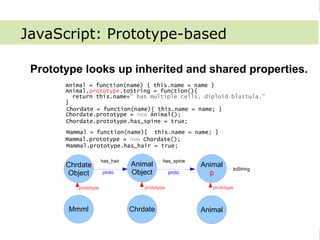
The document provides an overview of learning bottom up JavaScript, including the key things it will cover: the JavaScript language, Document Object Model (DOM), how JS and DOM cooperate, libraries, development tools, and resources. It describes the main aspects of JavaScript like being dynamic, weakly typed, prototype-based, and using first-class functions. It also explains the three main things done with JS: attaching event listeners, getting/modifying data, and updating the page.





![Bottom Up JavaScript
JavaScript: Weakly Typed
Type associated with value, not variable.
var a = 1;
a = “one”;
a = [1];
a = {one: 1};
Use typeof, instanceof, or other duck typing
techniques to determine type.
typeof “abc” -> “string”
typeof 1 -> “number”
typeof [] -> “object”
©Jupiter IT JavaScriptMVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bottomup-090629051717-phpapp01/85/Bottom-Up-6-320.jpg)


![Bottom Up JavaScript
JavaScript: Data Types
Basic data types:
● Undefined -> undefined
● Null -> null
● Boolean -> true, false
● String -> “hello”
● Number -> 2, 0.2
● Object -> {name: “value”}
● Function -> function(){}
● Array -> [1,2,3]
● Date -> new Date()
● RegExp -> /.*/g, new RegExp(“.*”,”g”)
©Jupiter IT JavaScriptMVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bottomup-090629051717-phpapp01/85/Bottom-Up-10-320.jpg)
![Bottom Up JavaScript
Document Object Model
JS Representation of HTML and browser.
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<h1>hi</h1>
</body>
</html>
document = {
documentElement: {
nodeName: “HTML”
childNodes: [
{nodeName: “HEAD”, childNodes: []},
{
nodeName : “BODY”
childNodes: [{nodeName: 'h1', innerHTML: "hi"}]
}
]
},
getElementById : function(id){ ... }
}
©Jupiter IT JavaScriptMVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bottomup-090629051717-phpapp01/85/Bottom-Up-11-320.jpg)




![Bottom Up JavaScript
Libraries
Exist to make things easier:
Browser inconsistencies
attachEvent vs addEventListener
XMLHttpRequest vs ActiveXObject
DOM API weaknesses
$('#sidebar .ul').height()
document.getElementById('sidebar').
childNodes[2].offsetHeight
Common tasks
Drag/drop, AutoComplete, Slider, Sortable Tables
Language improvements
[].each(), “isRed”.startsWith(“is”)
Do you need a library -> YES!!!
©Jupiter IT JavaScriptMVC](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bottomup-090629051717-phpapp01/85/Bottom-Up-16-320.jpg)






