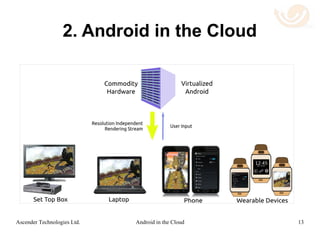
This document discusses using Ascender's technology to enable Android applications to run remotely in the cloud on a variety of client devices. It describes three main use cases: 1) running Android apps from Chromebooks and other clients, 2) enabling BYOD by hosting enterprise apps securely in the cloud, and 3) allowing wearable devices to access Android apps by streaming them from mobile phones. The technology transmits rendering commands instead of pixels, making it more efficient than traditional VDI and allowing Android apps to run smoothly on different client platforms using low bandwidth. This expands Android's reach and helps solve problems with mobile enterprise security and management.