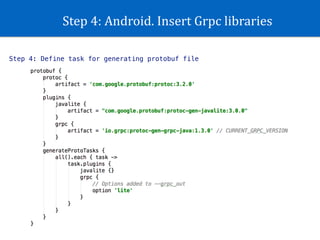
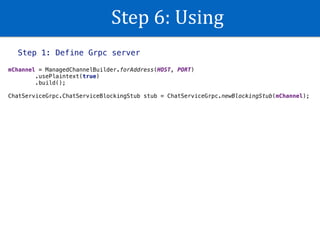
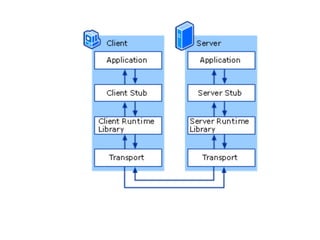
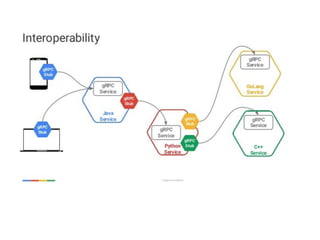
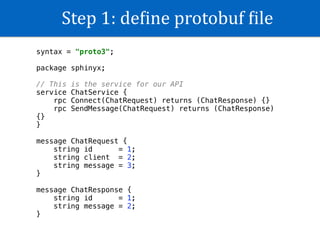
The document discusses GRPC in Android. It provides an overview of GRPC, explaining that GRPC is Protobuf + RPC made by Google. It supports many languages and uses Protobuf format to transfer data. The document then outlines the step-by-step process to use GRPC in an Android project, including defining a Protobuf file, generating code, creating a GRPC server, adding libraries to Android, and making calls. It also mentions the four types of RPC methods and provides a reference link for more information on GRPC in Android.






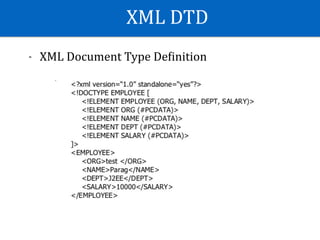
























![100,Category 1,Description 1
200,Category 2,Description 2
[id],[category name], [category description]
[id],[category name], [category description]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidgrpc-180130093637/85/Android-GRPC-35-320.jpg)
![CSV
100,Category 1,Description 1
200,Category 2,Description 2
[id],[category name], [category description]
[id],[category name], [category description]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidgrpc-180130093637/85/Android-GRPC-36-320.jpg)
![CSV
100,Category 1,Description 1
200,Category 2,Description 2
[id],[category name], [category description]
[id],[category name], [category description]
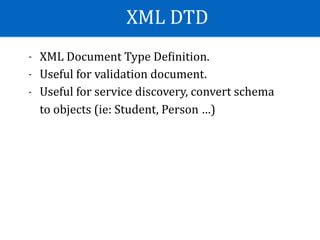
- JSON, XML are human-readable/editable format.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidgrpc-180130093637/85/Android-GRPC-37-320.jpg)
![CSV
100,Category 1,Description 1
200,Category 2,Description 2
[id],[category name], [category description]
[id],[category name], [category description]
- JSON, XML are human-readable/editable format.
- Output footprint is large.
- Not efKicient for transferring data.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidgrpc-180130093637/85/Android-GRPC-38-320.jpg)
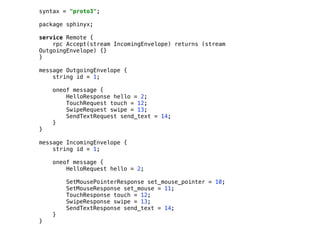





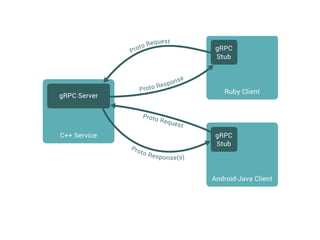

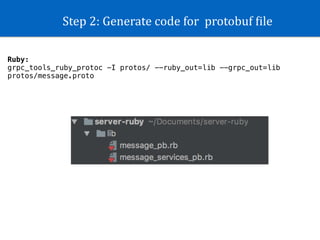


![Step 3: Create GRPC from generated code
class GrpcChatServer < Sphinyx::ChatService::Service
@clients = []
def connect(hello_req, _unused_call)
puts "Hello Client:#{hello_req.client} with id=#{hello_req.id}"
new_id = "#{hello_req.client}-#{hello_req.id}"
Sphinyx::ChatResponse.new(id: new_id, message: "Hello #{new_id}")
end
end
def main
s = GRPC::RpcServer.new
s.add_http2_port('0.0.0.0:50051', :this_port_is_insecure)
s.handle(GrpcChatServer)
s.run_till_terminated
end
main](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidgrpc-180130093637/85/Android-GRPC-57-320.jpg)