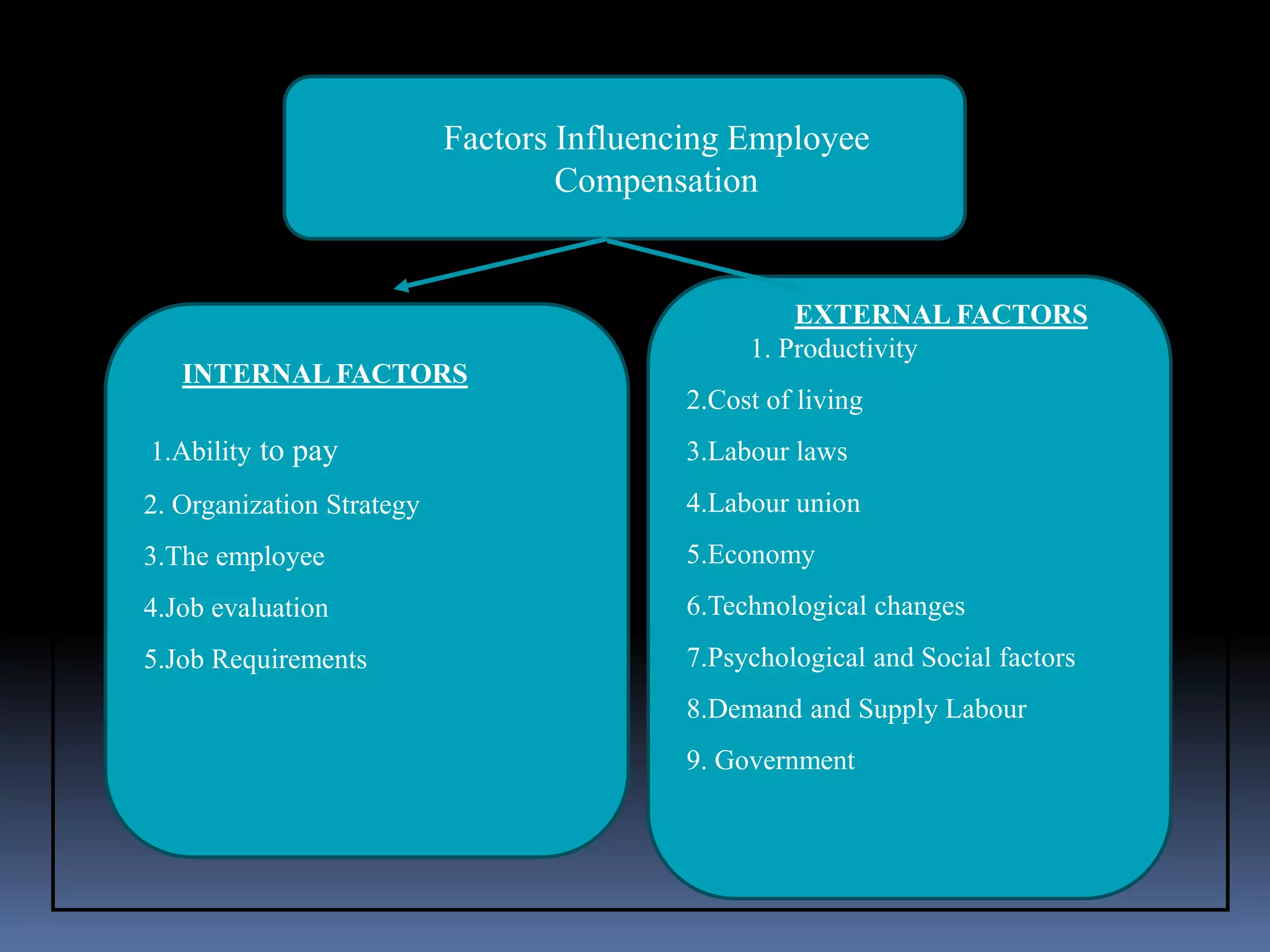
This document discusses compensation and the factors that influence it. Compensation includes both financial compensation like wages and salaries as well as non-financial compensation like benefits and recognition programs. It is determined based on both internal factors like ability to pay, job requirements, and employee performance as well as external factors like cost of living, labor market conditions, government regulations, and technological changes. The goal of compensation is to attract, motivate, and retain qualified employees in a fair and competitive way.