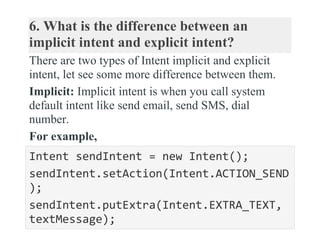
This document provides summaries of 19 common Android developer interview questions and their answers. Some key topics covered include how to find views, why Android uses Dalvik VM instead of standard Java bytecode, declaring activities in the manifest, different storage options in Android like shared preferences and internal storage, implicit vs explicit intents, and using intents to perform actions provided by other apps like sending email.

![1. How do you find any view element into your
program?
Findviewbyid : Finds a view that was identified by
the id attribute from the XML processed
inActivity.OnCreate(Bundle).
Syntax
[Android.Runtime.Register("findViewById
", "(I)Landroid/view/View;", "GetFindVi
ewById_IHandler")]
public virtual View FindViewById (Int32
id)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/androidenginerinterviewquestionswithanswerspdf-181225171457/85/Android-developer-interview-questions-with-answers-pdf-2-320.jpg)